(Press-News.org) BARCELONA, Catalonia, Spain, 8 April 2025 – A new Brevia (peer-reviewed research report) published in Brain Medicine reveals that a single dose of the drug Osanetant, administered shortly after a traumatic event, significantly dampens fear expression in female mice. The findings provide strong preclinical support for using Nk3R antagonism as a sex-specific, time-sensitive intervention to reduce the risk of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Targeting fear memory at its roots
Fear memory is a core feature of PTSD, especially when neutral cues become emotionally loaded after trauma. The research team from the Institut de Neurociències of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona explored how fear consolidation could be interrupted shortly after exposure to stress, using Osanetant—a selective blocker of the neurokinin 3 receptor (Nk3R), which is part of the Tachykinin 2 (Tac2) pathway involved in emotional regulation.
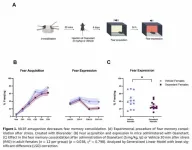
In the study, female mice underwent immobilization stress (a validated PTSD-like model), followed by a single injection of Osanetant 30 minutes later. Six days afterward, the animals were trained and tested using standard fear conditioning protocols. Those that received Osanetant showed significantly lower freezing behavior compared to controls (p = 0.038), indicating impaired consolidation of fear memory.
“This is an especially important window,” said Neha Acharya and Jaime Fabregat, co-first authors of the paper. “We’re not preventing fear learning—but reducing how intensely it gets biologically stored.”
Why focus on female mice?
The study zeroes in on sex as a biological variable, a critical but historically underrepresented factor in neuroscience. PTSD is twice as prevalent in women, yet most rodent models are still male-dominated. The team aimed to directly address this imbalance.
“We’ve known for years that female and male brains don’t process trauma the same way,” said Dr. Raül Andero who is an ICREA Research Professor and, senior author and principal investigator. “Yet female-focused pharmacological strategies remain rare. This study takes a first step toward closing that gap.”
Context matters: stress flips the drug’s effect
Curiously, earlier work from the same lab showed that Osanetant actually increased fear expression in non-stressed female mice—opposite to what was seen here. The authors suspect that stress exposure rewires neural circuits, potentially engaging different plasticity mechanisms. Factors like β-catenin, BDNF, GSK-3β, and mTOR are all candidates for mediating this switch.
Could trauma ‘prime’ the brain to respond differently to drugs? Does Nk3R antagonism only work when stress thresholds are crossed? And how might these findings translate to acute treatment in humans, such as post-assault or post-accident interventions?
“These are urgent questions,” said Dr. Andero. “Especially since Osanetant is already proven safe in clinical trials.”
Toward fast-track translation
The study is not without limitations: only female mice were tested, estrous cycles weren’t tracked, and no molecular markers were analyzed. Still, the behavioral outcome is robust—and the pharmacological window is both narrow and actionable.
Given Osanetant’s safety profile, the researchers suggest future studies could explore its use in emergency room settings, offering a rapid-response pharmacological shield against trauma-induced memory overconsolidation.
The peer-reviewed Brevia Article “NK3R antagonism reduces fear expression in a PTSD-like model of female mice” appears online on 8 April 2025 in Brain Medicine (Genomic Press) and is freely accessible at https://doi.org/10.61373/bm025l.0035.
About Brain Medicine: Brain Medicine (ISSN: 2997-2639) is a peer-reviewed medical research journal published by Genomic Press, New York. Brain Medicine is a new home for the cross-disciplinary pathway from innovation in fundamental neuroscience to translational initiatives in brain medicine. The journal’s scope includes the underlying science, causes, outcomes, treatments, and societal impact of brain disorders across all clinical disciplines and their interface.
END
For hundreds of years, the Amazon has been exploited for its gold. Today, the precious metal is just as sought after, but the remaining tiny gold particles are much harder to find. Mining often happens in artisanal and small-scale mining operations that release mercury (Hg) into the air, polluting the environment and harming human health.
An international team of researchers has now examined tree rings of species native to the Peruvian Amazon to determine if trees could be used to show approximately where and when atmospheric mercury was released.
“We show that Ficus insipda tree cores can be used as a biomonitor for characterizing ...
The research team led by Dr. Jongwon Yoon, Dr. Jeongdae Kwon, and Dr. Yonghoon Kim from the Energy & Environmental Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), has successfully developed the world’s first ammonia (NH₃) gas sensor based on a copper bromide (CuBr) film that can be fabricated through a simple solution process at low temperatures. This breakthrough technology not only enables sensor flexibility, ultra-sensitivity, and high selectivity but also significantly reduces manufacturing costs.
Ammonia gas sensors detect airborne ammonia and are utilized in indoor and outdoor ...
Hot flashes, mood swings, weight gain and insomnia are all signs of hormonal changes and symptoms of menopause, when a woman no longer has menstrual cycles. They can also signal perimenopause, when the body is preparing for this next season of life.
“Perimenopause is when the menstrual cycle has started to change, and it is persistent,” explained Lauren Baker, DO, an obstetrics and gynecology physician at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and certified practitioner with the Menopause Society. “The formal definition is periods fluctuate by at least seven days for at least 10 months.”
A new survey by Ohio State ...
SINGAPORE – Researchers from the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and the National Healthcare Group (NHG) have jointly pioneered an innovative imaging technique combining Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography (MSOT) with artificial intelligence (AI) that could significantly improve the diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), the most common form of skin cancer worldwide.
This advanced technique uses photoacoustic imaging (PAI), enhanced by an automated segmentation algorithm, to provide real-time, high-resolution, three-dimensional (3D) images of skin tumours. By accurately mapping tumour boundaries, ...
New Australian technology is set to transform the way that gastrointestinal cancers are detected and treated with precise, minimally invasive surgery.
Backed by the Federal Government’s Economic Accelerator (AEA) Ignite Grant, researchers from the University of South Australia (UniSA) are using quantum technology to develop a first-of-its-kind laparoscopic probe that will allow surgeons to accurately map the spread of tumours.
The technology has the potential to improve cancer survival rates and patient quality of life worldwide.
Led by Dr Nicole Dmochowska from UniSA’s ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Physicians have long observed a mystifying phenomenon: After a bout of infection or an autoimmune disease flare-up, some people experience prolonged mood swings, emotional dysregulation, and changes in behavior. But the precise connection between inflammation, mood, and behavior has remained elusive.
Now, two new studies from Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, published April 7 in Cell, detail the steps of an intricate brain-immune crosstalk that accounts for this long-known but poorly understood observation.
The work, conducted ...
Researchers have successfully demonstrated the UK’s first long-distance ultra-secure transfer of data over a quantum communications network, including the UK’s first long-distance quantum-secured video call.
The team, from the Universities of Bristol and Cambridge, created the network, which uses standard fibreoptic infrastructure, but relies on a variety of quantum phenomena to enable ultra-secure data transfer.
The network uses two types of quantum key distribution (QKD) schemes: ‘unhackable’ encryption keys hidden inside particles of light; and distributed entanglement: a phenomenon that causes quantum particles to be intrinsically ...
As many as one in 3,000 people could be carrying a faulty gene that significantly increases their risk of a punctured lung, according to new estimates from Cambridge researchers. Previous estimates had put this risk closer to one in 200,000 people.
The gene in question, FLCN, is linked to a condition known as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, symptoms of which include benign skin tumours, lung cysts, and an increased risk of kidney cancer.
In a study published today in the journal Thorax, a team from the University of Cambridge examined data from UK Biobank, the 100,000 Genomes Project, and East London Genes & Health – three large genomic datasets encompassing more than ...
Thinking creatively, solving complex problems, and working in teams… all add up to Design Thinking (DT). A study conducted by the Escuela Superior Politécnica del Litoral (ESPOL) and Ghent University provides a step-by-step guide for teaching this methodology as a university course.
The main objective of this study is to share the implementation of DT in the first year of all undergraduate programs at ESPOL, considering that previous research has shown that this course fosters essential DT skills in a world of constant change, allowing students to build their own knowledge through experiential learning.
In practice, this study ...
The American College of Cardiology is recognizing the 2025 winners of its Young Investigator Awards, which took place at the ACC’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25) in Chicago.
The Young Investigator Awards competition invites promising, young scientific investigators to present their cutting-edge research. The finalists competed in three categories: Basic and Translational Science, Clinical Investigations and Outcomes Research. This year’s awardees are:
Young Investigator Awards in Basic ...