Genetic switch could help control leaf growth in poor soils
2025-02-27
(Press-News.org)
A new study has identified a genetic circuit in plants that controls individual leaf growth and allows the plants to adapt to their environment. The findings could help the development of more drought-resistant crops.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Biosciences investigated the growth of maize leaves in plants cultivated in three different soils containing differential amounts of nutrients and water. They found that microbes colonising plant leaves across these soils influence the growth of the leaves independently of the concentration of nutrients and soil properties. The findings have been published today in Cell, Host and Microbe.
The leaf is one of the most important organs of a plant, they produce food for the plant through photosynthesis. Plant leaves are colonised by microbes that are vital for the survival and health of the plants, particularly in dry weather conditions. The complex microbiota help the plant to ‘digest’ the nutrients it needs.
This new study was led by Associate Professor Gabriel Castrillo, he said: “In nature, plant leaves are colonised by microbes. Whether and how these microbial communities modulate the growth of leaves is something poorly understood. We have now revealed more about this process through experiments of recolonization with synthetic communities of microbes. We demonstrated that abundant bacteria inhabiting young leaves promote individual leaf growth.”
By analysing and sequencing the RNA molecules in the leaf the team uncovered a genetic circuit related to plant defence that controls microbiota effect on individual leaf growth.
Dr Castrillo continues: “We consider that the mechanism discovered here is responsible for balancing the growth of different leaves through differential activation of the growth-defense trade-off. We predict that this mechanism intersects with other branches of the leaf growth regulatory network to establish a hierarchy of biotic or abiotic stress responses to ensure plant survival in nature where the present of multiple stresses is frequent.
“We envision that it might now be possible to optimise endogenous growth and defence trade-off mechanisms in crops such as maize via engineering leaf microbiota to increase plant growth in poor soils without compromising the plant’s defence against pathogens.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-27
Mothers who were given access to virtual breastfeeding support (or telelactation) through a free app tended to report more breastfeeding than peers who did not receive such help, with a more-pronounced effect observed among Black mothers, according to a new RAND study.
Reporting results from the first large trial of telelactation services, researchers found that mothers who were given access to video telelactation services reported slightly higher rates of breastfeeding six months after giving birth, as compared to mothers who did not receive the service.
The ...
2025-02-27
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of U.S. homicide rates, substantial variation was found across and within county, race and ethnicity, sex, and age groups; American Indian and Alaska Native and Black males ages 15 to 44 had the highest rates of homicide. The findings highlight several populations and places where homicide rates were high, but awareness and violence prevention remains limited.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paula D. Strassle, PhD, MSPH, email pdstrass@umd.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
2025-02-27
About The Study: This study found that the prevalence of adults with diabetes did not significantly change between 2013 and 2023, but glycemic control among those with diagnosed disease worsened in 2021-2023 after nearly a decade of stability. This trend was most pronounced among young adults. The increase of 1% in mean HbA1c levels and 20% decrease in glycemic control would increase the lifetime risk of cardiovascular events. Potential explanations for these findings include increased sedentary behavior, reduced social support, heightened mental health ...
2025-02-27
About The Study: In this cohort study of 46,000 U.S. residents, nearly two-thirds of participants had suboptimal 5-year sleep duration trajectories. Suboptimal sleep duration trajectories were associated with as much as a 29% increase in risk of all-cause mortality. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining healthy sleep duration over time to reduce mortality risk.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, email k.full@vumc.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.62117)
Editor’s ...
2025-02-27
Key Takeaways
Surgical adhesions — internal bands of scar tissue that form between organs or tissues after surgery— can lead to severe complications such as bowel obstructions, chronic pain, and infertility while increasing the difficulty of future operations.
Surgical adhesions negatively impact patient outcomes and drive up health care costs.
There is currently no standard measure of the severity of surgical adhesions or their impact on a patient’s quality of life.
CHICAGO – Scarring is expected after most operations, but surgical adhesions present a unique ...
2025-02-27
Age-related macular (AMD) degeneration is a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness in the elderly population. In so-called wet AMD, new, abnormal blood vessels grow in the central part of the retina called macula, which is required for high-acuity central vision, leading to fluid and blood leakage and macular damage or dysfunction. Although wet AMD accounts for a minority of AMD cases, 90% of AMD-related cases of blindness are due to wet AMD.
Wet AMD in its early stages can be treated with drugs to reduce the formation of new blood vessels, but this treatment is inefficient in cases where blood vessel formation is already in ...
2025-02-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Astronomers have long grappled with the question, “How do planets form?” A new collaboration among Michigan State University, Arizona State University and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory will seek to answer this question with the help of a powerful telescope and high-performance computers.
The team of researchers will use 154 hours on the James Webb Space Telescope, or JWST, to probe the atmospheres of seven planets beyond our solar system – all of which were formed less than 300 million years ago, around the time dinosaurs roamed ...
2025-02-27
Since the discovery of actin in relation to muscle function more than 80 years ago by Albert Szent-Gyorgyi in Szeged, Hungary, actin research has become extremely diverse and now extends to plants and prokaryotes, as well as biochemical, biophysical, molecular, and cellular biology fields. The need for an international actin conference with comprehensive topics, where the latest results and research directions are presented, is critical for the community. Therefore, we decided to bring together the best experts in actin biology from across the world to build research synergies to tackle long-standing questions ...
2025-02-27
Astronomers have long grappled with the question, “How do planets form?” A new collaboration among Arizona State University (ASU) , Michigan State University (MSU) and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) will seek to answer this question with the help of a powerful telescope and high-performance computers.
The team of researchers will use 154 hours on the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), to probe the atmospheres of seven planets beyond our solar system – all of which were formed less than 300 million years ago, around the time dinosaurs roamed the Earth. In conjunction with JWST, this collaboration, called the KRONOS program, will use computers ...
2025-02-27
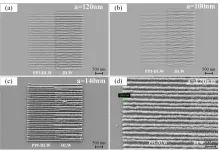
WASHINGTON — For the first time, researchers have used high-speed laser writing to create lines spaced just 100 nm apart on a glass substrate. The optimized printing approach could enable super-resolution 3D direct laser writing (DLW) of microlenses, photonics crystals, micro-optical devices, metamaterials and more.
DLW is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a focused laser beam to selectively solidify, or polymerize, a material with nanoscale precision. DLW typically uses multi-photon polymerization to polymerize materials in a precise, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Genetic switch could help control leaf growth in poor soils