Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model
2025-04-13
(Press-News.org)
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
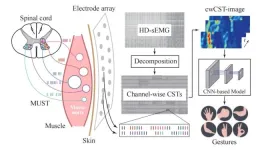
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) and reconstructing these into two-dimensional images based on the spatial layout of the electrodes.
Gesture recognition, as a natural human-computer interaction method, has broad application prospects in fields such as prosthetic control, rehabilitation training, and mixed reality. The commonly used surface electromyography (sEMG) signal analysis methods, such as those based on time-frequency domain features (such as RMS), often only capture rough neural control information, are susceptible to noise interference, and ignore the inherent spatial distribution characteristics of muscle movement. “With the development of high-density surface electromyography (HD sEMG) technology, the discharge sequences (Spike Trains) of motor units (MUs) obtained through decomposition can more directly reflect the neural system's control over muscles, providing more representative low dimensional neural control information for gesture recognition.” said the author Yang Yu, a researcher at Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
The research process of this paper is divided into the following steps: Firstly, the HD-sEMG electrode array is used to collect the electrical signals of the forearm muscles, and the signals are filtered, denoised, and abnormal channels are removed. Then, using an algorithm based on spatial propagation characteristics, the cumulative discharge sequence of each channel (cw-CST), is decomposed from the HD-sEMG signal to reflect the activity of adjacent motion units. Next, the cw-CST data of each channel is reconstructed into a two-dimensional image (cw-CST image) based on the spatial distribution of electrodes to capture the spatial activation patterns of neural control. Finally, a customized convolutional neural network is designed and trained for hand gesture recognition.
The experimental results show that the proposed cwCST-CNN method achieves a classification accuracy of 96.92 ± 1.77% in recognizing 10 gestures, which is significantly better than other comparative methods. Comparative analysis shows that features constructed based on cw-CST have better separability between different gestures (higher Separability Index) and consistency between training and testing data (lower Repeatability Index), providing strong support for improving recognition accuracy. “Our study provides a novel and effective solution for high-precision gesture recognition, with the potential for widespread application in human-computer interaction fields such as prosthetic control and rehabilitation training.” said Yang Yu.
Authors of the paper include Yang Yu, Zeyu Zhou, Yang Xu, Chen Chen, Weichao Guo, and Xinjun Sheng.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 52205025, 52175021, 52205024.
The paper, “Towards Hand Gesture Recognition Using a Channel-Wise Cumulative Spike Train Image-Driven Model” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Mar. 21, 2025, at DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0219.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
2025-04-12
A landmark study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that over 3 million children worldwide lost their lives in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.1
The study underscores the urgent need for both regional and global strategies to control paediatric AMR, particularly in high-burden areas such as South-East Asia and Africa. AMR poses a critical threat to children, who are highly vulnerable to infections.2 Access to new antibiotic formulations is often much more limited for children because of product development delays.
The study data found ...
2025-04-12
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that the proportion of adolescents living with overweight or obesity in England has increased by 50% from 2008-2010 (22%) to 2021-2023 (33%). The research, presented in two studies, is by Dr Dinesh Giri, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Bristol Royal Hospital for Children and Honorary Senior Lecturer, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, and Dr Senthil Senniappan, Consultant Paediatric Endocrinologist, Alder Hey Children’s Hospital, Liverpool, UK, and colleagues.
Previous ...
2025-04-12
The First International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems (ICCBS 2025) will be held in Singapore, Republic of Singapore, from July 24 to July 26, 2025. This conference aims at providing a free, open, and diverse platform for experts, scholars, students and industry professionals from the fields of robotics, biomedical engineering, neural engineering, and related domains. The sponsor of the conference is Beijing Institute of Technology, and the organizer of the conference is the Journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.
We look forward to welcoming experts, scholars and industry leaders from around ...
2025-04-11
Breakthrough study identifies promising biomarker for early sepsis detection in neonates, children, and pregnant women
A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has uncovered the potential of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a powerful diagnostic biomarker for the early detection of sepsis in high-risk patient groups, including neonates, children and pregnant women. This study is the first to evaluate IL-6’s diagnostic performance in a real-world cohort across all three populations.1
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition resulting from the immune system’s overreaction to infection, remains a leading global cause of mortality, accounting ...
2025-04-11
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows that around two thirds of participants of the SURMOUNT-1 trial had only regained 5% or less of their so-called nadir (or lowest weight) three years after beginning treatment with tirzepatide. The study is by Professor Louis Aronne, Comprehensive Weight Control Center, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA, and co-authors from Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, USA, which funded the study.
Obesity management is a long-term journey during which fluctuations ...
2025-04-11
Once-weekly treatment with tirzepatide can produce clinically meaningful and sustained weight loss for at least 3 years in adults with overweight or obesity who do not have diabetes, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Malaga, Spain (11-14 May). The findings also indicate that females and those without obesity-related complications may be more responsive to tirzepatide treatment.
The study, led by Dr Luca Busetto from the University of Padova in Italy and colleagues from Eli Lilly and Company that manufacture tirzepatide, is a continuation of the SURMOUNT-1 phase 3 trial of tirzepatide, a medication approved in ...
2025-04-11
Common respiratory condition nearly triples the risk of death in adults, new study finds
A major study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that adults with respiratory syncytial virus-associated acute respiratory infection (RSV-ARI) face a 2.7-fold higher risk of death within one year compared to the general population.1
The findings underscore the significant, yet often under-recognised, long-term health and economic burden of RSV-ARI in adults, particularly among those with underlying conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
RSV-ARI refers ...
2025-04-11
New research recently published in Archives of Sexual Behavior suggests children’s gender biases can be reflected in their facial emotional expressions.
Psychology professor Doug VanderLaan and his colleagues at the University of Toronto Mississauga, studied 296 children (148 boys and 148 girls) in Canada between the ages of four and nine years old while Wang Ivy Wong, Karen Kwan and their colleagues at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University studied 309 children (155 boys and 154 girls) in Hong Kong. All children watched four short stories that included five illustrations with pre-recorded audio narratives. ...
2025-04-11
Woods Hole, Mass. (April 11, 2025) - Being a geophysicist can sometimes feel like being a detective —uncovering clues, and then building a case based on the evidence.
In a new article published in Science Advances, a collaborative team led by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), presents a never-before-seen image of an oceanic transform fault from electromagnetic (EM) data collected at the Gofar fault in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The National Science Foundation funded work reveals ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model