(Press-News.org) About The Study: Hormonal contraceptive initiation postpartum was associated with an instantaneous increased risk of developing depression in this cohort study. The associated risk was higher the earlier it was initiated postpartum, at least for combined oral contraceptives. This finding raises the issue of whether the incidence of depression postpartum is increased by routine hormonal contraceptive initiation after childbirth.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Vibe Gedsø Frokjaer, PhD, email vibe.frokjaer@nru.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2474)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2474?guestAccessKey=c0957767-f5eb-4d6d-88a4-15c747418b57&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=033125
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Postpartum hormonal contraceptive use and risk of depression
JAMA Network Open
2025-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CU research poised to change oxygen standards for trauma patients
2025-03-31
When a critically injured patient is admitted to the hospital, how much supplemental oxygen should they receive? New research published this week in JAMA Network Open led by investigators at the University of Colorado School of Medicine suggests it’s often less than the current standard.
“The idea has traditionally been that severe trauma causes stress to patients’ bodies, and we want to deliver as much oxygen as possible to the brain and to vital organs because they are losing blood,” says Adit Ginde, MD, MPH, professor ...
Brain-to-voice neuroprosthesis restores naturalistic speech
2025-03-31
Marking a breakthrough in the field of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), a team of researchers from UC Berkeley and UC San Francisco has unlocked a way to restore naturalistic speech for people with severe paralysis.
This work solves the long-standing challenge of latency in speech neuroprostheses, the time lag between when a subject attempts to speak and when sound is produced. Using recent advances in artificial intelligence-based modeling, the researchers developed a streaming method that synthesizes brain ...
NCSA research offers new diagnostic tool for anxiety, major depressive disorder
2025-03-31
Scientists at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications and the University of Illinois College of Medicine Peoria (UICOMP) were authors of a research paper published in the Journal of Acoustical Society of America Express Letters that demonstrates improved, automated screening methods for anxiety and major depressive disorders.
In the project titled, “Automated acoustic voice screening techniques for comorbid depression and anxiety disorders,” Mary Pietrowicz, along with colleagues from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and UICOMP, explored how machine ...
Single protein mimics retinoic acid therapy to help leukemia cells mature
2025-03-31
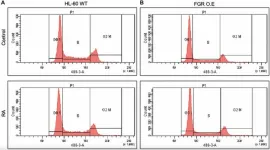
“This study reveals that the expression of the Src-family kinase (SFK), FGR, alone can induce cell differentiation similar to RA.”
BUFFALO, NY – March 31, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 21, 2025, titled “FGR Src family kinase causes signaling and phenotypic shift mimicking retinoic acid-induced differentiation of leukemic cells.”
A research team led by first author Noor Kazim and corresponding author Andrew Yen from Cornell University discovered that the FGR protein—traditionally ...
Research: Top scientists issue urgent warning on fossil fuels
2025-03-31
WASHINGTON— In a review published today in the peer-reviewed journal Oxford Open Climate Change, top scientists issued an urgent warning that fossil fuels and the fossil fuel industry are driving interlinked crises that threaten people, wildlife, and a livable future.
Today’s review synthesizes the extensive scientific evidence showing that fossil fuels and the fossil fuel industry are fueling not only the climate crisis but also public health harms, environmental injustice, biodiversity loss, and the plastics ...
Thinner Arctic sea ice may affect the AMOC
2025-03-31
One of the ocean currents in the Arctic Ocean is at risk of disappearing this century because of climate change, according to a new joint study from the University of Gothenburg and the German Alfred Wegener Institute. As a result, the North Atlantic could be flooded with freshwater which would weaken the global ocean circulation.
The weakening of the AMOC, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, is a hot topic among the world's climate scientists. However, it is unclear what the consequences will be when ...
How dreams, novelty, and emotions can shape memories: lessons from smartphone studies
2025-03-31
BOSTON - March 31, 2025 - A memory is not a straight line from one point to another, even if we sometimes think of them like linear stories. This key insight that cognitive neuroscientists have known for many years is now guiding a new type of research—to explore not only how memories evolve over time but also how they can be strengthened or changed. Assisting researchers with this new exploration is a powerful tool: smartphones.
“Smartphones are an incredible tool for understanding patterns of feelings, behavior, ...
Leveraging Preexisting Cardiovascular Data to Improve the Detection and Treatment of Hypertension
2025-03-31
About The Study: In the NOTIFY-LVH randomized clinical trial, a centralized population health coordinator–led notification and clinical support pathway for individuals with left ventricular hypertrophy on prior echocardiograms increased the initial treatment of hypertension. This work highlights the potential benefit of leveraging preexisting but potentially underutilized cardiovascular data to improve health care delivery through mechanisms augmenting the traditional ambulatory care system.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jason H. Wasfy, MD, MPhil, email jwasfy@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Study highlights barriers to including non-English speakers in research
2025-03-31
Health researchers omit including speakers of languages other than English (LOE) in their studies due to lack of training, challenges securing interpreter services, budget constraints and other barriers, according to a new JAMA Network Open study.
“Non-English-speaking individuals are being excluded from research, and we wanted to understand why,” said senior author Maya Ragavan, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh. “Ensuring that everyone can participate in research, regardless of the languages that they speak, helps ensure that the findings are representative of the entire community, ...
Queen Mary launches new regenerative medicine spinout to repair joint damage and prevent arthritis
2025-03-31
The method is substantially cheaper and easier to administer than even the best of today’s approaches – making it significantly more viable for healthcare providers.
The invention paves the way for a future restorative treatment for osteoarthritis.
Scientists at Queen Mary University of London have invented a new way to repair osteochondral defects – a common form of joint damage often caused by sports injuries or trauma – and to prevent progression to osteoarthritis.
The treatment uses Agrin, the protein which builds and maintains the link between our motor neurons and muscle fibres. A small soluble polypeptide ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
[Press-News.org] Postpartum hormonal contraceptive use and risk of depressionJAMA Network Open