(Press-News.org) An analysis of a 30,000-year-old fossil vulture from Central Italy has revealed for the first time that volcanic rock can preserve microscopic details in feathers - the first ever record of such a preservation.
An international team, led by Dr Valentina Rossi (University College Cork, Ireland), discovered a new mode of preservation of soft tissues that can occur when animals are buried in ash-rich volcanic sediments.
The new research, published in the scientific journal Geology, reveals that the feathers are preserved in a mineral phase called zeolite, a mode of preservation of soft tissues never reported before.
The fossil vulture was found in 1889 near Rome by a local landowner who recognized its remarkable preservation. The entire body was preserved as a three-dimensional impression, with fine details such as the eye lids and wing feathers. The new research shows that preservation of feathers extends to tiny microscopic feather pigment structures.
Dr Rossi said: “Fossil feathers are usually preserved in ancient mudrocks laid down in lakes or lagoons. The fossil vulture is preserved in ash deposits, which is extremely unusual. When analysing the fossil vulture plumage, we found ourselves in uncharted territory. These feathers are nothing like what we usually see in other fossils”.
By analysing tiny samples of the fossil feathers using electron microscopes and chemical tests, the team revealed that the feathers are preserved in the mineral zeolite, a mode of fossil preservation never reported before.
“Zeolites are minerals rich in silicon and aluminium and are common in volcanic and hydrothermal geological settings” Rossi explains “zeolites can form as primary minerals (with pretty crystals) or can form secondarily, during the natural alteration of volcanic glass and ash, giving the rock a “mudrock-like” aspect”. The alteration of the ash due to passage of water induced the precipitation of zeolites nanocrystals that, in turn replicated the feathers to the tiniest cellular detail.
"The fine preservation of the feather structures indicates that the vulture carcass was entombed in a low temperature pyroclastic deposit."
Prof. Dawid A. Iurino (University of Milan), coordinator of the study said: “We are used to think that volcanic deposits are associated with hot, fast-moving pyroclastic currents that will destroy soft tissues. However, these geological settings are complex and can include low temperature deposits that can preserve soft tissues at the cellular level.”
Prof. Maria McNamara (UCC) said “The fossil record is continually surprising us, be it new fossil species, strange new body shapes, or in this case, new styles of fossil preservation. We never expected to find delicate tissues such as feathers preserved in a volcanic rock. Discoveries such as these broaden the range of potential rock types where we can find fossils, even those preserving fragile soft tissues.”
The discovery of a new mode of preservation of soft tissues potentially specific of volcanic rocks indicates that these deposits can contain remarkable fossils and should be the focus of new research.
ENDS
END
New fossil discovery reveals how volcanic deposits can preserve the microscopic details of animal tissues
2025-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New chromosome barcode system unveils genetic secrets of alfalfa
2025-03-18
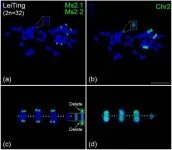
In a recent study, scientists have developed a revolutionary chromosome identification system for alfalfa, one of the world's most economically vital forage crops. Leveraging an advanced Oligo-fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) barcode technique, researchers successfully mapped and identified all chromosomes in alfalfa, uncovering unexpected chromosomal anomalies, including aneuploidy and large segment deletions. This breakthrough not only enhances molecular cytogenetics but also sheds light on the genetic stability ...
Reusing old oil and gas wells may offer green energy storage solution
2025-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Moving from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like wind and solar will require better ways to store energy for use when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing. A new study by researchers at Penn State found that taking advantage of natural geothermal heat in depleted oil and gas wells can improve the efficiency of one proposed energy storage solution: compressed-air energy storage (CAES).
The researchers recently published their findings in the Journal of Energy Storage.
CAES plants compress air and store it underground when energy demand is low and then extract the air to create electricity when demand ...
Natural insect predators may serve as allies in spotted lanternfly battle
2025-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Insect predators found in the United States could help keep spotted lanternfly populations in check while potentially reducing reliance on chemical control methods, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Penn State.
Led by entomologists in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences and published in Arthropod-Plant Interactions, the study evaluated the effectiveness of various insects in potentially controlling spotted lanternfly populations. The invasive pest, first detected in the United States in 2014, has spread across at least 18 states, causing significant damage to vineyards, orchards ...
Rice research team creates universal RNA barcoding system for tracking gene transfer in bacteria
2025-03-18
In the microscopic world of bacteria, gene transfer is a powerful mechanism that can alter cellular function, drive antibiotic resistance and even shape entire ecosystems. Now an interdisciplinary group of researchers at Rice University has developed an innovative RNA “barcoding” method to track these genetic exchanges in microbial communities, providing new insights into how genes move across species. The findings were recently published in Nature Biotechnology.
“We’ve long known that bacteria swap genes in ways that impact human health, biotechnology and environmental stability,” said James Chappell, associate professor of biosciences ...
New genetic pathway unlocks drought-resistant cucumbers with fewer branches
2025-03-18
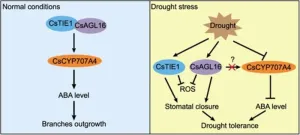
A new discovery has unveiled a genetic module, CsTIE1-CsAGL16, that simultaneously regulates lateral branch development and drought tolerance in cucumbers. This dual-function genetic pathway offers a promising new approach to breeding cucumber varieties that are both resilient to water scarcity and tailored to market preferences. By deciphering how these genes coordinate water conservation and branch growth, researchers have opened new doors for improving crop adaptability and productivity in the face of climate change.
Drought stress poses a major challenge to ...
New high-definition pictures of the baby universe
2025-03-18
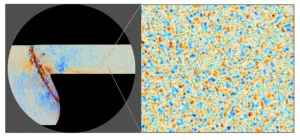
New research by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) collaboration has produced the clearest images yet of the universe’s infancy – the earliest cosmic time yet accessible to humans. Measuring light that traveled for more than 13 billion years to reach a telescope high in the Chilean Andes, the new images reveal the universe when it was about 380,000 years old – the equivalent of hours-old baby pictures of a now middle-aged cosmos.
“We are seeing the first steps towards making the earliest stars and galaxies,” says Suzanne Staggs, director of ACT and Henry ...
Zhou conducting GPU modeling research
2025-03-18
Keren Zhou, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), received funding for: “GPU Modeling Research of Smart Modeling and Simulation for HPC (SMASH).”
Zhou and his collaborators will complete research and development tasks.
Zhou received $65,648 from Brookhaven National Laboratory on a subaward from the U.S. Department of Energy for this research. Funding began in Feb. 2025 and will end in late Sept. 2025.
...
Twenty-two year study: Adolescents engaged in fewer external risky behaviors but some report increasing mental health concerns
2025-03-18
Between 1999-2021, U.S. adolescents steadily desisted from risky behaviors such as substance use and violence, and from reporting a combination of both risky behaviors and mental health symptoms. Yet a comparatively small but growing proportion of youth demonstrated elevated symptoms of depression, according to a report to be published in the April 2025 issue of Pediatrics.
The study, published online on March 18, and titled “Trends in Mental and Behavioral Health Risks in Adolescents: 1999-2021,” analyzed data from the national biennial Youth Risk Behavior Surveys distributed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A ...
Leafcutter ants recognize and fight pathogen even 30 days after initial contamination, study shows
2025-03-18
A study conducted by researchers from São Paulo State University (UNESP), in Brazil, and collaborators shows that lemon leafcutter ants (Atta sexdens) exhibit behaviors that go beyond so-called social immunity, i.e. the ability to detect pathogens and try to get rid of them for the benefit of the colony.
In an article published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, scientists report that these insects are able to recognize a pathogenic fungus they have already been exposed ...
Terrorists time their attacks during periods of security or financial crisis
2025-03-18
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Terrorists time their attacks during periods of security or financial crisis, according to new research from political scientists at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
To a bystander, a terrorist attack may seem an indiscriminate act of violence, timed solely to inflict maximum damage on its victims.
But the timing of such attacks is strategic, involving a series of tradeoffs to strike vulnerable targets while preserving the group’s reputation, according to research by Binghamton University Professor of Political Science Seden ...