(Press-News.org) The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has announced the 2025 class of Senior Members, comprised of 162 emerging inventors from NAI’s Member Institutions. This year’s class of NAI Senior Members is the largest to date and hails from 64 NAI Member Institutions across the nation. Collectively, they are named inventors on over 1200 U.S. patents.
“To see this program grow year over year is a testament to the dedication our Member Institutions have to fostering innovation on their campuses and supporting their inventive staff and faculty,” said Paul R. Sanberg, President of NAI. “This year’s class comes from a multitude of impressive fields and research backgrounds from across the world. We applaud their pursuit of commercialization to ensure their groundbreaking technologies can make a difference by tackling the world’s most pressing issues, improving quality of life across society, and advancing the economy.”
A full list of NAI Senior Members is available here.
The 2025 class of Senior Members will be celebrated during the Senior Member Induction Ceremony at NAI’s 14th Annual Conference taking place June 23-26th, 2025 in Atlanta, Georgia. The conference is the premiere opportunity for visionaries and innovators to converge to share ideas, foster collaborations, and celebrate advancements in invention. The prestigious Senior Member Induction Ceremony is one of the cornerstones of the conference, exemplifying the spirit of creativity and discovery that drives the global inventor community.
To learn more about the event and register, visit https://academyofinventors.org/annual-conference/.
The ability to nominate an individual for NAI Senior Member recognition is an exclusive opportunity afforded to NAI Member Institutions to recognize their outstanding innovators and foster a culture of innovation and invention on their campuses. These Member Institutions are widely regarded as innovation powerhouses that continuously promote and foster the spirit of innovation at their institutions and in their communities.
To learn more about the Senior Member pogram, visit https://academyofinventors.org/about-the-senior-members-program/.
About the National Academy of Inventors
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) is a member organization comprising U.S. and international universities, and governmental and non-profit research institutes, with over 4,600 individual inventor members and Fellows spanning more than 260 institutions. It was founded in 2010 to recognize and encourage inventors with patents issued from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, enhance the visibility of academic technology and innovation, encourage the disclosure of intellectual property, educate and mentor innovative students, and translate the inventions of its members to benefit society. The Academy and the USPTO have enjoyed a collaborative partnership since the founding of NAI. Most recently this has been reflected in their joint mission to expand access to individuals and institutions participating in the invention and innovation ecosystem. www.academyofinventors.org
END
National Academy of Inventors welcomes 162 emerging inventors
2025-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Narcissists more likely to feel ostracized
2025-02-20
Narcissists feel ostracized more frequently than their less self-absorbed peers, according to research published by the American Psychological Association. This may stem not only from being shunned due to their personalities but from a tendency to misinterpret ambiguous social signals as exclusion.
“Feeling ostracized is a subjective experience based on the perception of social cues by the individual. Some may be intentionally ostracized, while others may merely believe they are being excluded when that’s not the case,” said lead author Christiane Büttner, PhD, of the University of Basel. “Our findings suggest that ...
Unfolded protein response: A key regulator of intestinal health and disease
2025-02-20
The intestinal epithelium is a highly dynamic barrier that regulates digestion, absorption, immune responses, and communication between the gut microbiota and the nervous system. To maintain homeostasis, intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) must efficiently manage protein production and secretion, a process tightly controlled by the unfolded protein response (UPR).
New research published in eGastroenterology demonstrates that disruptions in the UPR contribute to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), colorectal cancer, and other gut-related disorders. This highlights potential therapeutic strategies to restore ...
Small amounts of moderate to vigorous physical activity are associated with big reductions in dementia risk
2025-02-20
A little movement could help prevent dementia, even for frail older adults, suggests a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers found that engaging in as little as 35 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week, compared to zero minutes per week, was associated with a 41% lower risk of developing dementia over an average four-year follow-up period. Even for frail older adults—those at elevated risk of adverse health outcomes—greater activity was associated with lower dementia risks.
The ...
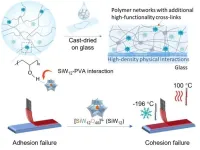
Enhancing adhesive performance of polyvinyl alcohol with sub-nanoscale polyoxotungstate clusters under extreme conditions
2025-02-20
Water-based adhesives face several challenges despite their environmental benefits. One major issue is that achieving high adhesion strength on various substrates, especially in wet or humid conditions, is difficult due to the inherent properties of water-based systems. Additionally, the volatility of water also leads to issues like bubble formation and uneven drying, affecting the adhesive's performance and appearance. Moreover, formulating water-based adhesives with both high solids content and low viscosity is technically demanding, ...
Recognizing the evolution of clinical syndrome spectrum progression in individuals with single large-scale mitochondrial DNA deletion syndromes (SLSMDS))
2025-02-20
Philadelphia, February 20, 2025 – Researchers from the Mitochondrial Medicine Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have better characterized a spectrum of what were classically considered discrete mitochondrial DNA deletion disease syndromes. The findings offer new insights into genetic causes, potential symptoms, and disease progression, and may inform future clinical trial development. The findings were published today in the journal Genetics in Medicine.
Mitochondrial disease refers to a group of disorders that affect the mitochondria, which are tiny compartments present in almost every cell of the body that ...
Another way longer paternity leaves help new parents
2025-02-20
A longer paternity leave after the birth of a child can improve the co-parenting relationship between moms and dads in a key way, a new study finds.
Researchers found that mothers were less likely to discourage fathers’ involvement in parenting if the dads had taken more time off after their child was born.
“When fathers take longer leaves, mothers might take that as a sign that fathers are more interested in being an active parent and be less likely to try to prevent them from participating in child care,” said Reed Donithen, ...
Johnson & Johnson MedTech celebrates inaugural National Heart Recovery Awareness Day
2025-02-20
DANVERS, Mass., February 20, 2025 – Johnson & Johnson MedTech, the global leader in heart recovery, is proud to celebrate the inaugural National Heart Recovery Awareness Day today, February 20. Recognized through a U.S. Congressional resolution, this designation will help increase awareness of heart health and how innovative medical technology helps patients return home to their families – with their native heart. There are events taking place across the country where patients are sharing their stories, including heart recovery reunions and sessions to educate healthcare providers, which underscore the impact that heart recovery has ...
Novel inhalable gene therapy trialled for people with cystic fibrosis
2025-02-20
An inhalable medicine with the potential to improve lung disease in people with cystic fibrosis, irrespective of their mutation type, is being tested in human trials in the UK and Europe.
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by defects in the CFTR gene, which causes a buildup of thick sticky mucus in the lungs and digestive system. It causes lung infections and gradually affects the ability to breathe. The new lentiviral vector-based gene therapy works by inserting a functioning copy of the CFTR gene in the DNA of the epithelial cells in a patient’s airway.
At ...
Plasma arc cutting: PNU and KIMM scientists together decode gas flow dynamics
2025-02-20
Plasma arc cutting (PAC) is a thermal cutting technique widely used in manufacturing applications such as shipbuilding, aerospace, fabrication, nuclear plants decommissioning, construction industry, and the automotive industry. In this process, a jet of plasma or ionized gas is ejected at high speeds, which melts and subsequently removes unwanted parts of materials from electrically conductive workpieces such as metals. The plasma jet is typically produced in two steps: pressuring a gas through a small nozzle hole and generating an electric arc via power supply. Remarkably, the introduced arc ionizes ...
Exercise your way to lower blood pressure: Brain pathway to fight high blood pressure
2025-02-20
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a debilitating condition and a major cause of premature death worldwide. Chronic stress plays a significant role, but the underlying mechanism involving biochemical pathways by which stress leads to hypertension has not been well understood. Understanding these pathways could lead to the development of therapeutic agents to combat hypertension. Now, a new study from Juntendo University, Japan, led by Professor Hidefumi Waki, Dr. Keisuke Tomita, and Dr. Ko Yamanaka, published online in the journal Acta Physiologica on January 13, 2025, has shown that voluntary ...