(Press-News.org) Six Lehigh University professors have been named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors. The 2025 cohort comprises 162 academic inventors representing 64 NAI Member Institutions across the United States. Collectively, they are named inventors on over 1200 U.S. patents.
“This year’s class comes from a multitude of impressive fields and research backgrounds from across the world,” said NAI President Paul R. Sanberg. “We applaud their pursuit of commercialization to ensure their groundbreaking technologies can make a difference by tackling the world’s most pressing issues, improving quality of life across society, and advancing the economy.”
The following faculty members of the P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science have been named Senior Members of the NAI:
Jonas Baltrusaitis, associate professor, chemical and biomolecular engineering
Xuanhong Cheng, professor, bioengineering and materials science and engineering
Siddha Pimputkar, associate professor, materials science and engineering
Yahong Rosa Zheng, professor, electrical and computer engineering
Also named NAI Senior Members are two faculty members in Lehigh’s College of Arts and Sciences: Volkmar Dierolf (physics) and Xiaoji Xu (chemistry). Dierolf holds a joint appointment in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in the Rossin College.
The 2025 class of Senior Members will be celebrated during a ceremony at the NAI’s 14th Annual Conference, June 23-26, in Atlanta.
about the faculty members, their research and patents, and their other accomplishments on their faculty profiles linked below. Learn more about the National Academy of Inventors and the Senior Member program on the NAI website.
Related Links:
Faculty Profile: Jonas Baltrusaitis
Faculty Profile: Xuanhong Cheng
Faculty Profile: Siddha Pimputkar
Faculty Profile: Yahong Rosa Zheng
END
Lehigh Engineering faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
Innovators in chemical engineering, materials science, bioengineering, and electrical and computer engineering are among the six Lehigh University faculty members recognized as emerging inventors
2025-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers outline new approach for better understanding animal consciousness
2025-02-20
A team of researchers has outlined a new approach for better understanding the depths of animal consciousness, a method that may yield new insights into the similarities and differences among living organisms.
The essay, which appears in the journal Science, describes a “marker method” that scientists can use to assess animal consciousness. It involves identifying behavioral and anatomical features associated with conscious processing in humans and searching for similar properties in nonhumans. By making progress in the science of animal consciousness, the authors propose, we can make progress on foundational questions about the nature of consciousness, ...
Bioinspired robot collectives that can act like solids or fluids on demand
2025-02-20
Inspired by the cooperation of cells in tissues, researchers have developed a robotic collective system capable of transitioning between rigid and solid structures that can also support hundreds of times its own weight. The advancement overcomes a core challenge in the development of so-called “robotic materials” – cohesive networks of individual robotic units that function as a single dynamic, adaptive structure. Realizing these systems presents a fundamental challenge: this “material” must at once be strong and stiff enough to support loads, ...
AI-assisted diagnosis for immunological disease
2025-02-20
A novel machine learning framework – Mal-ID – can decipher an individual’s immune system’s record of past infections and diseases, according to a new study, providing a powerful tool with the potential for diagnosing autoimmune disorders, viral infections, and vaccine responses with precision. Traditional clinical diagnostic methods for autoimmune diseases or other immunological pathologies tend to rely on a combination of physical examination, patient history, and various laboratory testing for cellular or molecular abnormalities – a lengthy process often complicated by initial misdiagnoses and ambiguous systems. These approaches make limited use of data from ...
A new approach for breaking plastic waste down to monomers
2025-02-20
Researchers have reported a method for breaking down commercial polymers like Plexiglass into monomers, a form more desirable for reuse. This could help alleviate the growing plastic waste stream. Most current plastic recycling methods rely on macroscopic mechanical shredding, cleaning and reprocessing. As a result, the properties degrade relative to the virgin polymer. Chemical decomposition to the original monomer would enable more thorough purification and then repolymerization to restore ideal performance. Here, Hyun Suk Wang and colleagues report the discovery that in dichlorobenzene solvent, violet light irradiation ...
High-performance computing at a crossroads
2025-02-20
High-performance computing (HPC) systems – advanced computing ensembles that harness deliver massive processing power – are used for a range of applications, and the demand for them has increased with the rise of generative artificial intelligence (AI). However, for both traditional uses and to advance the power of AI, technical advances in HPC are greatly needed, say Ewa Deelman and colleagues in a Policy Forum. “With international competition for leadership in computing intensifying, without a renewed commitment, ...
Chemists find greener path to making key industrial chemical
2025-02-20
Scientists have discovered a potentially greener way to produce a crucial industrial chemical used to make many everyday products from plastics and textiles to antifreeze and disinfectants, according to a new study published in Science and co-authored by Tulane University chemical engineer Matthew Montemore.
The breakthrough could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the manufacture of ethylene oxide, which has an estimated $40 billion global market. The current production process requires chlorine, which is toxic and ...
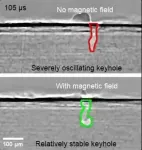
Giant X-ray facility shows that magnets can reduce flaws in 3D printed components
2025-02-20
Safety critical components for aircraft and Formula 1 racing cars could one day be 3D printed via a new technique, developed by researchers at UCL and the University of Greenwich, that substantially reduces imperfections in the manufacturing process.
The technique was developed after the team used advanced X-ray imaging to observe the causes of imperfections that formed in complex 3D printed metal alloy components. If this technique becomes widely deployed it could make a range of these components, from artificial hip joints to aircraft parts, stronger and more durable.
The study, published in Science, observes the forces at play during ...
Cooling materials – Out of the 3D printer
2025-02-20
Rapid, localized heat management is essential for electronic devices and could have applications ranging from wearable materials to burn treatment. While so-called thermoelectric materials convert temperature differences to electrical voltage and vice versa, their efficiency is often limited, and their production is costly and wasteful. In a new paper published in Science, researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) used a 3D printing technique to fabricate high-performance thermoelectric materials, reducing production costs significantly.
Thermoelectric coolers, also called solid-state ...
New knowledge portal adiposetissue.org enhances obesity and metabolism research with centralized data
2025-02-20
Addressing the Challenge of Dispersed Data
For years, adipose tissue research has generated vast amounts of omics data, but these datasets remained scattered across different repositories, making comprehensive analysis challenging. Adiposetissue.org now brings insights together, integrating transcriptomic and proteomic with clinical data from more than 6,000 individuals, enabling researchers to explore obesity-related changes, weight-loss effects, and cellular mechanisms with unprecedented depth.
“We developed ...
Study suggests new molecular strategy for treating fragile X syndrome
2025-02-20
Building on more than two decades of research, a study by MIT neuroscientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory reports a new way to treat pathology and symptoms of fragile X syndrome, the most common genetically-caused autism spectrum disorder. The team showed that augmenting a novel type of neurotransmitter signaling reduced hallmarks of fragile X in mouse models of the disorder.
The new approach described in Cell Reports works by targeting a specific molecular subunit of “NMDA” receptors that they discovered plays a key role in how neurons synthesize ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
CU Anschutz School of Medicine receives best ranking in NIH funding in 20 years
Mayo Clinic opens patient information office in Cayman Islands
Phonon lasers unlock ultrabroadband acoustic frequency combs
Babies with an increased likelihood of autism may struggle to settle into deep, restorative sleep, according to a new study from the University of East Anglia.
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
[Press-News.org] Lehigh Engineering faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of InventorsInnovators in chemical engineering, materials science, bioengineering, and electrical and computer engineering are among the six Lehigh University faculty members recognized as emerging inventors