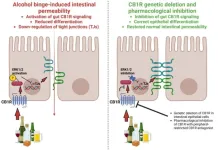
(Press-News.org) Heavy alcohol consumption is a leading cause of gastrointestinal diseases, with binge drinking linked to increased intestinal permeability—a condition commonly known as "leaky gut." Despite the significant health impact of alcohol-associated gastrointestinal disorders, effective pharmacological treatments remain limited. A new study published in eGastroenterology explores the role of gut cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) in alcohol binge-induced intestinal permeability and reveals how its inhibition can help protect the gut barrier.
The research, conducted by scientists from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), demonstrates that alcohol bingeing increases endocannabinoid levels in the proximal small intestine, triggering CB1R activation in intestinal epithelial cells. This activation disrupts tight junction proteins, which generally maintain the integrity of the gut lining, leading to increased intestinal permeability. This process can allow harmful substances, such as bacteria and toxins, to enter the bloodstream, contributing to inflammation and other health complications.
To investigate the role of CB1R, the researchers developed genetically modified mice with intestinal epithelial-specific CB1R deletion (CB1IEC−/− mice). They found that alcohol bingeing significantly increased gut permeability in normal mice, but this effect was absent in CB1IEC−/− mice, indicating that CB1R is a key mediator of alcohol-induced leaky gut.
Additionally, the study examined the effects of pharmacological CB1R inhibition using a peripherally restricted CB1R antagonist (S)-MRI-1891. When administered to normal mice before alcohol bingeing, this compound successfully prevented the increase in intestinal permeability. However, the drug had no effect in CB1IEC−/− mice, further confirming that CB1R in the intestinal epithelium is responsible for alcohol-induced gut barrier disruption.
Mechanistic studies revealed that CB1R activation in the gut epithelium triggers the ERK1/2 signalling pathway, which leads to the downregulation of tight junction proteins and a reduction in villus length—key factors contributing to a leaky gut. By inhibiting CB1R, researchers could reverse these changes, restoring gut barrier function and improving overall gut health.
These findings hold significant implications for the treatment of alcohol-related digestive disorders. Currently, there are no FDA-approved drugs specifically designed to treat alcohol-induced intestinal permeability. The study suggests that targeting CB1R with peripherally restricted antagonists could provide a novel therapeutic approach, potentially preventing systemic inflammation and other complications associated with alcohol-induced gut barrier dysfunction.
These insights could have broader applications in gastrointestinal health beyond alcohol-related gut disorders. The endocannabinoid system is known to influence gut motility, immune function, and microbiota composition, and its role in intestinal permeability suggests that CB1R inhibition may be beneficial in other conditions characterized by increased gut permeability, such as inflammatory bowel disease and metabolic disorders.
However, the study also highlights some limitations. While CB1R inhibition effectively prevented alcohol-induced leaky gut, it did not significantly impact metabolic parameters or liver disease progression. This suggests that although a leaky gut contributes to alcohol-related health issues, other mechanisms are also at play in the development of liver disease and metabolic dysfunction.
Future research will explore whether combining CB1R inhibitors with other therapeutic strategies could offer more comprehensive protection against alcohol-induced organ damage. Additionally, further studies are needed to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of CB1R antagonists in clinical settings.
This groundbreaking study advances our understanding of the gut’s response to alcohol and opens new avenues for targeted therapies. By identifying CB1R as a crucial mediator of alcohol-induced intestinal permeability, researchers have paved the way for potential pharmacological interventions that could help mitigate the harmful effects of binge drinking on gut health.
See the article:
Luca Maccioni, Szabolcs Dvorácskó, Grzegorz Godlewski, Resat Cinar, Malliga R Iyer, Bin Gao, George Kunos - Gut cannabinoid receptor 1 regulates alcohol binge-induced intestinal permeability: eGastroenterology 2025;3:e100173.
https://doi.org/10.1136/egastro-2024-100173
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery). eGastroenterology is now indexed by PubMed, Scopus, CAS, DOAJ, Dimensions, OpenAlex, ROAD, and COPE, with more to come!
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Environmental conditions can cause damaging stress to plants, posing challenges for home gardeners and farmers. Therefore, early detection — before leaves visibly discolor, wilt or wither — is crucial. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sensors have created a wearable patch for plants that quickly senses stress and relays the information to a grower. The electrochemical sensor attaches directly to live plant leaves and monitors hydrogen peroxide, a key distress signal.
Pests, drought, extreme temperatures and infections all cause stress ...
BUFFALO, NY, March 19, 2025 — For the third year the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, and the Buffalo Bills are working together to bring compression-only cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), known as Hands-Only CPR and automated external defibrillator (AED) training and equipment to community events, organizations and youth sports groups across Western New York. Known in the community as the HeartBEAT initiative, this work is adding more people to the ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Campylobacter infections are the most common foodborne illnesses in the U.S., sickening an estimated 1.5 million people each year. A new study examined records of Campylobacter jejuni infections from 10 states, plotting regional, age-related, and drug-resistance trends from 2013 to 2019.
The study found that drug-resistant C. jejuni infections were highest in the 20-39 age group and that quinolone-resistant C. jejuni infections increased from 22.6% of those tested in 2013 to 33.54% in 2019. The researchers also identified regional differences in C. jejuni resistance to quinolones and six other classes of antibiotics. The new findings are reported in ...
Covering a vast sky area in three mosaics, the data release also includes numerous galaxy clusters, active galactic nuclei and transient phenomena. This first survey data unlocks a treasure trove of information for scientists to dive into and tackle some of the most intriguing questions in modern science. Euclid enables us to explore our cosmic history and the invisible forces shaping our universe.
With its exceptionally large field of view for a space telescope, capturing an area 240 times larger in a single shot than the Hubble Telescope, Euclid delivers outstanding image quality in both the visible and infrared light spectrum.
Crucial contributions from Germany
Euclid is particularly ...
The invasive Pacific oyster have adapted to life in less salty seas and are reproducing off the coast of Skåne, although having been there for less than ten years. This discovery by researchers from the University of Gothenburg suggests that the oysters could colonise the western Baltic Sea in the future.
Pacific oysters were imported to oyster farms in Europe in the 1970s to replace native oysters whose stocks had collapsed. But they quickly began to spread from the farms, reaching northern ...
The latest advance in wearable robotic technology promises to solve a 200-year-old problem by revolutionising the fit of prosthetic limbs, transforming the lives of millions of amputees worldwide.
The new material, ‘Roliner,’ offers amputees the power to change the shape, volume, and stiffness of the liner that is used to attach a prosthetic limb’s socket to a residual leg. Amputees could make these tweaks using their smartphone in real-time, providing a more comfortable and personalised fit.
After eight years of prototype development and clinical investigation, researchers at the Department of Bioengineering at Imperial College ...
Electronic cigarettes use may pose lower cardiovascular risks in people living with HIV compared to tobacco cigarette use, new UCLA-led research shows. The study, published in JAHA, uses a novel laboratory model to examine the early stages of atherogenesis—the buildup of fats and cholesterol in the arteries. The findings suggest that electronic cigarettes (ECs) have a lower likelihood of causing changes associated with atherogenesis, compared to tobacco cigarettes (TCs), among those living with HIV.
While smoking has dropped to all-time low levels in the U.S., this hasn’t been the case for people living ...
Toronto, Canada – Every year, millions of family members and friends provide care for loved ones undergoing cancer treatment, often at great emotional cost. A new scoping review, published this week in Archives of Geriatrics and Gerontology Plus, confirms the toll that this work can take on caregivers’ mental health. According to the review, most studies show that more than 15% of those who care for loved ones with cancer suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
“Caregivers remain largely overlooked in psychosocial oncology care, leaving many without the support they need,” says lead author Elizaveta Klekovkina, ...
Using seawater, electricity and carbon dioxide (CO2), Northwestern University scientists have developed a new carbon-negative building material.
As Earth’s climate continues to warm, researchers around the globe are exploring ways to capture CO2 from the air and store it deep underground. While this approach has multiple climate benefits, it does not maximize the value of the enormous amounts of atmospheric CO2.
Now, Northwestern’s new strategy addresses this challenge by locking away CO2 permanently and turning it into valuable materials, which can be used to manufacture concrete, cement, plaster and paint. The process to generate ...
The ocean can be harnessed to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, effectively storing it in water layers and acting as a carbon sink. In research published in Advanced Sustainable Systems, investigators optimized an electrochemical method called seawater splitting for trapping and sequestering carbon dioxide into stable solid mineral deposits.
When applying voltage or current to seawater during seawater splitting, or electrolysis, hydrogen gas evolves at the cathode, while oxygen or chlorine gas is generated at the anode. Deposits of carbon-trapping minerals ...