(Press-News.org) Among the many marvels of life is the cell’s ability to divide and thus enable organisms to grow and renew themselves. For this, the cell must duplicate its DNA – its genome – and segregate it equally into two new daughter cells. To prepare the 46 chromosomes of a human cell for transport to the daughter cells during cell division, each chromosome forms a compact X-shaped structure with two rod-like copies. How the cell achieves this feat remains largely unknown.
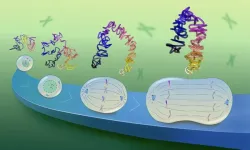
Now, for the first time, EMBL scientists have directly observed this process in high resolution under the microscope using a new chromatin tracing method. The new study shows that the long DNA molecules of each chromosome form a series of overlapping loops during cell division that repel each other. As a result of this repulsion, the DNA loops then stack up to form rod-shaped chromosomes.
Tracing chromosomal DNA in high resolution
Scientists have long hypothesised the importance of DNA loops in building and maintaining chromosomal structure. First identified in the 1990s, condensins are large protein complexes that bind DNA during cell division and extrude it to create loops of varying sizes. Previous studies from EMBL have shed light on the structural mechanics of this process and their essential role in packing chromosomes into forms that can be easily moved between cells.
In fact, mutations in condensin structure can result in severe chromosome segregation defects and lead to cell death, cancer formation, or rare developmental disorders called ‘condensinopathies'.
“However, observing how this looping process occurs on the cellular scale and contributes to chromosome structure is challenging,” said Andreas Brunner, postdoc in EMBL Heidelberg's Ellenberg Group and a lead author of the new paper. “This is because methods for visualising DNA with high resolution are usually chemically harsh and require high temperatures, which together disrupt the native structure of DNA.”
Kai Beckwith – former postdoc in the Ellenberg Group and currently an associate professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) – set out to solve this problem. Beckwith and colleagues used a method to gently remove one strand of DNA in cells at various stages of cell division, keeping the chromosome structure intact. They could then use targeted sets of DNA-binding labels to observe the nanoscale organisation of this uncovered DNA strand. This technique, called LoopTrace, helped the researchers directly observe DNA in dividing cells as it progressively formed loops and folds.
“Andreas and I were now able to visualise the structure of chromosomes as they started to change shape,” said Beckwith. “This was crucial for understanding how the DNA was folded by the condensin complexes.”
Loops within loops
From their data, the scientists realised that during cell division, DNA forms loops in two stages. First, it forms stable large loops, which then subdivide into smaller, short-lived nested loops, increasing the compaction at each stage. Two types of condensin protein complexes enable this process.
To understand how this looping eventually gives rise to rod-shaped chromosomes, the researchers built a computational model based on two simple assumptions. First, as observed, DNA forms overlapping loops – first large and then small – across its length with the help of Condensins. Second, these loops repel each other due to their structure and the chemistry of DNA. When the scientists fed these two assumptions into their model, they found that this was sufficient to give rise to a rod-shaped chromosome structure.
“We realised that these condensin-driven loops are much larger than previously thought, and that it was very important that the large loops overlap to a significant extent”, said Beckwith. “Only these features allowed us to recapitulate the native structure of mitotic chromosomes in our model and understand how they can be segregated during cell division.”
In the future, the researchers plan to study this process in more detail, especially to understand how additional factors, such as molecular regulators, affect this compaction process. In 2024, Jan Ellenberg and his team received funding of €3.1 million as an ERC Advanced Grant, to study the folding principles of chromosomes during and following cell division.
“Our newest paper published in the scientific journal Cell marks a milestone in our understanding of how the cell is able to pack chromosomes for their accurate segregation into daughter cells,” said Jan Ellenberg, Senior Scientist at EMBL Heidelberg. “It will be the basis to understand the molecular mechanism of rescaling the genome for faithful inheritance and thus rationally predict how errors in this process that underlie human disease could be prevented in the future.”
In the meantime, a second study from the Ellenberg Team, led by Andreas Brunner and recently published in the Journal of Cell Biology, shows that the nested loop mechanism is fundamental to the biology of cells, and continues during the cell’s growth phase with another family of DNA loop forming protein complexes, called cohesins.
“We were surprised to find that the same core principle of sequential and hierarchical DNA loop formation is used to either tightly pack chromosomes during division into safely movable entities, or to unpack them afterwards to read out the information they contain,” said Ellenberg. “In the end, small, but key mechanistic differences, such as the non-overlapping nature of cohesin-driven loops compared to the strongly overlapping condensin-driven loops might be sufficient to explain the vast differences that we see in the shape the genome takes in interphase and mitosis under the microscope.”
END
How chromosomes shape up for cell division
EMBL scientists have shown how overlapping loops of DNA stack upon each other in dividing cells to give rise to rod-shaped chromosomes
2025-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study identifies gut sensor that propels intestines to move
2025-03-24
After every meal, the intestines perform an action called peristalsis — moving food through their hollow interiors with coordinated contractions and relaxations of the smooth muscle.
For more than a century, scientists have known that nerve cells in the gut propel the colon to move, allowing the organ to perform its life-sustaining function. But exactly how these intestinal nerve cells do their job has remained elusive.
Now a new NIH-funded study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified ...
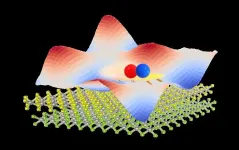
Moiré than meets the eye
2025-03-24
A moiré pattern appears when you stack and rotate two copies of an image with regularly repeating shapes, turning simple patterns of squares or triangles into a groovy wave pattern that moves across the combined image in an optical delight.
Similarly, stacking single layers of sub-nanometer-thick semiconductor materials known as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) can generate a moiré potential, and novel electronic and optoelectronic properties may emerge between the layers.
A moiré potential is a “seascape” of potential energy with regularly repeating peaks and valleys. They were previously thought to be stationary. But a team of ...
AI reshapes how we observe the stars
2025-03-24
AI tools are transforming how we observe the world around us — and even the stars beyond. Recently, an international team proved that deep learning techniques and large language models can help astronomers classify stars with high accuracy and efficiency. Their study, “Deep Learning and Methods Based on Large Language Models Applied to Stellar Light Curve Classification,” was published Feb. 26 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The team introduced the StarWhisper LightCurve series, a trio of AI models, and evaluated their performance ...
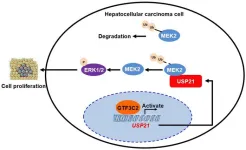
GTF3C2 promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the USP21/MEK2/ERK1/2 pathway
2025-03-24
Background and Aims
General transcription factor IIIC subunit 2 (GTF3C2) is one of the polymerase III transcription-related factors. Previous studies have revealed that GTF3C2 is involved in regulating cell proliferation. However, the role of GTF3C2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. This study aimed to determine its expression, biological function, and mechanism in HCC.
Methods
The expression of GTF3C2 in HCC and non-tumor tissues, along with its clinical significance, was investigated using public databases and clinical samples. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase ...
Embrace change with dynamic conservation models
2025-03-24
A recent article in BioScience, the journal of the American Institute of Biological Sciences, challenges conventional conservation wisdom, suggesting that protected areas such national parks and designated wilderness areas must embrace natural landscape dynamics rather than trying to preserve static conditions and landscape features.
Dr. Gavin M. Jones (USDA Forest Service) and colleagues contend that current conservation models often resist natural ecosystem processes such as wildfire, leading to a "backfire effect" that makes ecosystems more vulnerable ...
Some depression prevention programs may not help Black youth
2025-03-24
WASHINGTON – A depression prevention program that has helped white youth wasn’t effective for Black youth, raising concerns about the need for more research to help racially diverse groups, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
“I was very surprised that we couldn’t help Black youth as much as white youth, and we don’t know why there was such a profound difference in the outcomes.” said lead researcher Patrick Pössel, Dr. rer. soc., a professor of counseling psychology ...
White-collar crimes: ‘Fall from grace’ and the stigma of reentry into society
2025-03-24
People convicted of federal white-collar crimes come from different social and demographic backgrounds compared to those convicted of other offenses. Typically older and from the middle class, white-collar offenders face unique challenges during reentry into society. Yet, research on how social class influences their reintegration remains scarce.
A study by Florida Atlantic University, in collaboration with the University of Cincinnati, explores these challenges, focusing on how stigma, social background and emotional factors impact white-collar offenders as they transition into society ...
Engineers develop a better way to deliver long-lasting drugs
2025-03-24
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT engineers have devised a new way to deliver certain drugs in higher doses with less pain, by injecting them as a suspension of tiny crystals. Once under the skin, the crystals assemble into a drug “depot” that could last for months or years, eliminating the need for frequent drug injections.
This approach could prove useful for delivering long-lasting contraceptives or other drugs that need to be given for extended periods of time. Because the drugs are dispersed in a suspension before injection, they can be administered through a narrow needle that is easier for patients to tolerate.
“We showed that we can have very controlled, sustained delivery, ...
MIT scientists engineer starfish cells to shape-shift in response to light
2025-03-24
Life takes shape with the motion of a single cell. In response to signals from certain proteins and enzymes, a cell can start to move and shake, leading to contractions that cause it to squeeze, pinch, and eventually divide. As daughter cells follow suit down the generational line, they grow, differentiate, and ultimately arrange themselves into a fully formed organism.
Now MIT scientists have used light to control how a single cell jiggles and moves during its earliest stage of development. The team studied the motion of egg cells produced by starfish — an organism that scientists have long used as a classic model for ...
Research spotlight: A generalized epilepsy network derived from brain abnormalities and deep brain stimulation
2025-03-24
Frederic L.W.V.J. Schaper, MD, PhD, director of Epilepsy Network Mapping at the Center for Brain Circuit Therapeutics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and an instructor of neurology at Harvard Medical School, is the senior author of a paper published in Nature Communications, “A generalized epilepsy network derived from brain abnormalities and deep brain stimulation.”
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Generalized epilepsy has traditionally been considered a seizure of the ‘whole brain.’ However, new research has challenged this longstanding idea, since carefully targeting specific brain areas through deep brain stimulation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] How chromosomes shape up for cell divisionEMBL scientists have shown how overlapping loops of DNA stack upon each other in dividing cells to give rise to rod-shaped chromosomes