(Press-News.org) A urinal designed to avoid urine splashback on the user and the floor will improve sanitation, bathroom cleanliness, and user experience.
Urinal designs have not materially changed in over a century. The style of urinal that was elevated to the status of artistic landmark by Marcel Duchamp in his 1917 dada art piece “La Fontaine” would not look out of place in today’s public restrooms. Use of a typical public urinal often results in splatter of urine outside the confines of the device—onto the floor and, most unpleasantly, onto the user, a situation that creates costly messes to clean and risks transmitting disease. Zhao Pan, Kaveeshan Thurairajah, and colleagues calculated that when the flow of urine impinges on the surface of the fixture at 30◦ or less, splashback is greatly reduced. Experimental results confirmed this. The authors then designed urinals by solving differential equations, dubbed Cornucopia and Nautilus, which have impinging angles at or below 30◦ across their entire area. The Nautilus design has an additional advantage: it fits a range of urination heights, making it easier for children and people who use wheelchairs to use. According to the authors, if the 56 million urinals in public restrooms in the US were replaced with the Nautilus, it would prevent one million liters of urine from splashing onto the floor each day.
END
Urinals without splashback
2025-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Even under stress, male-female pairs had each other’s backs
2025-04-08
When faced with a potential threat, mice often freeze in place. Moreover, when two animals are together, they typically freeze at the same time, matching each other’s periods of immobility.
In a new study, researchers found that coordination during fear looks different in males and females — and changes when stress is involved.
Male-female mouse pairs consistently stayed in sync during stressful situations, even when the animals were strangers. Same-sex pairs were more likely to fall out of step.
The findings, published in Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science, suggest that opposite-sex pairs may rely on a more flexible or complex coordination ...
Predictable visual stimuli as an early indicator for autism spectrum disorder in children
2025-04-08
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often experience social communication impairments and engage in restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs). Early identification of these symptoms is critical for timely intervention, but detecting RRBs, in particular, remains a challenge. Previous studies using eye-tracking methods have revealed that children with ASD tend to favor non-social stimuli over social ones, a preference that aligns with ASD symptoms. However, the developmental timeline of this preference—especially regarding repetitive versus random movements—remains poorly understood. Research has shown that children with ASD may spend ...
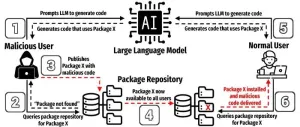
AI threats in software development revealed in new study from The University of Texas at San Antonio
2025-04-08
UTSA researchers recently completed one of the most comprehensive studies to date on the risks of using AI models to develop software. In a new paper, they demonstrate how a specific type of error could pose a serious threat to programmers that use AI to help write code.
Joe Spracklen, a UTSA doctoral student in computer science, led the study on how large language models (LLMs) frequently generate insecure code. His team’s paper has been accepted for publication at the USENIX Security Symposium 2025, a premier cybersecurity ...
Funding to support mental health at work is failing to deliver results
2025-04-08
EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY 8TH APRIL AT 10:30 CEST
FUNDING TO SUPPORT MENTAL HEALTH AT WORK IS FAILING TO DELIVER RESULTS
Tuesday 8th April 2025 – 10:30 CEST - New research presented at the 2025 European Congress of Psychiatry reveals that in the last 25 years, although there has never been this level of funding, guidelines and regulation aimed towards mental health at work, employees are now reporting greater workplace demands and increasingly less control over work deadlines. Many also report that they fear their job will make them ill. These stressors have a stronger negative impact ...
The Lancet: Nearly 500,000 children could die from AIDS-related causes by 2030 without stable PEPFAR programmes, expert policy analysis estimates
2025-04-08
Peer-reviewed/ Review, Analysis and Opinion / People
The Lancet: Nearly 500,000 children could die from AIDS-related causes by 2030 without stable PEPFAR programmes, expert policy analysis estimates
Experts assessed the potential impacts on HIV/AIDS treatment and prevention efforts in sub-Saharan Africa if the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is suspended or only receives limited, short-term funding, estimating that 1 million additional children could become infected with HIV and nearly 500,000 children could ...
Eclipse echoes: groundbreaking study reveals surprising avian vocal patterns during solar eclipse
2025-04-08
A new study published today in Scientific Reports reveals how birds responded to the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse across North America. The study finds bird vocalizations significantly declined only where more than 99% solar obscuration occurred. Researchers from Loggerhead Instruments, Inc. and the K. Lisa Yang Center for Conservation Bioacoustics at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology analyzed data from 344 community-based acoustic monitoring devices, called Haikuboxes, using a novel neural network approach. Unlike previous studies, ...
Mirvie announces results from largest molecular study in pregnancy and clinical validation of simple blood test to predict risk for preeclampsia months before symptoms
2025-04-08
South San Francisco, CA (April 8, 2025) - Today, Mirvie announced results of a breakthrough study published in Nature Communications, revealing new advances in the biological understanding of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), including preeclampsia - a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality as well as preterm birth. Researchers used data from more than 9,000 pregnancies within the multi-center Mirvie-sponsored Miracle of Life prospective study to discover and validate RNA signatures capable of distinguishing between severe and mild hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including preeclampsia, months before ...
Eating only during the daytime could protect people from heart risks of shift work
2025-04-08
A study led by researchers at Mass General Brigham suggests that, when it comes to cardiovascular health, food timing could be a bigger risk factor than sleep timing
Numerous studies have shown that working the night shift is associated with serious health risks, including to the heart. However, a new study from Mass General Brigham suggests that eating only during the daytime could help people avoid the health risks associated with shift work. Results are published in Nature Communications.
“Our prior research has shown that circadian misalignment – the mistiming of our behavioral cycle relative to our internal body clock – increases cardiovascular risk factors,” ...
Discovery of mitochondrial protein by researchers at Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University opens path to therapeutic advances for heart and Alzheimer’s disease
2025-04-08
(Philadelphia, PA) – Calcium transport into and out of mitochondria – the powerhouses of cells – is central to cellular energy production and cell death. To maintain the balance of calcium within these powerhouses, cells rely on a protein known as the mitochondrial sodium-calcium exchanger, or NCLX. Now, in new research, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have discovered a novel regulator of NCLX activity, a protein called TMEM65, which helps move ...
Recognizing the bridge builders between neuroscience and psychiatry
2025-04-08
Mental health is in crisis worldwide. While the neurosciences are advancing rapidly, psychiatry still struggles to diagnose and effectively treat many disorders. The Synapsy Center for Neuroscience and Mental Health Research at the University of Geneva, Switzerland, is launching a new international prize to reward those who bring these two worlds closer together.
A new research model is needed
Depression, schizophrenia, anxiety or bipolar disorders: psychiatric illnesses affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are among the leading causes of disability, suffering and mortality. Yet clinical advances remain limited. Many diagnoses ...