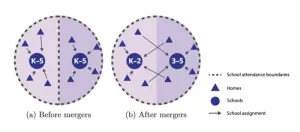
(Press-News.org) Racial segregation remains common in US schools, 70 years after federal legislation formally outlawing segregation by race. But previous research has demonstrated that integration can benefit students of all races and ethnicities. Students at integrated schools learn how to make connections with children from different backgrounds, developing empathy and mutual respect. Madison Landry and Nabeel Gillani explored whether merging schools could help integrate schools. One school could offer kindergarten through second grade for the current catchment areas of two elementary schools, while the remaining school could serve third through fifth graders for the same two catchment areas. This approach may be preferable to redistricting for some parents, because it does not break up groups of friends. The authors modeled the approach in elementary schools across 200 large school districts serving over 4.5 million students, finding that combining two or three schools could reduce racial/ethnic segregation by a median of 20% and up to 60% in some school districts. Driving commutes to school would rise by just 3.7 minutes, on average. Mergers could, however, reduce walkability. The utility of the approach depends on socio-geography. In Miami, where White students cluster by the water, there are few interfaces between racially dissimilar school catchment areas. However in Plano, Texas, pairing 36 schools into 18 clusters and creating one triplet could halve the amount of racial/ethnic segregation districtwide. The authors share their results with the public at mergers.schooldiversity.org, where the expected outcomes of elementary school mergers can be explored at the district level.
END
Merging schools to reduce segregation
2025-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ending pandemics with smartwatches
2025-03-04
Your smartwatch can probably tell that you are sick before you can—and if everyone followed their watch’s advice to self-isolate, incipient epidemics could be stopped in their tracks, according to a study.
During the early days of COVID-19, research showed that 44% of infections were spread before people even felt sick, making early detection critical for stopping outbreaks. Recent studies have demonstrated that smartwatches can detect infections before symptoms appear by picking up subtle physiological changes, ...
Mapping consensus locations for offshore wind
2025-03-04
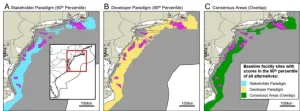
Ideal locations and scales for offshore wind installations depend on both physical conditions and social acceptability. Rudolph Santarromana and colleagues conducted a spatial multi-criteria analysis considering both techno-economics and a socio-environmental impacts, including a broad range of possible concerns, including visual, fishing, marine life, and vessel traffic impacts. Fifty-eight percent of plant location alternatives are suitable from the perspective of developers (techno-economic perspective), but just eighteen percent of sites are suitable from the perspective of a broad range of external stakeholders (socio-environmental perspective). ...
Breakthrough in clean energy: Palladium nanosheets pave way for affordable hydrogen
2025-03-04
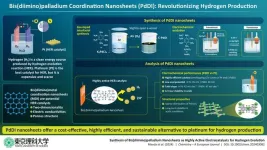
Hydrogen energy is emerging as a key driver of a clean, sustainable future, offering a zero-emission alternative to fossil fuels. Although it is promising, the large-scale production of hydrogen relies heavily on expensive platinum-based catalysts, and hence affordability remains a major challenge for the industry.
To surpass this, researchers from the Tokyo University of Science (TUS) have developed a novel hydrogen evolution catalyst, bis(diimino)palladium coordination nanosheets (PdDI), that offers platinum-like efficiency at a fraction of the cost. Their groundbreaking study, which was published on November ...
Novel stem cell therapy repairs irreversible corneal damage in clinical trial
2025-03-04
An expanded clinical trial that tested a groundbreaking, experimental stem cell treatment for blinding cornea injuries found the treatment was feasible and safe in 14 patients who were treated and followed for 18 months, and there was a high proportion of complete or partial success. The results of this new phase 1/2 trial published March 4, 2025 in Nature Communications.
The treatment, called cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), was developed at Mass Eye and Ear, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The innovative procedure consists of removing stem cells from a healthy eye with ...
News article or big oil ad? As native advertisements mislead readers on climate change, Boston University experts identify interventions
2025-03-04
In the battle against climate disinformation, native advertising is a fierce foe. A study published on March 4, 2025 in npj Climate Action led by Boston University (BU) researchers, in collaboration with Cambridge University colleagues, evaluates two promising tools to fight misleading native advertising campaigns put forth by big oil companies.
Many major news organizations now offer corporations the opportunity to pay for articles that mimic in tone and format the publication’s regular reported content. These ‘native advertisements’ are designed to camouflage seamlessly into ...
Advanced genetic blueprint could unlock precision medicine
2025-03-04
Creation of a comprehensive genetic representation for more than 2.5 billion people across the Middle East and South Asia could make a major contribution towards advancing precision medicine, a publication in Nature Medicine reveals.
Traditional genetic research has mainly relied on linear reference genomes, which is like having a single, standard version of human DNA that scientists compare everyone's genetic information against. This works well for studying individual genetics but does not capture all the complexities and differences found in diverse populations.
The Arab Pangenome Reference (APR) takes a different approach. Instead of relying on just one ...
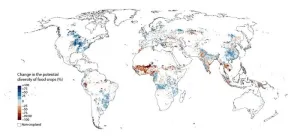
Study: World’s critical food crops at imminent risk from rising temperatures
2025-03-04
Study: World’s critical food crops at imminent risk from rising temperatures
Global food security could be notably impacted by a marked decline in crop diversity if temperatures rise by more than 1.5°C, reveals new research.
Global warming is already reshaping our daily lives, with storms, floods, wildfires and droughts around the world. As temperatures continue to rise, a third of global food production could be at risk. Now, a new study in Nature Food offers a more precise picture of exactly where and how warming will affect our ability to grow food.
Researchers at Aalto ...
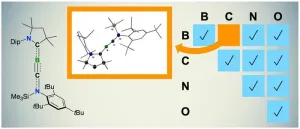
Chemistry: Triple bond formed between boron and carbon for the first time
2025-03-04
Boron, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen: these four elements can form chemical triple bonds with each other due to their similar electronic properties. Examples of this are the gas carbon monoxide, which consists of one carbon and one oxygen atom, or the nitrogen gas in the earth's atmosphere with its two nitrogen atoms.
Chemistry recognizes triple bonds between all possible combinations of the four elements – but not between boron and carbon. This is astonishing because there have long been stable double bonds between boron and carbon. In addition, ...
How a broken bone from arm wrestling led to a paradigm shift in mental health: Exercise as a first-line treatment for depression
2025-03-04
OTTAWA, Ontario, Canada, 4 March 2025 – In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview published today in Brain Medicine, psychiatry resident Dr. Nicholas Fabiano reveals how a personal injury transformed into groundbreaking research on the intersection of physical and mental health. The interview showcases Dr. Fabiano's innovative work in lifestyle psychiatry and his mission to bridge the historical divide between physical and mental wellness.
"The arbitrary line we have drawn between mental and physical health is one of the biggest mistakes in medicine," Dr. Fabiano explains in the interview. His perspective was profoundly shaped by a broken bone due to ...
Alarming levels of microplastics discovered in human brain tissue, linked to dementia
2025-03-04
OTTAWA, Ontario, Canada, 4 March 2025 – In a comprehensive Commentary published today in Brain Medicine (https://doi.org/10.61373/bm025c.0020), researchers discuss alarming new evidence about microplastic accumulation in human brain tissue, providing critical insights into potential health implications and prevention strategies. This Commentary examines findings from a groundbreaking Nature Medicine article by Nihart et al. (2025) on bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03453-1).
The ...