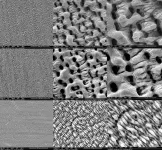
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Feb. 25, 2025 – Keeping work surfaces clean during meat processing is a challenge. Bacteria from meat can attach, grow, and build up to create a biofilm that is difficult to remove, even on stainless steel surfaces used in industrial facilities. It can also aggregate, clumping together into an invisible mass that is stronger than individual cells, making it harder to kill using food-grade antibacterial surface cleaners.
In a paper published this week in Journal of Laser Applications, from AIP Publishing and the Laser Institute of America, researchers from the Hopkirk Research Institute, New Zealand Food Safety Science and Research Centre, and Applied Technologies Group in New Zealand deliver key insights into a solution that could replace the current practice altogether: Instead of constantly battling to prevent bacteria buildup, they created surfaces that stop bacteria from attaching in the first place.
“Antimicrobial interventions currently approved and used commercially have a limited capacity to reduce well-established bacterial biofilms and spores, and complete decontamination is rarely achieved,” author Sebastiampillai Raymond said.
Using lasers to etch and alter the surface of the metal, Raymond and his colleagues were able to create micro- or nanoscale textures that make it difficult for microbial cells to attach to the surface. The technique, known as laser-induced surface texturing, also alters the metal’s water-repellent properties, a key factor impacting bacterial growth.
“Laser-textured surfaces possess antibacterial properties, because they physically disrupt bacterial adhesion, growth, and proliferation,” Raymond said. “These nanoscale and microscale surface textures mimic natural antimicrobial surfaces, such as those found on cicada wings and shark skin.”
The researchers discovered the laser-texturing technique is highly effective for carefully controlling and tuning textures on metal. Different bacteria can be targeted using specific textures designed around the shape of the bacterial cells, making it particularly difficult for those cells to attach to the surface. They are also working on developing machine learning models that could help manufacturers optimize and automate laser surface texturing.
“Compared to some conventional approaches, laser surface texturing does not introduce non-native materials or require chemical etchants or sensitizers on treated surfaces,” Raymond said. “This could lower barriers to introducing new technology into a regulated environment and eliminates any risk of potential chemical contamination from the coating.”
###
The article “Antibacterial effectiveness of laser surface textured metal on meat-borne bacteria” is authored by Aswathi Soni, Amanda Gardner, Gale Brightwell, Lan Le-Ngoc, and Sebastiampillai Raymond. It will appear in Journal of Laser Applications on Feb. 25, 2025 (DOI: 10.2351/7.0001535). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.2351/7.0001535.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Laser Applications (JLA) is the scientific platform of the Laser Institute of America and is co-published in partnership with AIP Publishing. The journal covers a broad range of research from fundamental and applied research and development to industrial applications. JLA presents the latest breakthroughs in laser applications related to photonic production, sensing and measurement, as well as laser safety. See https://pubs.aip.org/lia/jla.
###
END
Mimicking shark skin to create clean cutting boards
Laser-textured metal inspired by shark skin and cicada wings creates antibacterial surfaces
2025-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and obesity-linked cancer risk
2025-02-25
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a modest reduction in the risk of obesity-related cancers, independent of adiposity measures. Further research is needed to clarify the mechanisms by which the Mediterranean diet may contribute to cancer prevention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Inmaculada Aguilera-Buenosvinos, PhD, email iaguilerabuenosvinos@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.61031)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
New technique reveals how the same mutations give rise to very different types of leukaemia
2025-02-25
Barcelona, 25 February 2025 - Myeloid leukaemias are among the most aggressive blood cancers and have low survival rates. Today, leukaemia patients undergo genetic analysis to identify mutations and select the most appropriate treatment. However, even among patients with the same mutation, disease progression and response to therapy can vary significantly.
A study led by ICREA researcher Dr. Alejo Rodríguez-Fraticelli at IRB Barcelona, and funded by Fundación CRIS contra el cáncer, has now revealed these differences can be explained by the fact that not all blood stem cells ...
New insights into how gut cells respond to bacterial toxins
2025-02-25
Researchers from the Organoid group at the Hubrecht Institute have found that specific gut cells, BEST4/CA7+ cells, regulate electrolyte and water balance in response to bacterial toxins that cause diarrhea. Their findings, published in Cell Stem Cell, show that these cells greatly increase in number when exposed to the cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ), presenting a promising target for therapeutic strategies.
In the gut, a variety of cell types collaborate to keep a balance of electrolyte and water. Bacterial infections can disrupt this balance, leading ...
Designing self-destructing bacteria to make effective tuberculosis vaccines
2025-02-25
Working toward more effective tuberculosis (TB) vaccines, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have developed two strains of mycobacteria with "kill switches" that can be triggered to stop the bacteria after they activate an immune response. Two preclinical studies, published, Jan. 10 in Nature Microbiology, tackle the challenge of engineering bacteria that are safe for use in controlled human infection trials or as better vaccines. While TB is under control in most developed countries, the disease still kills over a million people a year worldwide.
Spreading easily through ...
SwRI-led PUNCH spacecraft poised for launch into polar orbit
2025-02-25
SAN ANTONIO — February 25, 2025 —Four small suitcase-sized spacecraft, designed and built by Southwest Research Institute headquartered in San Antonio, are poised to launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California no earlier than Feb. 28. NASA’s Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere, or PUNCH, spacecraft is sharing a ride to space with the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer (SPHEREx) observatory.
“The PUNCH mission will study the solar corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, and the solar wind that fills ...
Orthopedic team from Peking Union Medical College Hospital publishes longest-term follow-up study on post-TKA outcomes in Chinese patients with knee osteoarthritis
2025-02-25
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is prevalent among middle-aged and elderly populations, can cause disability and significantly impairs quality of life. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an effective treatment for end-stage KOA; however, long-term outcome and prosthesis survivorship were limited reported, particularly in Chinese cohorts.
Led by Professor Weng Xi-sheng and Professor Feng Bin, the orthopedic team at Peking Union Medical College Hospital conducted a landmark follow-up study spanning over two decades. The research analyzed KOA patients who underwent primary ...
Lung abnormalities seen in children and teens with long COVID
2025-02-25
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An advanced type of MRI uncovers significant lung abnormalities in children and adolescents with long COVID, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Post-COVID-19 condition, commonly known as long COVID, can affect individuals of all ages and is diagnosed when symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks after an initial COVID-19 infection. Children and adolescents typically experience a milder form of the condition, but common symptoms such as chronic fatigue, headaches and poor concentration can negatively impact school performance and social activities.
While ...
NBA and NBA G League Player Ambassadors urge fans to learn lifesaving CPR in 90 seconds
2025-02-25
DALLAS, February 25, 2025 — More than half of people who experiencing sudden cardiac arrest out of hospital don’t receive immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), contributing to a high death rate. A many as 9 out of 10 people who experience sudden cardiac arrest die[1]. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. To save more lives, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, and National Basketball Association/NBA G League players are working to educate about the lifesaving skill.
More Americans than ...
Hormones may have therapeutic potential to prevent wrinkles, hair graying
2025-02-25
WASHINGTON—Hormones may be leveraged to treat and prevent signs of aging such as wrinkles and hair graying, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society journal Endocrine Reviews.
Until now, only a limited number of hormones, mainly topical retinoids (retinol and tretinoin) and estrogen which is typically used to treat side effects of menopause, have been used in clinical practice as anti-skin aging compounds. This study reviews a new class of hormones and their anti-aging properties.
“Our paper highlights key hormone players that orchestrate pathways of skin aging such as ...
Clashing with classmates: Off-putting traits spark enemy relationships
2025-02-25
It is unpleasant to have an enemy. Most people try to avoid hostilities that escalate to the point of mutual antagonism. Which raises the question: What does it take to make an enemy? One possible answer is that aversive or off-putting behaviors increase the likelihood of clashes with others that lead to lasting enmity. Yet without longitudinal data, it’s unclear which comes first – being aversive or being disliked – making it hard to distinguish between the causes and the consequences of having an enemy.
New research from Florida Atlantic University clearly establishes the order of effects. The results, published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
[Press-News.org] Mimicking shark skin to create clean cutting boardsLaser-textured metal inspired by shark skin and cicada wings creates antibacterial surfaces