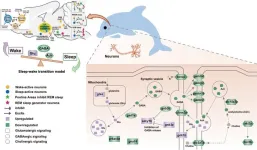
(Press-News.org) Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4c9g5gm
Article Title: Evolution of canonical circadian clock genes underlies unique sleep strategies of marine mammals for secondary aquatic adaptation
Author Countries: China
Funding: This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development (R&D) Program of China (grant no. 2022YFF1301600) to G.Y. & S.X., the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32030011) to G.Y., the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 32070409, 32270453, 31772448, 32270442, and 32200348), the National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2019YFA0802400) to H. W, the National Key Program of Research and Development the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the Qinglan Project of Jiangsu Province to S.X.. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Whales and dolphins sleep by turning off one half of their brains at a time; scientists discover more about the genes and pathways that enable this phenomenon
2025-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new clue to how multicellular life may have evolved
2025-03-31
Life emerged on Earth some 3.8 billion years ago. The “primordial soup theory” proposes that chemicals floating in pools of water, in the presence of sunlight and electrical discharge, spontaneously formed organic molecules. These building blocks of life underwent chemical reactions, likely driven by RNA, eventually leading to the formation of single cells.
But what sparked single cells to assemble into more complex, multicellular life forms?
Nature Physics published a new insight about a possible driver of this key step in evolution — the fluid ...
ALL ALS consortium launches website to advance ALS research
2025-03-31
ALL ALS Consortium Launches Website to Advance ALS Research
The Access for All in ALS (ALL ALS) Consortium announced the launch of its official website, creating a central hub for information about its initiatives and clinical research studies. ALL-ALS.org is designed to inform and engage researchers, clinicians, and current and prospective study participants.
The ALL ALS Consortium formed in fall 2023 with funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The consortium consists of 35 clinical sites in the United States and Puerto Rico, led by researchers at Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix, Arizona and Massachusetts ...
Many TB cases may have gone undetected in prisons in Europe and the Americas during COVID-19
2025-03-31
EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:30 P.M. EST on Monday, March 31, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Many TB Cases May Have Gone Undetected in Prisons in Europe and the Americas During COVID-19
A new study found that reported diagnoses for tuberculosis were consistently lower than expected throughout the pandemic, even though incarceration rates remained largely consistent and TB detection among the general population managed to reverse after an early-pandemic decline.
Incarcerated populations have a high risk of developing tuberculosis ...
Predicting older people’s frailty helps doctors intervene earlier
2025-03-31
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00.01 AM BST ON TUESDAY 1 APRIL
The new Electronic Frailty Index 2 (eFI2) is now available to 60% of England’s GPs thanks to research funded by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) and conducted by researchers at the University of Leeds and UCL
GP data on 36 health problems such as dementia, falls and fractures will help medical professionals to more accurately identify older people’s frailty and intervene earlier
Interventions may include a holistic assessment and treatment plan, falls prevention, targeted medicines review, and resistance exercise ...
New study validates lower limits of human heat tolerance
2025-03-31
A study from the University of Ottawa’s Human and Environmental Physiology Research Unit (HEPRU) has confirmed that the limits for human thermoregulation—our ability to maintain a stable body temperature in extreme heat—are lower than previously thought.
This research, led by Dr. Robert D. Meade, former Senior Postdoctoral Fellow and Dr. Glen Kenny, Director of HEPRU and professor of physiology at uOttawa's Faculty of Health Sciences, highlights the urgent need to address the impacts of climate change on human health.
The study found that many regions may soon experience heat and humidity levels that exceed the safe limits ...
UTA takes lead with mobile lab to address rural health care crisis
2025-03-31
Texas has the most rural residents of any state, with nearly 3 million people spread across a vast landscape. If rural Texas were its own state, it would rank as the 36th most populous.
Yet, rural Texans face significant barriers to health care that their urban counterparts do not. More than a quarter of the state’s 172 rural counties lack a hospital, and those with at least one hospital often struggle with a shortage of qualified health care personnel, such as nurses and first responders.
To address these growing challenges, The University of Texas at Arlington introduced its new Mobile Simulation Lab on Friday. It’s the first in Texas dedicated ...
New flexible hydrogel could improve drug delivery for post-traumatic osteoarthritis treatment
2025-03-31
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA) is a condition that affects joints after an injury. Current treatments focus on relieving symptoms but do not prevent or stop the progression of the condition. Although emerging therapies have shown promise in preclinical studies, a major obstacle is delivering these therapies effectively into the joint, a highly dynamic environment subjected to constant mechanical stress. Researchers at Mass General Brigham have created a new hydrogel to improve drug delivery for treating PTOA. The hydrogel, ...
Association for Molecular Pathology celebrates U.S. District Court’s decision to vacate FDA rule on laboratory-developed test procedure regulation
2025-03-31
ROCKVILLE, Md. – March 31, 2025 – The Association for Molecular Pathology, the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, and pathologist Michael Laposata, M.D., Ph.D., today announced a favorable ruling in their lawsuit against the U.S. Food and Drug Administration over the regulation of laboratory-developed test procedures. The ruling by Judge Sean D. Jordan of the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas granted AMP’s motion for summary judgment ...
Dr. Christopher Kramer is new American College of Cardiology President
2025-03-31
Christopher M. Kramer, MD, FACC, today assumed the role of president of the American College of Cardiology, an almost 60,000-member global cardiovascular organization working to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health for all.
“I see significant challenges and opportunities for the field of cardiology in the coming years, including workforce issues, health equity, diversity and inclusion, and AI-driven solutions, that need to be addressed to achieve ACC’s mission of transforming cardiovascular care for all,” ...
Dr. David Winchester is new Chair of ACC Board of Governors
2025-03-31
Effective today, David E. Winchester, MD, MS, FACC, will serve as chair of the American College of Cardiology Board of Governors (BOG) and secretary of the Board of Trustees. His term will run one year from 2025-2026.
Winchester will lead governors from chapters representing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico and representatives from the U.S. health services. The BOG serves as the grassroots governing body of the ACC, a leading cardiovascular organization representing over 56,000 cardiovascular care team members around the world.
“Being Chair of the Board ...