(Press-News.org) Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) is commonly known for causing blisters and sores. But in some cases, the virus can migrate to the eye or nervous system, causing severe, chronic symptoms.
Now, a study from University of Illinois Chicago researchers finds that herpes infection through the nose can lead to anxiety, motor impairment and cognitive issues. The research is the first to show that, by exploiting a cellular enzyme, the virus can produce behavioral symptoms. The finding emphasizes the need for prevention and treatment of a virus carried by billions of people worldwide.
The research, published in mBio, is the latest from the College of Medicine group led by Deepak Shukla, the Marion H. Schenk Esq. Professor in Ophthalmology for Research of the Aging Eye and UIC professor of microbiology and immunology.
Shukla’s laboratory previously studied how the virus spreads to the eye and brain and can lead to blindness, encephalitis and other conditions. The new research looked at intranasal infection, where viral particles enter the body through the nose and have more direct access to the nervous system.
“If an infected individual is shedding virus via tears, it could reach the nasal cavity, where it could go more directly to the brain,” Shukla said. “I think it’s underdiagnosed and understudied, but the neurological consequences, we believe, are much more severe than you would normally see with fever blisters or ocular infection.”
In animal experiments, the researchers observed high levels of inflammation and neuronal damage just days after HSV-1 infection. For several months after — equivalent to decades of life in humans — infected animals performed more poorly on tests of motor coordination and memory and exhibited more anxiety-like behavior when compared to controls.
“There is definitely nerve damage if you take the intranasal route, and the effects are long-term, which is alarming,” Shukla said.
The researchers also studied heparanase, a cellular enzyme the group previously studied for its role in HSV-1 reinfection and long-term effects. Animals with a deactivated gene for heparanase did not show the same neurobehavioral deficits after infection as control animals. That suggests the enzyme mediates some of the virus’ damaging effects in the brain.
“These insights open the door to potential therapeutic approaches to mitigate the effects of neuroinflammation and prevent long-term brain injury caused by viral infections,” said Hemant Borase, a UIC postdoctoral researcher and first author of the study.
Herpes simplex virus-1 is extremely common. The World Health Organization estimates that nearly two-thirds of the global population carry the virus.
“The virus reactivates throughout life; it’s a lifelong infection” said Chandrashekhar Patil, research assistant professor in the College of Medicine and co-author of the paper. “So, I think this awareness will be really important among the large population which is carrying this virus.”
Tibor Valyi-Nagy, professor of pathology, is also a co-author of the paper. The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
END
Intranasal herpes infection may produce neurobehavioral symptoms, UIC study finds
2025-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Developing treatment strategies for an understudied bladder disease
2025-03-10
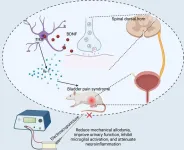
Despite its increasing prevalence, a painful condition called bladder pain syndrome, or interstitial cystitis, remains understudied with limited treatment options. In a new eNeuro paper, Min-Zhi Su and colleagues, from Sun Yat Sen University, used a rat model of bladder pain syndrome to explore if electroacupuncture can alleviate pain and improve bladder function. Electroacupuncture nerve stimulation therapy has shown promise in treating conditions like Huntington’s disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, but researchers have not explored its utility in this context. The researchers discovered that this ...
Investigating how decision-making and behavioral control develop
2025-03-10
Many psychiatric disorders are linked to altered functioning of brain networks that drive reward processing and executive functions like making decisions, taking risks, planning, and memory. But a better understanding of how these networks typically develop to support reward-related executive functions is needed. New in JNeurosci, Samuel Klein and Monica Luciana, from the University of Minnesota, led a longitudinal study to explore how brain networks for reward processing and executive functioning ...
Rutgers researchers revive decades-old pregnancy cohort with modern scientific potential
2025-03-10
The Camden Study, a pregnancy cohort of 4,765 women recruited between 1985 and 2006 from one of America’s poorest cities, has found new life at Rutgers University – where it promises to unlock critical insights into maternal and child health for researchers worldwide.
According to a recent paper in Nutrients, the project was designed to study nutritional status in adolescent pregnancies but expanded into a comprehensive repository of maternal and infant health data that yielded more than a decade of significant ...
Rising CO2 likely to speed decrease in ‘space sustainability’
2025-03-10
Currently more than 8,000 satellites are orbiting at altitudes of between 300 and 1000 km in the Earth’s upper atmosphere – also called the thermosphere. While changes in space weather, such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares, can cause temporary changes in the density of this region, scientists at the University of Birmingham suggest the effects caused by global warming are likely to be much longer term.
This is because of the effects caused by greenhouse gases (GHGs) ...
Study: Climate change will reduce the number of satellites that can safely orbit in space
2025-03-10
MIT aerospace engineers have found that greenhouse gas emissions are changing the environment of near-Earth space in ways that, over time, will reduce the number of satellites that can sustainably operate there.
In a study that will appear in Nature Sustainability, the researchers report that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases can cause the upper atmosphere to shrink. An atmospheric layer of special interest is the thermosphere, where the International Space Station and most satellites orbit today. When the thermosphere contracts, the decreasing density reduces atmospheric drag— a force that pulls old satellites and other debris down to altitudes where they will ...
Mysterious phenomenon at center of galaxy could reveal new kind of dark matter
2025-03-10
A mysterious phenomenon at the centre of our galaxy could be the result of a different type of dark matter.
Dark matter, the mysterious form of unobserved matter which could make up 85% of the mass of the known universe, is one of science’s biggest manhunts.
In this first of its kind study, scientists have taken a step closer to understanding the elusive mystery matter. They believe a reimagined candidate for dark matter could be behind unexplained chemical reactions taking place in the Milky Way.
Dr Shyam Balaji, Postdoctoral Research Fellow at King’s College London and one of the lead authors of the study explains, “At the ...
Unlocking the secrets of phase transitions in quantum hardware
2025-03-10
Phase transitions, like water freezing into ice, are a familiar part of our world. But in quantum systems, they can behave even more dramatically, with quantum properties such as Heisenberg uncertainty playing a central role. Furthermore, various spurious effects can cause the systems to lose, or dissipate, energy to the environment. When they happen, theses “dissipative phase transitions” (DPTs) push quantum systems into new states.
There are different types or “orders” of DPTs. First-order DPTs are like flipping a switch, causing abrupt jumps between states. ...
Deep reinforcement learning optimizes distributed manufacturing scheduling
2025-03-10
A recent study published in Engineering presents a significant advancement in manufacturing scheduling. Researchers Xueyan Sun, Weiming Shen, Jiaxin Fan, and their colleagues from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and the Technical University of Munich have developed an improved proximal policy optimization (IPPO) method to address the distributed heterogeneous hybrid blocking flow-shop scheduling problem (DHHBFSP).
The DHHBFSP is a complex optimization challenge in manufacturing. In distributed manufacturing settings, jobs with diverse requirements arrive randomly at different hybrid flow shops. These shops have varying numbers of machines ...
AACR announces Fellows of the AACR Academy Class of 2025 and new AACR Academy President
2025-03-10
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) today announced its newly elected 2025 class of Fellows of the AACR Academy.
The mission of the Fellows of the AACR Academy is to recognize and honor extraordinary scientists whose groundbreaking contributions have driven significant innovation and progress in the fight against cancer. Fellows of the AACR Academy constitute a global brain trust of leading experts in cancer science and medicine, working to advance the AACR’s mission to prevent and cure all cancers through ...
TTUHSC’s Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences hosts 37th Student Research Week
2025-03-10
Student researchers from the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) participated in the 37th Student Research Week Feb. 26-28. Organized by the TTUHSC Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Student Research Week is an opportunity for TTUHSC student investigators to showcase their work and hear presentations from distinguished national speakers related to the year’s theme.
The Department of Cell Physiology and Molecular Biophysics hosted the 2025 event. The Student Research Week committee chose “Let’s Get Biophysical” as the ...