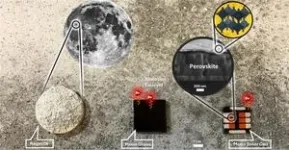
(Press-News.org) The same dirt that clings to astronauts’ boots may one day keep their lights on. In a study publishing April 3 in the Cell Press journal Device, researchers created solar cells made out of simulated Moon dust. The cells convert sunlight into energy efficiently, withstand radiation damage, and mitigate the need for transporting heavy materials into space, offering a potential solution to one of space exploration's biggest challenges: reliable energy sources.
“The solar cells used in space now are amazing, reaching efficiencies of 30% to even 40%, but that efficiency comes with a price,” says lead researcher Felix Lang of the University of Potsdam, Germany. “They are very expensive and are relatively heavy because they use glass or a thick foil as cover. It’s hard to justify lifting all these cells into space.”
Instead of hauling solar cells from Earth, Lang’s team is looking to materials available on the Moon itself. They aim to replace Earth-made glass with glass crafted from lunar regolith—the Moon’s loose, rocky surface debris. This change alone could cut a spacecraft’s launch mass by 99.4%, slash 99% of transport costs, and make long-term lunar settlements more feasible.
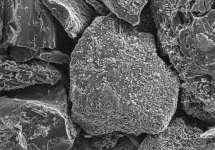
To test the idea, the researchers melted a substance designed to simulate Moon dust into moonglass and used it to build a new kind of solar cell. They crafted the cells by pairing moonglass with perovskite—a class of crystals that are cheaper, easier to make, and very efficient in turning sunlight into electricity. For every gram of material sent to space, the new panels produced up to 100 times more energy than traditional solar panels.
“If you cut the weight by 99%, you don’t need ultra-efficient 30% solar cells, you just make more of them on the Moon," says Lang. "Plus, our cells are more stable against radiation, while the others would degrade over time.”
When the team zapped the solar cells with space-grade radiation, the moonglass versions outperformed the Earth-made ones. Standard glass slowly browns in space, blocking sunlight and reducing efficiency. But moonglass has a natural brown tint from impurities in the Moon dust, which stabilizes the glass, prevents it from further darkening, and makes the cells more resistant to radiation.
Making moonglass, the team found, is surprisingly simple. It does not require complex purification and concentrated sunlight alone can provide the extreme temperatures needed to melt lunar regolith into glass. By tweaking the thickness of the moonglass and fine-tuning the solar cell’s composition, the team managed to achieve 10% efficiency. With clearer moonglass that lets in more light, they believe they could reach 23%.
Still, the Moon poses challenges that Earth doesn’t. Lower gravity could change how moonglass forms. The solvents currently used to process perovskite won’t work in the Moon’s vacuum. Wild temperature swings could threaten the materials’ stability. To find out if their moon dust solar cells are truly viable, the team hopes to launch a small-scale experiment to the Moon to test them out in real lunar conditions.
"From extracting water for fuel to building houses with lunar bricks, scientists have been finding ways to use Moon dust," says Lang. "Now, we can turn it into solar cells too, possibly providing the energy a future Moon city will need."
###
This research was supported by funding from the Volkswagen Foundation for funding via the Freigeist Q14 Program.
Device, Ortiz et al., “Moon photovoltaics utilizing lunar regolith and halide perovskites.” https://www.cell.com/device/fulltext/S2666-9986(25)00060-2.
Device (@Device_CP), is a physical science journal from Cell Press along with Chem, Joule, and Matter. Device aims to be the breakthrough journal to support device- and application-oriented research from all disciplines, including applied physics, applied materials, nanotechnology, robotics, energy research, chemistry, and biotechnology under a single title that focuses on the integration of these diverse disciplines in the creation of the cutting-edge technology of tomorrow. Visit http://www.cell.com/device/home. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
About The Study: More than 1 million noncitizen immigrants (one-third of them undocumented) work in health care in the U.S. Their ranks include skilled personnel who would be difficult to replace, especially if legal immigration is further restricted. Many health care workers may be removed if President Trump implements plans to deport undocumented immigrants and those losing temporary protected status (e.g., from Haiti and Venezuela).
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lenore S. Azaroff, MD, ScD, email Lenore_Azaroff@yahoo.com.
To ...
About The Study: The findings of this qualitative study of emergency medical services (EMS) clinicians suggest that migration has a complex, multidimensional influence on EMS clinicians in the border region. Deterrence-focused actions have not decreased the number of crossings but rather pushed migrants to cross in more dangerous ways, leading to more injuries and deaths. The findings suggest that the strain placed on local EMS clinicians is unsustainable and may be exacerbated by increased deterrence-based policies. Instead, border-region EMS clinicians need increased federal funding to support their work.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
About The Study: In this survey study, most resident physicians reported either being in a union or supporting unionization at their institution, citing pay and financial security as critical factors in their consideration of unionization. Future research should investigate other factors and whether unionization achieves its goals of increased pay and benefits, work hours, and well-being.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Laura K. Barger, PhD, email lkbarger@hms.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
In 2022, the American Cancer Society (ACS) updated its nutrition and activity guidelines for cancer survivors, recommending they avoid obesity, stay physically active, eat a healthy diet, and limit alcohol intake. New research by ACS scientists shows a lifestyle aligned with these guidelines is associated with a lower mortality risk among non-smoking survivors of obesity-related cancers in the United States. Survivors who maintained a healthy lifestyle both before and after their diagnosis — or those who improved their habits after diagnosis — also had a lower mortality risk. The study is out today in the Journal of the National ...
Age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression are a debilitating part of growing older, but people can lower their risk of these diseases through behavioral and lifestyle changes. In a new extensive systematic review, Mass General Brigham researchers identified 17 modifiable risk factors that are shared by stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Modifying any one of them can reduce your risk of all three conditions. The findings, which provide evidence to inform novel tools, such as the Brain Care Score, are ...
April 3, 2025, ONTARIO – The Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) has announced its support for five Ontario research teams working to develop the next generation of medicines that kill tumours more effectively, cause fewer side effects and reduce the risk that cancer will come back.
The projects will be funded as part of OICR’s Cancer Therapeutics Innovation Pipeline (CTIP) awards, which provides research teams with up to $300,000 over two years to help advance promising drug discovery research so that new cancer drugs can more quickly and safely reach patients.
“Ontario ...
‘Vast majority’ of direct air capture research through air’s moisture swings relies on engineered ion exchange resins to sequester CO2
Other previously untested materials with dual functions like aluminum oxide and activated carbon would reduce associated energy and cost
Cheap, scalable carbon capture will be critical to reducing worldwide carbon footprint
EVANSTON, Ill. --- Researchers at Northwestern University have expanded the potential of carbon capture technology that plucks CO2 directly from the air by demonstrating that there are multiple ...
Photos and b-roll package available for download here.
LOS ANGELES — USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of Keck Medicine of USC, has opened Keck Medicine of USC – Newport Beach Radiation Oncology and Imaging, a state-of-the-art radiation oncology and imaging center, at 4590 MacArthur Blvd. in Newport Beach.
The 12,500 square-foot clinical space houses new-to-market imaging and radiation therapy technology in a serene, beach-inspired space designed to help patients feel at ease.
“Our new radiation oncology and imaging center demonstrates our ongoing commitment to providing Orange County with world-class care,” said Rod ...
New York City, New York (April 3, 2025) – The Chan Zuckerberg Biohub New York (CZ Biohub NY) today announced nine new investigators to its growing roster of talented researchers. Joining from Columbia University, The Rockefeller University, and Yale University, the eight projects will focus on the Biohub’s mission to harness and bioengineer immune cells for the early detection, prevention, and treatment of a broad spectrum of age-related diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and aggressive cancers. The funded projects support a variety of innovative strategies, including leveraging synthetic biology to address the limitations of current ...
New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science shows that White Americans living in counties with higher Black poverty rates are more likely to believe racial equality of opportunity exists, while attributing racial disparities to lack of effort.
Led by Dr. Nicolas Sommet, the research included three studies with over 17,000 participants across hundreds of U.S. counties, using both observational and experimental methods to examine how exposure to racial inequality shapes beliefs about its causes.
"Our findings highlight how the environment we live in shapes how we understand racial inequality," explains ...