(Press-News.org)
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 24, 2025: Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi’s Advanced Microfluidics and Microdevices Laboratory (AMMLab) have developed an innovative sensing system that restores the missing tactile feedback in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), enhancing precision, ease of use, and safety. The new "off-the-jaw" system integrates force and angle sensors into the handle of laparoscopic tools, providing surgeons with real-time measurements of grasping forces and insights into tissue stiffness and thickness.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves small incisions, reducing pain, shortening recovery times, and lowering infection risks. However, traditional MIS tools eliminate the surgeon’s sense of touch, making it difficult to determine the appropriate force to apply or distinguish between different types of tissue. This lack of tactile sensation can lead to errors, such as over- or under-grasping delicate tissues.
The NYU Abu Dhabi researchers’ unique "off-the-jaw" design, detailed in IEEE Access, marks a significant departure from previous approaches, which typically placed sensors at the jaws of surgical tools. It is the first solution to separate the sensing mechanism from the surgical site itself. This solution offers a simplified, cost-effective alternative that seamlessly integrates with any commercially available laparoscopic tool, addressing challenges related to sensor integration, wiring complexity, contamination, and sterilization requirements.
Beyond improving surgical precision and safety, this new technology could also shorten the learning curve for new surgeons by providing objective tactile feedback, accelerating their mastery of MIS techniques. Its scalability means it could be adapted for robotic-assisted surgery, endoscopy, telemedicine, and other medical applications.
"Minimally invasive surgery has revolutionized the field, but the lack of tactile feedback remains a challenge," said NYU Abu Dhabi Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Bioengineering Mohammad A. Qasaimeh. "Our new system restores this missing sense of touch, giving surgeons real-time data on tissue stiffness and thickness. This 'off-the-jaw' approach not only eliminates contamination risks but also makes the technology easier to integrate without requiring complex modifications to existing surgical tools."
"Early trials have demonstrated a 30 percent improvement in surgical task efficiency, highlighting the practical impact of this technology on surgical performance," added Wael Othman, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Researcher at the AMMLab. "Looking ahead, we plan to refine this system for robotic-assisted surgeries and explore even more sensitive microfluidic-based sensors for enhanced tissue differentiation."
ENDS
About NYU Abu Dhabi
www.nyuad.nyu.edu
NYU Abu Dhabi is the first comprehensive liberal arts and research campus in the Middle East to be operated abroad by a major American research university. Times Higher Education ranks NYU among the top 30 universities in the world, making NYU Abu Dhabi the highest-ranked university in the UAE and MENA region. NYU Abu Dhabi has integrated a highly selective undergraduate curriculum across the disciplines with a world center for advanced research and scholarship. The university enables its students in the sciences, engineering, social sciences, humanities, and arts to succeed in an increasingly interdependent world and advance cooperation and progress on humanity’s shared challenges. NYU Abu Dhabi’s high-achieving students have come from over 120 countries and speak over 100 languages. Together, NYU's campuses in New York, Abu Dhabi, and Shanghai form the backbone of a unique global university, giving faculty and students opportunities to experience varied learning environments and immersion in other cultures at one or more of the numerous study-abroad sites NYU maintains on six continents.
END
BACKGROUND
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) rank among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally. Traditional urine culture methods have significant limitations in detection time and sensitivity, prompting the need to evaluate targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) as a potential diagnostic tool.
METHODS
The study included a discovery cohort of 400 suspected UTI patients (202 analyzed) and a validation cohort of 200 patients (110 analyzed). The study assessed detection time, concordance rates, ability to identify polymicrobial infections, and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Both clear and turbid ...
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the ...
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study Approach: In this cluster ...
Original Research
Background and Goal: Regular follow-up visits are critical for managing chronic conditions, yet some primary care clinics achieve higher visit regularity than others. This study aimed to identify specific strategies used by high-performing clinics to promote consistent follow-up visits for adults with chronic conditions.
Study Approach: This qualitative study used semi-structured interviews with 15 primary care physicians, 12 nurses, 15 administrative staff, and 4 pharmacists from 12 clinics—half with high temporal regularity (patients attending follow-ups consistently) and half with low temporal regularity, identifying strategies that helped high–temporal ...
Original Research
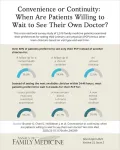
Background and Goal: This study focuses on how primary care patients balance the trade-off between continuity of care and access to timely appointments. It examines whether patients prefer to wait longer to see their own primary care physician (PCP) or prefer to see another clinician for faster care.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from a cross-sectional online survey of adult primary care patients in Michigan. Patients were presented with scenarios in the survey for different visit types—annual checkups, chronic and mental health follow-ups, ...
Research Brief
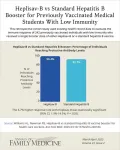
Background and Goal: Health care workers are at higher risk of hepatitis B infection due to occupational exposure to blood and body fluids. They are considered protected if they have a hepatitis B surface antigen antibody (anti-HBs) titer of ≥10 mIU/mL after completing a full vaccination series. This study compared the effectiveness of Heplisav-B, a new hepatitis vaccine, vs. standard hepatitis B vaccines as a booster in previously vaccinated individuals.
Study Approach: Researchers ...
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study ...
Background and Goal: Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are commonly prescribed for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but not recommended as first-line treatment unless patients have asthma/COPD overlap or frequent exacerbations. This study examined whether long-term ICS use (more than two years) increases the risk of serious health conditions compared with short-term use (less than 4 months).
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 20 million patients, focusing on individuals aged 45 and ...
Research Brief
Background and Goal: The COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown measures in France affected health care access and prescribing patterns, leading to significant changes in outpatient (ambulatory) antibiotic use. This study examined how systemic antibiotic use in France changed from 2020 to 2022 compared to expected trends.
Study Approach: Researchers used nationwide health insurance data covering 67 million people to track monthly antibiotic prescriptions from January 2010 to March 2022. ...
Original Research
Background and Goal: Prompt treatment of chlamydia and gonorrhea following a confirmed diagnosis is essential to prevent complications and reduce transmission. Adherence to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) treatment guidelines in primary care settings remains a concern. This study aimed to quantify the overall treatment rate for chlamydia and gonorrhea and identify factors associated with treatment delays and disparities.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed electronic health record data from the PRIME registry, which includes information ...