(Press-News.org) A clinical trial has found that the medication omalizumab, marketed as Xolair, treated multi-food allergy more effectively than oral immunotherapy (OIT) in people with allergic reactions to very small amounts of common food allergens. OIT, the most common approach to treating food allergy in the United States, involves eating gradually increasing doses of a food allergen to reduce the allergic response to it. Thirty-six percent of study participants who received an extended course of omalizumab could tolerate 2 grams or more of peanut protein, or about eight peanuts, and two other food allergens by the end of the treatment period, but only 19% of participants who received multi-food OIT could do so. Researchers attributed this difference primarily to the high rate of allergic reactions and other intolerable side effects among the participants who received OIT, leading a quarter of them to discontinue treatment. When the participants who discontinued therapy were excluded from the analysis, however, the same proportion of each group could tolerate at least 2 grams of all three food allergens.
The findings were published in an online supplement to The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and presented at the 2025 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology/World Allergy Organization Joint Congress in San Diego on Sunday, March 2, 2025.
“People with highly sensitive multi-food allergy previously had only one treatment option—oral immunotherapy—for reducing their allergic response to moderate amounts of those foods,” said Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., director of NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), the study’s funder and regulatory sponsor. “This study shows that omalizumab is a good alternative because most people tolerate it very well. Oral immunotherapy remains an effective option if treatment-related adverse effects are not an issue.”
Omalizumab works by binding to the allergy-causing antibody called immunoglobulin E in the blood and preventing it from arming key immune cells responsible for allergic reactions. This renders these cells much less sensitive to stimulation by any allergen.
The current study is the second stage of a landmark clinical trial that found a 16-week course of omalizumab increased the amount of peanut, tree nuts, egg, milk and wheat that multi-food allergic children as young as 1 year could consume without an allergic reaction. This next stage of the trial was designed to directly compare omalizumab with OIT for the first time.
At 10 locations across the United States, the study team enrolled 177 children and adolescents ages 1 to 17 years and three adults ages 18 to 55 years, all with confirmed allergy to less than half a peanut and similarly small amounts of at least two other common foods among milk, egg, cashew, wheat, hazelnut or walnut. After completing the first stage of the trial, 117 individuals entered the second stage of the trial.
Upon beginning Stage 2, all participants received injections of omalizumab for eight weeks. Then the participants were randomly divided in half and placed into one of two groups. Group A received omalizumab injections and multi-allergen OIT for eight weeks, while group B received omalizumab injections and placebo OIT for eight weeks. Subsequently, group A received placebo injections and multi-allergen OIT for 44 weeks, while group B continued to receive omalizumab injections and placebo OIT for 44 weeks. Neither the participants nor the investigators knew who was in which treatment group.
Group A received omalizumab before and during their early months of OIT because data from prior studies suggested that pretreatment with the medication would significantly augment the safety of OIT, and continuing omalizumab during the early months of OIT would provide additional benefit.
During the study treatment period, 29 of 59 participants in group A discontinued therapy: 15 due to allergic reactions—some severe—or other intolerable symptoms of OIT, and 14 for other reasons, including aversion to the study foods or the burden of participating in the trial. No participants in group B had allergic reactions or other side effects from omalizumab that led them to discontinue therapy, but seven participants in group B left the study mainly due to the burden of participating in it. In all, 30 of the original 59 members of group A (51%) and 51 of the original 58 members of group B (88%) completed treatment.
After the study treatment period, the clinical trial team tested whether the participants who completed therapy could eat at least 2 grams of peanut protein and their two other study foods without an allergic reaction. Twenty-one of the original 58 participants in group B, or 36%, could tolerate at least 2 grams of all three foods, while only 11 of the original 59 participants in group A (the OIT-treated group), or 19%, could do so. When evaluating only the participants who completed therapy, however, the same proportion of each group could tolerate at least 2 grams of all three foods.
These results showed that omalizumab was more effective than OIT at treating multi-food allergy in people who originally had a very low tolerance to common food allergens. Investigators attributed this outcome mainly to the high rate of allergic reactions and other side effects leading to treatment discontinuation among the OIT-treated participants, despite receiving omalizumab before and during the early months of therapy.
The trial is called Omalizumab as Monotherapy and as Adjunct Therapy to Multi-Allergen OIT in Food Allergic Children and Adults, or OUtMATCH. The NIAID-funded Consortium for Food Allergy Research (CoFAR) is conducting the trial under the leadership of Robert Wood, M.D., and R. Sharon Chinthrajah, M.D. Dr. Wood is the Julie and Neil Reinhard Professor of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology and director of the Pediatric Clinical Research Unit at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Chinthrajah is an associate professor of medicine and of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology and the co-director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California.
NIAID funds the ongoing trial with additional financial support from and collaboration with Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, and Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The two companies collaborate to develop and promote omalizumab and are supplying it for the trial.
Further information about the OUtMATCH trial is available at ClinicalTrials.gov under study identifier NCT03881696.
Reference: RA Wood et al. Treatment of multi-food allergy with omalizumab compared to omalizumab-facilitated multi-allergen OIT. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.12.1022 (2025).
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 2, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
Risk reduced if treatment started within two years of diagnosis
MINNEAPOLIS – People with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, but if started early enough, continuous positive airway pressure ...
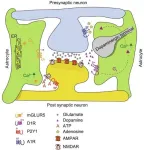
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex mechanisms of drug addiction, highlighting the crucial role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This research offers fresh perspectives on understanding and potentially treating substance-use disorders (SUDs).
For a long time, neuroscience research on drug addiction mainly focused on neuronal mechanisms. However, emerging evidence shows that astrocytes, the most abundant glial cells in the central nervous system, also play a significant part. Astrocytes ...
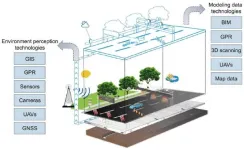
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the potential of digital twin (DT) technology in revolutionizing road engineering and its lifecycle applications. As road infrastructure worldwide faces the challenge of digitalization, DT has emerged as a promising solution.
The research, conducted by a team of scholars from Tongji University and Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), systematically reviews DT-enabling technologies, including model creation, condition sensing, data processing, and interaction. The development of DT in road engineering has been ...
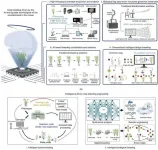
A new study published in Engineering explores how next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) and big data are revolutionizing crop breeding, with potential far-reaching implications for global food security.
Crop breeding has come a long way, evolving through distinct stages from domestication breeding to the current era of big data intelligent design breeding. The latest stage, “Breeding 4.0,” integrates biotechnology, big data, and AI. This convergence aims to achieve efficient, personalized breeding of new crop varieties, marking a significant shift from traditional “scientific” ...
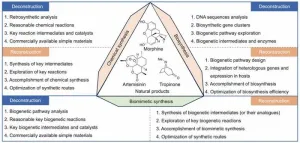
In a recent publication in Engineering, researchers from Jinan University in China and the University of Illinois Chicago in the US presented an in-depth perspective on the biomimetic synthesis of natural products. This research area, which bridges chemistry, biology, and pharmacy, has seen significant progress in recent years.
Natural products are crucial in drug discovery, providing essential scaffolds for developing new medications. However, obtaining sufficient quantities of these compounds for research and production is challenging due to resource limitations. Traditional chemical synthesis and biosynthesis methods also face their own set of ...
Tokyo, Japan – A team led by a member of Tokyo Metropolitan University have made advances in the search for dark matter, observing galaxies using new spectrographic technology and the Magellan Clay Telescope. With a mere 4 hours of observations, precise measurements in the infrared range have set new limits on the lifetime of dark matter. Their findings highlight the crucial utility of their technology and extend the search to less explored parts of the spectrum.
Over the past century, cosmologists have grappled with an apparent inconsistency in what they saw in the universe. Observations of the rotation of galaxies, for example, imply that there is a lot of mass out ...
WASHINGTON– The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) today expressed profound disappointment in the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) decision to deny the creation of the American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine (ABCVM).
The ABCVM was proposed by SCAI, the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) as a necessary step to establish cardiology as its own distinct medical specialty, separate from internal ...
In the race to meet the growing global demand for lithium — a critical component in batteries for electric vehicles — a team of researchers from Rice University’s Elimelech lab has developed a breakthrough lithium extraction method that could reshape the industry.
In their study published in Science Advances, the researchers demonstrated near-perfect lithium selectivity by repurposing solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) as membrane materials for aqueous lithium extraction. While originally designed for the rapid conduction of lithium ions in solid-state batteries — where there are no other ions or liquid solvents — the highly ordered and confined structure ...
American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine Chair Jeffrey Kuvin, MD, issued the following statement in response to the American Board of Medical Specialties denial of an independent board for cardiology:
“We are deeply disappointed with the American Board of Medical Specialties’ decision not to approve the American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine as a new, independent board for cardiology.
The decision ignores the evolution of cardiovascular medicine into its own distinct medical specialty, separate from the field of internal medicine, requiring its own set of knowledge, skills, and competencies to sustain professional excellence and effectively ...
Neuroblastoma is a solid tumor that occurs in children. When high-risk, the disease has a poor prognosis. Decades ago, adding the drug retinoic acid to neuroblastoma treatment increased survival by 10-15%. However, this effect was only evident in post-chemotherapy consolidation after bulky primary tumors had largely been eliminated. Why retinoic acid is effective in this setting but not against primary tumors, has been speculated about for nearly 50 years. St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists resolved the mystery in a new study, showing retinoic acid uses a novel mechanism to kill metastasized neuroblastoma. The drug “hijacks” ...