(Press-News.org) About The Study: The combination of coronary artery calcium (CAC) score with a primary prevention strategy in intermediate-risk patients with a family history of coronary artery disease was associated with reduction of atherogenic lipids and slower plaque progression compared with usual care. These data support the use of CAC score to assist intensive preventive strategies in intermediate-risk patients.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Thomas H. Marwick, MBBS, PhD, MPH, email Tom.Marwick@bakeridi.edu.au.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.0584)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2025.0584?guestAccessKey=df760f19-4a36-437b-adc9-753e8dac66b9&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_cotent=tfl&utm_term=030525
END
Effects of combining coronary calcium score with treatment on plaque progression in familial coronary artery disease
JAMA
2025-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer screening 3 years after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-05
About The Study: In 2023, reported breast and colorectal cancer screening rebounded from COVID-19 pandemic–related declines and surpassed pre-pandemic estimates. These findings are encouraging given larger-than-expected declines in early-stage breast and colorectal cancer diagnoses in 2020 and increases in distant-stage breast cancer diagnoses through 2021. Cervical cancer screening rates remained below pre-pandemic levels, a troubling trend as early-stage diagnoses continued to decrease in 2021. The persistent decline may in part reflect longer-term declines in patient knowledge and clinician recommendation of cervical cancer ...
Trajectories of sleep duration, sleep onset timing, and continuous glucose monitoring in adults
2025-03-05
About The Study: In this cohort study of middle-aged and older participants, persistent inadequate sleep duration and late sleep onset, whether alone or in combination, were associated with greater glycemic variability. These findings emphasize the importance of considering both sleep duration and timing for optimizing glycemic control in the general population.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Ju-Sheng Zheng, PhD, (zhengjusheng@westlake.edu.cn) and Yu-ming Chen, PhD, (chenyum@mail.sysu.edu.cn).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Sports gambling and drinking behaviors over time
2025-03-05
About The Study: This study found that over time, the trajectory of sports gambling frequency was associated with the trajectory of alcohol-related problems. Screening and treatment interventions are recommended for sport gamblers who also drink concurrently, especially because this group appears to be at an elevated risk for developing greater alcohol-related problems over time.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joshua B. Grubbs, PhD, email joshuagrubbs12@unm.edu
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2025.0024)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
For better quantum sensing, go with the flow
2025-03-05
Combine a garden-variety green laser, microwaves with roughly the energy of your wi-fi, and some diamond dust in drops of water, and what do you get? A precise chemical detection tool.
For the first time, researchers have combined nanodiamonds in microdroplets of liquid for quantum sensing. The new technique is precise, fast, sensitive, and requires only small amounts of the material to be studied – helpful when studying trace chemicals or individual cells. The results were published in the journal Science Advances in December.
“We weren’t even sure ...
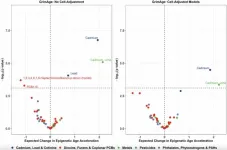
Toxic environmental pollutants linked to faster aging and health risks in US adults
2025-03-05
“Environmental chemical exposures represent a key modifiable risk factor impacting human health and longevity, and our findings provide evidence for associations between several environmental exposures and epigenetic aging in a large sample representative of the US adult population.”
BUFFALO, NY — March 5, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on February 11, 2025, Volume 17, Issue 2, titled “Exposome-wide association study of environmental chemical exposures ...
Jerome Morris voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
2025-03-05
Jerome E. Morris, the E. Desmond Lee Endowed Professor of Urban Education at the University of Missouri–St. Louis, has been voted president-elect of the American Educational Research Association (AERA). Morris joins the AERA Council in 2025–2026 as president-elect, and his presidency begins at the conclusion of the association’s 2026 Annual Meeting.
Morris leverages his upbringing in public housing and attending predominantly Black public schools in Birmingham, Alabama, to inform his research, which examines the intersection of ...
Study reveals how agave plants survive extreme droughts
2025-03-05
WASHINGTON — Agave plants may be best known for their role in tequila production, but they are also remarkably adept at retaining water in extremely dry environments. In a new study, researchers used terahertz spectroscopy and imaging to gain new insights into how these succulents store and manage water to survive in dry conditions.
“Understanding how plants adapt to dry conditions could lead to better farming practices and be used to develop crops that require less water,” said Monica Ortiz-Martinez ...
Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) launches a second funding opportunity to accelerate novel tool development to advance Parkinson's disease research
2025-03-05
The Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) initiative opened applications for research community members to apply for funding to develop novel tools to advance Parkinson’s disease (PD) research. The Collaborative Research Network (CRN) 2025 Technical Track grants will support the development of sustainable tools to accelerate validation and therapeutic research and discovery for emerging targets identified through ASAP discoveries, offering funding of up to $2M per year over three years, up to $6M total.
"By bringing researchers together to generate new preclinical tools for targets studied in our ASAP programs, our goal ...
New study: Eating mangos daily shown to improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control
2025-03-05
ORLANDO, Fla. – Mar. 5 2025 – New research has uncovered a potential gamechanger for improving cardiometabolic health: fresh mangos. A study recently published in the journal Nutrients finds that eating two cups of mango, just about 100 calories-worth, daily may help lower insulin concentration levels and improve insulin sensitivity in adults who are overweight or obese with chronic low-grade inflammation. The findings underscore how simple dietary choices could contribute to reducing the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, ...
Highly radioactive nuclear waste – how to keep it from oblivion
2025-03-05
Sweden’s radioactive nuclear waste will be stored in a sealed bedrock repository for 100,000 years. It will be hazardous for a very long time. So how can we ensure that humanity does not forget that it is there? Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have come up with a proposal for how to keep the memory alive over generations.
“We’re trying to do something that no one has ever done before. The person who eventually reads this might not even be human, but perhaps a kind of AI or something ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Effects of combining coronary calcium score with treatment on plaque progression in familial coronary artery diseaseJAMA