(Press-News.org) About The Study: The U.S. has achieved a new post-pandemic hospital occupancy steady state 11 percentage points higher than it was pre-pandemic. This persistently elevated occupancy appears to be driven by a 16% reduction in the number of staffed U.S. hospital beds rather than by a change in the number of hospitalizations. Experts in developed countries have posited that a national hospital occupancy of 85% constitutes a hospital bed shortage (a conservative estimate). The findings of the current study show that the U.S. could reach this dangerous threshold as soon as 2032, with some states at much higher risk than others.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Richard K. Leuchter, MD, email rleuchter@mednet.ucla.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.60645)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.60645?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=021925
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Health care staffing shortages and potential national hospital bed shortage
JAMA Network Open
2025-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity
2025-02-19
About The Study: After more than 10 years of follow-up in the Swiss Multicenter Bypass or Sleeve Study randomized clinical trial, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass demonstrated superiority over sleeve gastrectomy for patient excess body mass index loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ralph Peterli, MD, email ralph.peterli@clarunis.ch.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2024.7052)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Advances in AI can help prepare the world for the next pandemic, global group of scientists find
2025-02-19
In the next five years, integrating AI into country response systems could save more lives by anticipating the location and trajectory of disease outbreaks.
Global group of researchers call for better collaboration between academia, government and industry, to ensure safety, accountability and ethics in the use of AI in infectious disease research.
A study published in Nature today outlines for the first time how advances in AI can accelerate breakthroughs in infectious disease research and outbreak response.
The study – which ...
Emergency clinicians increase prescriptions of buprenorphine, effectively help patients get started on the path to recovery
2025-02-19
In the face of the alarming number of opioid-related deaths in the U.S., there have been national efforts to increase emergency clinician prescribing of buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. In a new study published in JAMA, UCLA Health researchers report on the extent and success rate of such efforts in California.
Opioid-related emergency department (ED) visits, hospitalizations, and deaths have increased markedly since 1999, and the growing number of cases was declared a public health emergency in 2024. Combined ...
New sensor can take any gas and tell you what’s in it
2025-02-19
Expert sommeliers can take a whiff of a glass of wine and tell you a lot about what’s in your pinot noir or cabernet sauvignon.
A team of physicists at CU Boulder and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have achieved a similar feat of sensing, only for a much wider range of substances.
The group has developed a new laser-based device that can take any sample of gas and identify a huge variety of the molecules within it. It is sensitive enough to detect those molecules at minute concentrations all the way down to parts per trillion. ...
How the brain balances risk and reward in making decisions
2025-02-19
At a glance:
Study in mice offers insights into the brain circuitry underlying certain types of reward-based choices.
Researchers identified distinct groups of brain cells activated when animals anticipate a reward to be above average or below average for a choice.
The findings enhance understanding of human decision-making and how the brain balances risk and reward.
Every day, our brain makes thousands of decisions, big and small. Any of these decisions — from the least consequential such as picking ...
Jumbled proteins paint a bold target on the backs of brain tumors
2025-02-19
Immune therapy has transformed how cancer is treated, but many tumors continue to evade these treatments, thanks to their resemblance to healthy tissue.
Now, researchers at UC San Francisco have found that some cancers, like deadly brain cancer (glioma), make unique, jumbled proteins that make them stand out. These newly recognized cancer-specific proteins, or antigens, could speed the development of potent immunotherapies that recognize and attack hard-to-treat tumors.
The study, which was supported through grants from the National Institutes of Health, appears in Nature on ...
Liver injury in immune Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Five new classification types
2025-02-19
Introduction
First identified by Stevens and Johnson in 1922, SJS and TEN are now recognized as disorders with a continuum of severity, from milder forms (SJS) to the most severe (TEN). SJS/TEN is associated with multiple etiological factors, most notably drug-induced liver injury (DILI), making the identification of the responsible agent crucial for patient management. However, previous studies have lacked uniformity in diagnostic approaches, limiting the ability to draw clear conclusions about causality.
Epidemiology
The incidence of SJS/TEN varies across regions, with notable differences between studies. For instance, ...
MSU study: Socioeconomic factors, unpredictability complicate diagnosis of episodic disabilities, like epilepsy
2025-02-19
Any patient suffering from new or worsening medical symptoms hopes for a relatively quick and accurate diagnosis.
However, for many people with episodic disabilities — periodic or intermittent conditions like migraines, lupus, Crohn’s disease and epilepsy, in which the presence and severity of symptoms fluctuate — a swift diagnosis is not guaranteed.
New research from Michigan State University focuses on diagnostic delays experienced by people with one such condition: epilepsy, a neurological disorder characterized by unpredictable seizures that affects over 3 million people in the United States and 50 million worldwide.
“Epilepsy ...
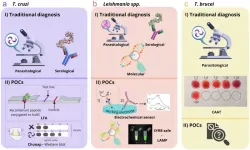
Revolutionizing tropical disease treatment: The future of conjugating nanomaterials with drugs
2025-02-19
Introduction
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) remain a significant health burden in tropical and subtropical regions, with limited treatment options and diagnostic capabilities. These diseases are often neglected in research and policy, yet they contribute to high mortality and morbidity worldwide. Nanotechnology, particularly the conjugation of nanomaterials with drugs, presents an innovative approach to improving both the diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. Nanomaterials have unique properties that allow for enhanced drug delivery, ...
Improving quality of life and end-of-life care: Standardizing goals of care notes in EHRs
2025-02-19
INDIANAPOLIS – It is important that a healthcare team is aware of and understands a patient’s goals of care, both medical and personal. But that information, if documented, typically is not placed in a standardized location and is difficult to find within a patient’s voluminous electronic health record (EHR).
A new study by researchers from Regenstrief Institute, the Indiana University School of Medicine and Indiana University Health presents the standardized goals of care note they developed, deployed and evaluated as a quality improvement initiative at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Health care staffing shortages and potential national hospital bed shortageJAMA Network Open