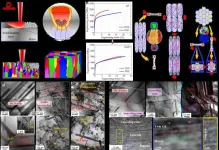
Long-term cocaine use may increase impulsivity
While being more impulsive does not necessarily escalate cocaine use, long-term cocaine use may increase impulsivity in otherwise healthy rats.
2025-03-03
(Press-News.org) Researchers have widely accepted that impulsivity increases the risk of drug addiction, but the evidence to support this belief is mixed. Exploring the relationship between impulsivity and cocaine use in rats, Yihong Yang and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found evidence that contradicts the prevailing view that high impulsivity predicts cocaine use.
One classification of impulsivity is impulsive choice, which can be studied with risky choice tasks and delay-discounting tasks (DDT). During DDT, impulsive individuals prefer smaller, immediate rewards over larger, delayed ones. In this eNeuro study, the researchers used DDT to categorize how impulsive rats were compared to their peers. After being classified by impulsivity level, the rats went through a cocaine self-administration paradigm; researchers can measure addiction-like behavior by continued cocaine use despite the known presence of unpleasant consequences—foot shocks, in this case. In addition to finding that impulsivity levels did not influence cocaine use, the researchers were surprised to discover that long-term cocaine use increased impulsivity in rats previously considered less impulsive than their peers. Brain imaging and other assessments revealed that rats with cocaine-driven impulsivity had fewer dopamine receptors and weaker communication between brain regions in a reward-related network. According to the authors, these findings advance our understanding of complex drug–brain circuit interactions and how they influence behavior.
###
Please contact media@sfn.org for the full-text PDF.
About eNeuro
eNeuro is an online, open-access journal published by the Society for Neuroscience. Established in 2014, eNeuro publishes a wide variety of content, including research articles, short reports, reviews, commentaries and opinions.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 35,000 members in more than 95 countries.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-03
London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) is transforming children’s journeys to school by making streets safer, improving perceptions of air quality and encouraging children to live healthier lives. A new study published today in BMJ Open, and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), highlights its benefits, with many families noticing cleaner air and safer roads. However, it also reveals challenges, particularly for those living in outer boroughs who are more reliant on the car and may struggle to adapt.
Road traffic is a major source of air pollution in London, posing serious health risks. One in 11 children in the city has asthma, a condition ...
2025-03-03
Tulane University researchers have developed a CRISPR-based test that diagnoses Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) — a life-threatening fungal infection primarily affecting children and immunocompromised patients — more quickly and less invasively, according to a new study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The highly accurate test detects RNA from live fungi in blood samples and throat swabs, eliminating the need for invasive bronchoscopy procedures currently used for diagnosis.
"Current diagnostic methods haven't evolved in ...
2025-03-03
Customized 3D-printed medical implants are becoming more common, and a new study has taken this technology to the next level. Researchers at Naton Biotechnology have developed the world’s first laser 3D-printed total knee implant, which has received official approval from China’s National Medical Products Administration as an innovative medical device.
The study focused on improving the strength and consistency of cobalt-chromium-molybdenum (CoCrMo) alloy implants made using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a 3D printing process. The team discovered and corrected inconsistencies in the structure of the material ...
2025-03-03
The South by Southwest (SXSW) Conference and Festivals — a renowned convergence of pioneers, storytellers, and global visionaries — will take place this year from March 7-15 in Austin, Texas, bringing together a vibrant mix of ideas and innovations. Once again, UC San Diego will take center stage, showcasing cutting-edge research, transformative discussions on critical global challenges and a film premiere.
“UC San Diego’s participation in the 2025 South by Southwest Conference and Festivals reinforces our institution’s passion for interdisciplinary ...
2025-03-03
On the shores of Lake Tahoe at Emerald Bay State Park grows what some consider to be the most iconic old-growth forest in the Lake Tahoe Basin. Giant ponderosa pines — some of the last remaining in the area — share space with at least 13 other tree species.
Yet despite its high conservation value and proximity to severely burned forests, the Emerald Point stand has not been managed to reduce its risk to drought or catastrophic wildfire. The fire-adapted forest has also not experienced fire for at least 120 years. This has led to massive increases in forest density, fuels, and insect- and drought-driven mortality.
A fire ...
2025-03-03
SAN ANTONIO — March 3, 2025 —Researchers at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and the University of Michigan (U-M) have published a new study showing an advanced new methane flare burner, created with additive manufacturing and machine learning, eliminates 98% of methane vented during oil production. The burner was designed by U-M engineering researchers and tested at SwRI.
Oil producers can generate methane during oil production and typically use flare stacks to burn off this gas. However, wind blowing across conventional ...
2025-03-03
Dental implants used to replace single teeth continue to function well after several decades, according to a study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. After nearly forty years, all examined implants were still in place and fully functional.
The study is the longest follow-up study of single dental implants in the world and is based on a follow-up of a small group of patients who received single implants to replace missing teeth between 1982 and 1985.
The implants are a result of research conducted by Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark ...
2025-03-03
When a droplet of water falls on a hot pan, it dances across the surface, skimming on a thin layer of steam like a tiny hovercraft; this is known as the Leidenfrost effect. But now, researchers know what happens when a hot droplet falls on a cool surface. These new findings, publishing in the Cell Press journal Newton on March 3, demonstrate that hot and burning droplets can bounce off cool surfaces, propelled by a thin layer of air that forms beneath them. This phenomenon could inspire new strategies for slowing the spread of fires and improving engine efficiency.
"We started with a very fundamental question: What will happen ...
2025-03-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A synthetic microbiome therapy, tested in mice, protects against severe symptoms of a gut infection that is notoriously difficult-to-treat and potentially life threatening in humans, according to a team of researchers at Penn State. The team developed the treatment for Clostridioides difficile, or C. difficile, a bacterium that can cause severe diarrhea, abdominal pain and colon inflammation. C. difficile can overgrow when the balance of the gut microbiome — the trillions of organisms that keep your body healthy — is disrupted. The team said their findings could lead to ...
2025-03-03
Many people who have tried to lose weight by cutting calories are familiar with this frustrating reality: at some point, the body stops shedding pounds. It senses the reduced calorie intake and responds by slowing down metabolism, causing it to burn fewer calories than before the diet.
This happens because the body perceives a potential starvation threat and adapts by conserving energy while still carrying out essential functions. It may seem incredibly unfair that the body doesn’t recognize the goal of weight loss and instead works against it by holding on to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Long-term cocaine use may increase impulsivity
While being more impulsive does not necessarily escalate cocaine use, long-term cocaine use may increase impulsivity in otherwise healthy rats.