Tomato plants delay shoot meristem maturation to achieve heat-stress resilience
2025-04-02
(Press-News.org)
As global temperatures continue to rise, extreme heatwaves pose a significant threat to agricultural productivity. Studies estimate that for every 1°C increase above pre-industrial levels, crop yields decline by approximately 6-8%. The ability of plants to withstand heat stress is therefore critical for ensuring food security, yet the underlying molecular mechanisms have largely remained elusive.
Now, however, a new study led by Prof. XU Cao's team at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology (IGDB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences sheds light on an adaptive strategy that may be pivotal in developing heat-resilient crop varieties amid escalating climate change. Specifically, the study reveals a novel mechanism by which tomato plants actively mitigate heat stress and stabilize yield through the developmental reprogramming of shoot apical stem cells.
The research was published in Developmental Cell on April 2.
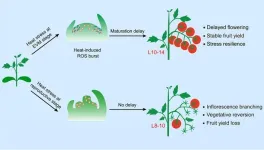
Stem cells in the shoot apical meristem (SAM) are essential for aerial morphogenesis—the process by which plants develop above-ground structures—and directly influence crop yield. However, heat stress can cause abnormal differentiation or even necrosis of these stem cells, resulting in developmental defects, plant mortality, and significant yield losses. Understanding how SAM stem cells adapt to heat stress is therefore critical for advancing cultivation techniques and breeding more resilient crop varieties.
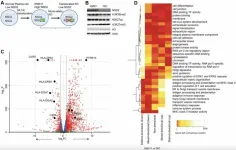
In their study, Prof. XU Cao and his team identified a key molecular adaptation mechanism in tomato plants. Under heat stress, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulate and promote the phase separation of TERMINATING FLOWER (TMF), a floral repressor. This modification prolongs the transcriptional repression of floral identity genes by TMF condensates, effectively reprogramming SAM development. By delaying shoot maturation, the plant extends vegetative growth, allowing it to avoid premature reproductive transitions under unfavorable conditions.
During early vegetative growth, tomato plants can enter a dormancy-like state in response to heat stress, temporarily suspending their maturation program. Once temperatures normalize, development resumes, ensuring stable yields. This strategic suspension has been shown to prevent 34–63% of yield losses in the first fruit truss, highlighting its significant role in heat resilience.
The study proposes that this redox-controlled bet-hedging mechanism functions as a survival strategy for sessile plants, enabling them to delay flowering during adverse conditions while ensuring reproductive success once environmental stresses subside.
The researchers emphasized that this discovery provides a new conceptual framework for developing climate-smart crops with environmentally responsive yield stability. The mechanistic insights identified in this study could guide precision breeding efforts aimed at improving agricultural productivity in a changing climate.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-02
When spring arrives and the heating season comes to an end, keeping warm becomes less of an issue. However, scientists remind us that it is not just a seasonal necessity – heat is also a valuable energy resource that can be stored and used when needed most. Researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU) have discovered an innovative solution beneath our feet: using soil as an efficient thermal energy storage system.
KTU professor Dr Tadas Ždankus and his team have been investigating how the ground can serve not only for construction purposes but also as a medium for heat storage. At the ...
2025-04-02
The American Sociological Association has led a coalition of leading sociological organizations to issue an open letter defending the vital role of sociology in universities and society while condemning recent federal actions that threaten academic inquiry and free speech. Signed by the presidents of ten major sociological associations, the letter calls on university leaders, policymakers, and the public to resist efforts that undermine the discipline and stifle research that benefits society.
The signatories express their growing concerns over abruptly canceled federal contracts, looming job losses for sociologists ...
2025-04-02
As the chemical industry seeks sustainable transformation, decarbonization requires intelligent solutions across multiple scales to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions. A research team led by Professor Xiaonan Wang at Tsinghua University has systematically reviewed AI-driven multi-scale smart systems for decarbonizing this energy-intensive sector. Published in Technology Review for Carbon Neutrality, the study explores innovations from materials discovery to industrial park optimization, highlighting ...
2025-04-02
Recently, Dr. Renheng Bo, Research Associate Professor at the State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics Technology, Tsinghua University, and his colleagues published a new review article entitled "Structured Locomotive Magnetic Soft Robots" in Flextech. This article focuses on the relationship between structural configurations and locomotion modes of magnetic soft robots, which systematically summarizes the material compositions, fabrication methods, locomotion mechanisms, and applications of existing magnetic soft robots. Furthermore, it emphasizes current challenges and future research directions in the field of structured ...
2025-04-02
ORLANDO, FL [April 2, 2025] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—celebrated 30 years of helping people with cancer to live better lives during the NCCN 2025 Annual Conference, March 28-30 in Orlando, Florida. The yearly event brings together leading minds and subject matter experts in front of a multidisciplinary audience to share the latest recommendations for cancer treatment and prevention.
“We are proud to honor our founders’ vision of sharing evidence-based, expert consensus-driven recommendations through clinical practice guidelines to improve ...
2025-04-02
“Our findings suggest a role for NSD2 in maintaining MM cell identity, with potential implications for future therapeutic strategies based on targeting of NSD2.”
BUFFALO, NY – April 2, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 21, 2025, titled “NSD2-epigenomic reprogramming and maintenance of plasma cell phenotype in t(4;14) myeloma.”
Researchers Andrea Gunnell, Scott T. Kimber, Richard Houlston, and Martin Kaiser from The Institute of Cancer Research, London, studied how a gene called ...
2025-04-02
NEW YORK—Thirty-two early career researchers, tackling issues from improving food security to developing better medical implants, were awarded up to two years of grant funding to pursue innovative interdisciplinary science, Schmidt Science Fellows announced today.
Now in its eighth year, the fellowship, a program of Schmidt Sciences, provides financial support for a postdoctoral placement of one to two years at a world-class research institution. The funding equips scientists to apply their knowledge to a new field of study with the goal ...
2025-04-02
Recent guidelines have restricted aspirin use in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. The American Heart Association (AHA)/American College of Cardiology (ACC) guidelines restricted aspirin to patients under 70, and more recently, the United States Preventive Services Task Force restricted aspirin use to patients under 60. However, heart attack and stroke risks both rise with age, leaving health care providers unsure about when to stop prescribing aspirin, whether it should be used for primary prevention, and which patients would benefit most.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s ...
2025-04-02
A new study by McGill University researchers yields insights into how the disruption of calcium transport in the brain is linked to autism and intellectual disability. The findings, published in the journal Nature, not only upend a long-held belief among neuroscientists, but could pave the way for treatments.
The researchers discovered that tiny protein structures on brain cells, known as AMPA receptors, can transport calcium. While previous research had suggested that disruptions in calcium ...
2025-04-02
In Sweden, around 18,000 workers are exposed to hexavalent chromium in their workplace. Hexavalent chromium is a powerful carcinogen that is released, for example, during welding of stainless steel or the manufacture of paints and rustproofing.
Thirty years ago, the limit for hexavalent chromium in Sweden was set at 5 micrograms per cubic metre of air. It is a technically calculated value that was determined based on what industry was considered to be able to handle at the time, rather than medical studies examining the level at which people start developing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tomato plants delay shoot meristem maturation to achieve heat-stress resilience