Experimental and numerical analysis of the potential drop method for defects caused by dynamic loads
2025-02-27
(Press-News.org)
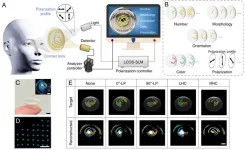
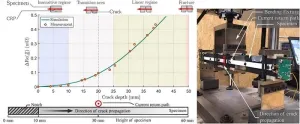
In our paper “Experimental and Numerical Analysis of the Potential Drop Method for Defects Caused by Dynamic Loads”, we investigate how the electrodynamic proximity effect can be utilized to enhance the defect sensitivity of PDM in SHM applications by proper arrangement of the measurement setup. We showed how eddy current effects present in our PDM setup can be modeled analytically and numerically. Lock-in technique and the application of the skin effect allow high- resolution impedance measurements and a parallel temperature measurement helps to compensate cross influences due to temperature effects. Our analysis shows that by proper arrangement of the measurement setup, the proximity effect enhances the defect sensitivity up to 300% compared to that of measurement setups in which the proximity effect is not utilized. Additionally, with proper arrangement of the setup, we found that the proximity effect linearizes the relationship between defect-induced resistance change and crack depth, facilitating the estimation of crack depth. We validated the results of the electrodynamic simulations for our PDM sensor experimentally by applying dynamic loads to a specimen via a resonance-testing machine while measuring the defect- induced resistance change caused by a growing fatigue crack.
In the experiment, we conducted measurements with our PDM sensor during the development of a fatigue crack generated by dynamic loading in a resonance-testing machine. The experimental findings agree well with the simulations.
This work introduces models that support the design of measuring systems for crack detection based on the potential drop method. Enhancing the defect sensitivity by making use of lock-in technique, the skin effect and the proximity effect enables the SHM of larger specimens.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-27
Chiral-structural-color materials produce color through microscopic structures that interact with light rather than through pigmentation or dyes. Some beetle exoskeletons, avian feathers, butterfly wings, and marine organisms feature these structures naturally, producing iridescent or polarization-dependent colors. Over the last 10–15 years, scientists have made progress in developing artificial chiral-structural-color materials.
Recently, Chinese researchers have made a breakthrough in the field by discovering that microdomes made from common polymers exhibit tunable chiral structural colors with broad-spectrum capabilities and multiple ...
2025-02-27
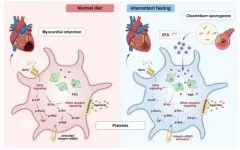
Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of death worldwide, with platelet hyperactivity and subsequent thrombosis playing a pivotal role in these conditions. While intermittent fasting has long been recognized for its metabolic benefits, including improvements in metabolic diseases, weight loss, and even lifespan extension, its effect on platelet activation and thrombosis formation remains less understood.
A recent study by Professor Junbo Ge team at Fudan University unveiled a novel mechanism by which intermittent fasting can significantly reduce the risk of platelet hyperactivity and thrombosis. That is, intermittent fasting elevates levels of the metabolite ...
2025-02-27
Curtin University researchers have developed a new technique to make glass water-repellent, a feature that could improve safety in vehicles, reduce cleaning costs for buildings and enhance filtration systems.
The research, published in the prestigious journal Advanced Functional Materials, shows how an innovative and non-toxic process using ultrasonic sound waves can alter the surface of glass, making it either hydrophobic (water resistant) or electrically charged.
Lead researcher Associate Professor Nadim Darwish, an ARC Future Fellow at Curtin’s ...
2025-02-27
A team of scientists at UNSW has discovered that some of the most important new refrigerants break down, in part, into persistent greenhouse gas pollutants, including compounds that have been banned internationally. Refrigerants are chemicals that turn from a liquid to a gas – and vice-versa – and transfer heat in the process, that are used for refrigeration and indoor heating and cooling. The chemicals are also used as aerosol propellants, fire retardants and in the manufacture of foamed plastics.
Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), which react rapidly in the lower atmosphere, have emerged as the lead synthetic chemical for refrigerants, and are considered a more environmentally friendly ...
2025-02-27
In soil, nitrogen (N), an essential macronutrient for plant growth, exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity. This necessitates plants to grapple with a complex array of environmental conditions in their quest for N sustenance. Roots, as the pivotal organs in N acquisition, manifest a remarkable morphological plasticity, including variations in the length and density of primary roots, lateral roots, and root hairs, in response to the form and content of available N, which is termed N-dependent root system architecture (RSA). For cultivated crops, the ...
2025-02-27
A research team at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has successfully developed a super-photostable organic dye after two years of dedicated research—demonstrating perseverance akin to that of Marie Curie, who painstakingly extracted just 0.1 grams of radium from eight tons of ore to earn her Nobel Prize.
Single-molecule imaging, a technique that uses fluorescent markers to track proteins with precision, plays a crucial role in cell biology, biochemistry, molecular biology, and drug discovery. However, conventional organic ...
2025-02-27
Benefits of the New Method:
Enhanced Efficiency: The filter membrane allows air exchange while preventing bacterial contamination, eliminating the need for frequent cap opening and reducing the risk of errors.
Improved Reproducibility: The standardized protocol ensures consistent results, with a 100% success rate in generating germ-free flies compared to the previous 70%–80% rate.
Streamlined Process: This method simplifies the entire process, making it more accessible to researchers and allowing for larger-scale experiments.
Implications for Research:
This advancement opens doors for deeper exploration of the intricate dance between hosts ...
2025-02-27
What if a critical piece of the puzzle of brain aging has been hiding in plain sight? While neuroscience has long focused on proteins and DNA, a team of Stanford researchers dared to shift their gaze to sugars – specifically the complex sugar chains that cover all our cells like chain mail.
Their investigation revealed how changes in this sugary armor on the brain’s frontline cells could be key to understanding cognitive decline and diseases like Alzheimer’s.
“This is like landing on a new planet,” ...
2025-02-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – Leveraging national surveys, big data, and machine learning, Cornell University researchers have developed a new approach to mapping poverty that could help policymakers and NGOs better identify the neediest populations in poor countries and allocate resources more effectively.
To eliminate extreme poverty, defined as surviving on less than $2.15 per person per day, governments and development and humanitarian agencies need to know how many people live under that threshold, and where. Yet that information ...
2025-02-27
They may both be Olympic host cities, but Salt Lake City and Los Angeles, the major population hubs of their respective states, are much different places. However, they both experience poor air quality and share valley topography that traps pollutants during weather inversions.
Utah and Southern California differ sharply in their approaches to this problem, with the latter implementing more stringent regulations and fuel standards aimed at reducing emissions from motor vehicles. New research from the University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Experimental and numerical analysis of the potential drop method for defects caused by dynamic loads