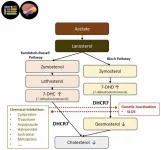
(Press-News.org) OMAHA, Nebraska, USA, 25 February 2025 - In a peer-reviewed Perspective (review) article, researchers at the University of Nebraska Medical Center have uncovered concerning evidence that commonly prescribed medications may interfere with crucial brain development processes by disrupting sterol biosynthesis. Their findings, published today in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press, New York), suggest that this previously overlooked mechanism could have significant implications for medication safety during pregnancy and early development.
"What we've discovered is that many prescription medications, while designed for entirely different purposes, can inadvertently interfere with the brain's ability to produce and process sterols, including cholesterol," explains Professor Károly Mirnics, lead author of the review. "This is particularly concerning because the brain requires precise sterol regulation for proper development and function."
The research reveals that the brain, which contains 25% of the body's cholesterol despite representing only 2% of body weight, maintains its own independent cholesterol production system behind the blood-brain barrier. This process is essential for numerous developmental processes, including nerve cell connection formation and myelin production.
Dr. Željka Korade, co-author of the study, emphasizes that the risk may be heightened in certain populations: "We've found that individuals with specific genetic variations in sterol processing genes, which may affect up to 3% of the population, could be particularly vulnerable to these medication effects."
The review highlights several key findings with significant clinical implications:
• Over 30 prescription medications have been identified as having sterol biosynthesis inhibiting effects
• The combination of multiple medications may produce synergistic or additive effects on sterol disruption
• Genetic variations in sterol processing genes may increase susceptibility to these effects
• Multiple developmental periods, including pregnancy and early childhood, may represent vulnerable windows
"These findings suggest we need to reevaluate how we assess medication safety, particularly during pregnancy," notes Professor Mirnics. "The interaction between medications and sterol biosynthesis represents a previously underappreciated mechanism that could affect brain development."
The researchers emphasize that patients should not discontinue prescribed medications without consulting their healthcare providers. However, they recommend that additional research is needed to fully understand the implications of these findings and to develop more targeted approaches for vulnerable populations.
The full peer-reviewed Perspective (review) article, titled "Sterol biosynthesis disruption by common prescription medications: critical implications for neural development and brain health," is available on 25 February 2025 in Brain Medicine, offering readers a comprehensive examination of how commonly prescribed medications may inadvertently affect brain development through sterol biosynthesis disruption. The article is freely available online at https://doi.org/10.61373/bm025p.0011.
About Brain Medicine: Brain Medicine (ISSN: 2997-2639) is a peer-reviewed medical research journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Brain Medicine is a new home for the cross-disciplinary pathway from innovation in fundamental neuroscience to translational initiatives in brain medicine. The journal’s scope includes the underlying science, causes, outcomes, treatments, and societal impact of brain disorders, across all clinical disciplines and their interface.
END
Common medications may affect brain development through unexpected cholesterol disruption
Groundbreaking review uncovers how common medications disrupt critical cholesterol synthesis in developing brains, sparking urgent pregnancy safety concerns
2025-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Laser-powered device tested on Earth could help us detect microbial fossils on Mars
2025-02-25
The first life on Earth formed four billion years ago, as microbes living in pools and seas: what if the same thing happened on Mars? If it did, how would we prove it? Scientists hoping to identify fossil evidence of ancient Martian microbial life have now found a way to test their hypothesis, proving they can detect the fossils of microbes in gypsum samples that are a close analogy to sulfate rocks on Mars.
“Our findings provide a methodological framework for detecting biosignatures in Martian sulfate minerals, potentially guiding ...
Non-destructive image sensor goes beyond bulkiness
2025-02-25
While photo-thermoelectric (PTE) sensors are potentially suitable for testing applications, such as non-destructive material-identification in ultrabroad millimeter-wave (MMW)–infrared (IR) bands, their device designs have primarily employed a single material as the channel. In general, PTE sensors combine photo-induced heating with associated thermoelectric (TE) conversion, and the employment of a single material channel regulates the utilization of devices by missing the opportunity for fully utilizing their fundamental parameters. ...
1st Japanese version of US psychological scale for esophageal symptoms
2025-02-25
Psychological factors have a greater impact on the severity of symptoms in esophageal diseases than objective evaluations, such as acid reflux and esophageal motility function. Although there are questionnaires that assess general psychological states in Japan, there were none that were specific to esophageal symptoms. In the United States, meanwhile, the Esophageal Hypervigilance and Anxiety Scale (EHAS) questionnaire that evaluates symptom-specific hypervigilance and anxiety for esophageal symptoms was developed in 2018.
In an effort to expand the use of EHAS, Dr. Akinari Sawada’s research group at Osaka Metropolitan ...
HikingTTE: a deep learning approach for hiking travel time estimation based on personal walking ability
2025-02-25
At the University of Electro-Communications, a research team led by Mizuho Asako, Yasuyuki Tahara, Akihiko Ohsuga, and Yuichi Sei has developed a new deep learning model called "HikingTTE" that significantly improves hiking travel time estimation. Hiking is popular worldwide, but accidents still occur when hikers underestimate the time needed to reach their destination.
This model could help reduce mountain accidents and improve hiker safety by providing more accurate travel time predictions. Previous hiking travel time estimation methods often use the relationship between slope (uphill or downhill) and walking speed. However, these ...
Environment nudges birds to fast, or slow, life lane
2025-02-25
Birds worldwide make strategic decisions about how they live based on their environmental conditions. Some live fast, die young, and leave as many chicks as possible. Others live long and prosper by not breeding.
A new study of non-migratory birds provides clues about how climate change may affect the long-standing evolutionary strategies of feathered friends. The work is reported in this week’s Ecology Letters and was led by Michigan State University postdoctoral fellows of the MSU Institute for Biodiversity, Ecology, Evolution, and Macrosystems (IBEEM).
The ...
The U-shaped relationship between admission peripheral oxygen saturation and all-cause hospital mortality in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective analysis using
2025-02-25
Highlight box
Key findings
• This study investigated the U-shaped nonlinear relationship between admission oxygen saturation (SpO2) and all-cause hospital mortality in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD). The results showed that the lowest all-cause hospital mortality was observed at an SpO2 of 89.5%. Additionally, SpO2 was identified as an independent risk factor for predicting all-cause hospital mortality in AECOPD patients, providing valuable guidance for optimizing oxygen therapy in this population.
What is known and what is new?
• Most studies indicate that maintaining SpO2 levels between 88–92% provides ...
New research highlights wide variation in prostate cancer testing between GP practices
2025-02-25
A largescale study has found huge variation between GP practices on whether they are likely to pick up prostate cancer using a blood test.
The University of Exeter led a study which aimed to investigate the proportion of patients whose prostate cancer was identified by using a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test when patients had no symptoms.
The research published in the British Journal of General Practice and funded by Cancer Research UK, and, has found that one in five patients with prostate cancer in England are diagnosed after PSA testing when they had no symptoms – fewer than previously thought. The PSA test ...
Antidepressants linked to faster cognitive decline in dementia
2025-02-25
New research suggests that antidepressants can accelerate cognitive decline in people with dementia. At the same time, some drugs appear to be less harmful than others, which can help doctors make better treatment decisions, according to the study published in BMC Medicine.
Antidepressants are often used to relieve symptoms such as anxiety, depression, aggressiveness, and sleep disturbances in dementia sufferers.
However, a new observational study based on data from the Swedish Dementia Registry (SveDem) shows that patients with dementia who are treated with antidepressants experience an increased cognitive decline compared to patients who do not ...
DNA origami suggests route to reusable, multifunctional biosensors
2025-02-25
Using an approach called DNA origami, scientists at Caltech have developed a technique that could lead to cheaper, reusable biomarker sensors for quickly detecting proteins in bodily fluids, eliminating the need to send samples out to lab centers for testing.
"Our work provides a proof-of-concept showing a path to a single-step method that could be used to identify and measure nucleic acids and proteins," says Paul Rothemund (BS '94), a visiting associate at Caltech in computing and mathematical sciences, and computation and neural systems.
A paper describing the work recently appeared in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The lead authors of ...
Virginia Tech study reveals that honeybee dance ‘styles’ sway food foraging success
2025-02-25
As far as animals go, honeybees are world-class dancers.
While not as deep and complex as a Super Bowl half-time show, the bees' moves, known as the “waggle" dance, convey very specific food foraging instructions to their nestmates. The direction the dancer moves explains to other bees which way to go, and the duration of the waggle dance, or the “run,” shows how far to go. Once other bees have been convinced to follow the directions, they are “recruited.” After receiving the instructions, these ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Common medications may affect brain development through unexpected cholesterol disruptionGroundbreaking review uncovers how common medications disrupt critical cholesterol synthesis in developing brains, sparking urgent pregnancy safety concerns