(Press-News.org) Businesses invest billions in marketing automation, and many assume that Automated Lead Nurturing (ALN) is a proven driver of sales. However, a new Journal of Marketing study reveals that ALN is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The research finds that while ALN improves engagement and enhances salesperson–lead interactions, its impact on sales conversions varies significantly across industries and customer segments.
Authored by Johannes Habel (University of Houston), Nathaniel Hartmann (University of South Florida), Phillip Wiseman (Texas Tech University), Michael Ahearne (University of Houston), and Shashank Vaid (McMaster University), the study examines when and how ALN effectively moves leads through the sales funnel. The findings indicate that ALN is most beneficial for new leads, short sales cycles, and lower-value deals. However, for high-value transactions and repeat customers, ALN’s impact is minimal.
“Many companies assume that automating lead nurturing will automatically drive sales, but our findings show that its effectiveness depends on the context,” says Habel. “For some businesses, ALN can significantly boost conversions, while for others, it may do little beyond increasing engagement.”
Key Findings
ALN Improves Engagement but Not Always Conversions While ALN increases interactions—such as email opens and website visits—these do not always translate into higher sales. Its effectiveness depends on the business model and the type of customer.
Best Fit: New Leads and Short Sales Cycles The study finds that ALN is most effective in industries with short sales cycles and lower-value deals, where potential buyers benefit from receiving automated, educational content before speaking with a salesperson.
Limited Impact on High-Value or Returning Customers ALN is less effective for high-value deals or returning customers who already have extensive knowledge about a company’s offerings. These buyers tend to rely on in-depth research and personalized consultations rather than automated messaging.
Implications for Business Leaders
For companies using ALN, these findings challenge the assumption that marketing automation always leads to higher sales. The study highlights the importance of measuring the right metrics to assess ALN’s true impact. “Many firms track vanity metrics like email open rates and clicks, but these don’t necessarily indicate sales success,” says Wiseman. “Instead, businesses should focus on ALN’s effect on actual revenue and deal closure rates.”
The research suggests that companies test ALN’s effectiveness within their specific context before fully committing. Firms should:
Assess customer type: Does ALN add value, or are leads already well-informed?
Analyze sales cycle complexity: Does automated nurturing provide useful guidance or do customers need direct engagement?
Measure real outcomes: Move beyond engagement metrics and track ALN’s impact on sales meetings and conversions.
Finding the Right Balance Between Automation and Human Interaction
The study also warns against over-reliance on ALN, particularly for industries that rely on relationship-based selling. While automation can enhance lead engagement, it should complement—not replace—human interactions.
“Companies using ALN should ensure it supports their sales teams rather than acting as a substitute for personalized engagement,” says Ahearne. “For high-value sales, a hybrid approach that blends automation with tailored conversations is often more effective.”
Moving Beyond the Hype
Marketing automation is a growing industry, but this study urges businesses to think critically about how they implement ALN. While automation can drive engagement, not all engagement leads to sales. Companies that tailor ALN strategies to their unique sales process will see better results than those blindly adopting automation tools. “ALN works best when used strategically,” says Vaid. “Businesses should test, refine, and measure how it aligns with their customers’ needs rather than assuming it will drive conversions for every lead.”
Full article and author contact information available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/00222429251321417
About the Journal of Marketing
The Journal of Marketing develops and disseminates knowledge about real-world marketing questions useful to scholars, educators, managers, policy makers, consumers, and other societal stakeholders around the world. Published by the American Marketing Association since its founding in 1936, JM has played a significant role in shaping the content and boundaries of the marketing discipline. Shrihari (Hari) Sridhar (Joe Foster ’56 Chair in Business Leadership, Professor of Marketing at Mays Business School, Texas A&M University) serves as the current Editor in Chief. https://www.ama.org/jm
About the American Marketing Association (AMA)
As the leading global professional marketing association, the AMA is the essential community for marketers. From students and practitioners to executives and academics, we aim to elevate the profession, deepen knowledge, and make a lasting impact. The AMA is home to five premier scholarly journals including: Journal of Marketing, Journal of Marketing Research, Journal of Public Policy and Marketing, Journal of International Marketing, and Journal of Interactive Marketing. Our industry-leading training events and conferences define future forward practices, while our professional development and PCM® professional certification advance knowledge. With 70 chapters and a presence on 350 college campuses across North America, the AMA fosters a vibrant community of marketers. The association’s philanthropic arm, the AMA’s Foundation, is inspiring a more diverse industry and ensuring marketing research impacts public good.
AMA views marketing as the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. You can learn more about AMA’s learning programs and certifications, conferences and events, and scholarly journals at AMA.org.
END
Automated lead nurturing boosts sales—but only under the right conditions
News from the Journal of Marketing
2025-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lessons from Venezuela’s democratic collapse: How opposition movements can defy autocratic leaders
2025-03-25
Until the 1990s, Venezuela was home to one of the most established democracies in Latin America. Today, however, it stands as one of the region’s most firmly entrenched authoritarian regimes.
How did this shift occur, and what can other countries learn from Venezuela’s transformation?
A new paper from political scientist Laura Gamboa at the University of Notre Dame chronicles the country’s 25-year evolution, during which Hugo Chávez and his successor, Nicolás Maduro, destroyed ...
USU ecologists document Utah's bee species and say beehive state is rich in bee diversity
2025-03-25
TOOELE, UTAH, USA -- Wildlife conservation is critical to sustaining the planet’s biodiversity and health. But putting together a conservation plan is a tall order. First of all, you need to determine what species you’re conserving, along with their numbers, habitat needs, threats and how they fit into a complex ecosystem.
As pollinators for native plants and food crops, bees play a pivotal role in our ecosystem, according to Utah State University ecologist Joseph Wilson. He and undergraduate researcher Anthony Hunsaker took on the herculean task of documenting Utah’s bee species using online occurrence records from the Symbiota Collection of Arthropods ...
A hit of dopamine tells baby birds when their song practice is paying off
2025-03-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- In his home office in Durham, Duke neuroscientist Richard Mooney shows a series of images of a bird’s brain on song.
In one, what looks like a pointillist painting illustrates a young zebra finch’s myriad attempts to sound more like an adult, capable of wooing a mate. In another, squiggly lines trace the ebb and flow of chemical signals in the reward circuit of the bird’s brain.
“Their songs don’t sound like much at first,” said Mooney, who has studied birdsong for four decades.
That’s because some things take considerable practice to master. Nobody walks onto a tennis court for the first time and plays ...
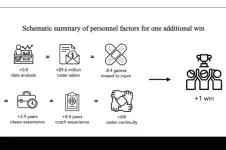
Basketball analytics investment is key to NBA wins and other successes
2025-03-25
If you filled out a March Madness bracket this month, you probably faced the same question with each college match-up: What gives one team an edge over another? Is it a team’s record through the regular season? Or the chemistry among its players? Maybe it’s the experience of its coaching staff or the buzz around a top scorer.
All of these factors play some role in a team’s chance to advance. But according to a new study by MIT researchers, there’s one member who consistently ...
Scientific cooperation is strategic for Brazil to strengthen relations with Europe
2025-03-25
Relations between Europe and South America – and especially with Brazil - are at a favorable moment, due to factors such as the free trade agreement between Mercosur and the European Union, signed in December 2024 and currently being approved. However, in order to take advantage of this window of opportunity and be competitive, Brazil must continue to expand scientific and technological cooperation with European partners.
This assessment was made by the Brazilian Ambassador to Germany, Roberto Jaguaribe, ...
Engineering antibodies with a novel fusion protein
2025-03-25
The Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 100 monoclonal antibodies to treat a range of diseases. Other antibodies are used by physicians to diagnose conditions or by scientists to advance research projects.
Even with significant expansion in the global market for antibodies used in clinical care and research, scientists recognize that there is still untapped potential for finding new antibodies. Many proteins group together in what are called protein complexes to carry out biological functions. The traditional method of generating antibodies by immunizing animals struggles to make antibodies related to these protein complexes.
The conventional ...
Transforming cardiovascular care through upfront combination therapy
2025-03-25
NEW ORLEANS - Ochsner Health Medical Director for Cardiac Rehabilitation and Preventive Cardiology, Carl J. “Chip” Lavie, Jr., MD, recently co-authored a groundbreaking research study featured in the prestigious Mayo Clinic Proceedings highlighting the comparative efficacy of lipid-lowering therapies for reducing cardiovascular risks and led by Maciej Banach, MD,PhD from Poland and leader of the International Lipid Expert Panel ( ILEP). Impact of Lipid-Lowering Combination Therapy With Statins ...
URI to host international XV Progress in Motor Control Conference
2025-03-25
Scientists from around the world specializing in motor control and neuroscience will travel to the University of Rhode Island this summer as the university hosts the international XV Progress in Motor Control Conference.
The university’s Department of Physical Therapy, its George & Anne Ryan Institute for Neuroscience, and the Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Program at URI, will host the biennial meeting of the International Society of Motor Control (ISMC) June 30 to July 2. This year’s conference will be held in the Center for ...
How Zika virus knocks out our immune defenses
2025-03-25
LA JOLLA, CA—Zika virus and dengue virus are very close relatives. Both are mosquito-borne flaviviruses, and both specialize in infecting a host's dendritic cells.
But a new Nature Communications study, led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) and UC San Diego shows that these two viruses have vastly different ways of making us sick.
Zika virus uses stealth. Zika virus slips into dendritic cells and blocks the dendritic cells from alerting nearby T cells to danger. It's the classic horror movie cliche—the creeper is already in the house, and ...
Could an arthritis drug unlock lasting relief from epilepsy and seizures? UW–Madison researchers see promising results in mice
2025-03-25
MADISON — A drug typically prescribed for arthritis halts brain-damaging seizures in mice that have a condition like epilepsy, according to researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
The drug, called tofacitinib, also restores short-term and working memory lost to epilepsy in the mice and reduces inflammation in the brain caused by the disease. If the drug proves viable for human patients, it would be the first to provide lasting relief from seizures even after they stopped taking it.
“It ticks all the boxes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Automated lead nurturing boosts sales—but only under the right conditionsNews from the Journal of Marketing