(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, 2 hours of mother-neonate skin-to-skin contact (SSC) in the delivery room did not enhance neurodevelopmental outcomes at 2 to 3 years of age. However, the SSC group demonstrated improved breastfeeding practices up to 12 months compared with standard care, suggesting that the feasible and low-cost SSC intervention should be encouraged in clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Laila Kristoffersen, RN, PhD, email laila.kristoffersen@ntnu.no.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.5467)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.5467?guestAccessKey=c0957767-f5eb-4d6d-88a4-15c747418b57&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041625
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Immediate skin-to-skin contact in very preterm neonates and early childhood neurodevelopment
JAMA Network Open
2025-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘Cosmic radio’ could find dark matter in 15 years
2025-04-16
Scientists have designed a ‘cosmic radio’ detector which could discover dark matter in 15 years.
Published today in Nature, scientists at King’s College London, Harvard University, UC Berkley and others have shared the foundation of what they believe will be the most accurate dark matter detector to date.
Dark matter is the unobservable form of matter could make up as much as 85% of mass in the Universe, but scientists are not sure exactly what it is.
Axions are one of the leading ...
Supercharged mitochondria spark aging-related blood disorders
2025-04-16
As we age, blood stem cells, the essential source of new blood cells in the body, can accumulate genetic mutations. These mutations can give the cells a growth advantage, laying the foundation for developing serious health conditions. Now, scientists at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX) have not only discovered the mechanism that fuels their unchecked growth but have also found a way to stop it.
Led by Jennifer Trowbridge, professor and The Dattels Family Chair at JAX, the study reported today in the April 16 issue of Nature Communications reveals that a common aging-associated mutation in the gene Dnmt3a boosts the power-generating function of mitochondria ...
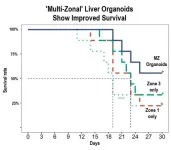
New human “multi-zonal” liver organoids improve injury survival in rodents
2025-04-16
One reason why our livers excel at clearing waste from our blood system is that the organ functions according to three key “zones” that perform specific major tasks. So, if scientists hope to create self-growing patches of liver organoid tissue that could help repair damaged organs, it’s important that the lab-grown tissue faithfully reproduce such zones.
In a groundbreaking paper published April 16, 2025, in the prestigious journal Nature, a team of organoid medicine experts at Cincinnati Children’s reports achieving just such a milestone – made from human stem cells. When these humanized organoids were transplanted into rodents whose own liver-bile duct system ...
Scientists achieve record-breaking growth in miniature, functional liver models
2025-04-16
Replicating the liver’s complexity
While organoids aim to mimic human organs, the liver’s repertoire of complex functions – and thus the energy it needs to operate – have made it challenging for researchers to grow organoids that proliferate and fully function, says Sato. When prioritizing growth and survival in laboratory settings, hepatocytes, the liver’s main cells, eventually transformed into cells resembling cholangiocytes, which line the bile duct. Hepatocyte functions only lasted 1-2 weeks at most.
The study team, led by Ryo Igarashi and Mayumi Oda at the Keio University School of Medicine, ...
Novel machine learning model can predict material failure before it happens
2025-04-16
A team of Lehigh University researchers has successfully predicted abnormal grain growth in simulated polycrystalline materials for the first time—a development that could lead to the creation of stronger, more reliable materials for high-stress environments, such as combustion engines. A paper describing their novel machine learning method was recently published in Nature Computational Materials.
“Using simulations, we were not only able to predict abnormal grain growth, but we were able to predict it far in advance of ...
Hereditary Alzheimer’s: Blood marker for defective neuronal connections rises early
2025-04-16
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease show altered blood levels indicating damaged neuronal contacts as early as 11 years before the expected onset of dementia symptoms. This is evident in the levels of the protein “beta-synuclein”. An international team, including researchers from DZNE, Ulm University Hospital and University Medicine Halle report these findings in the journal “Alzheimer’s & Dementia”. The biomarker studied here could potentially help to detect neurodegeneration at an early stage and thus ...
Nature-based activity is effective therapy for anxiety and depression, study shows
2025-04-16
Researchers evaluating a nature-based programme of activities for patients with mild to moderate mental health conditions have shown that improvements in mood and anxiety levels can be seen in as little as 12 weeks.
As part of the UK government’s commitment to transform mental health services, seven ‘test and learn’ green social prescribing sites were identified across England, which included a programme in Humber and North Yorkshire - the first of the seven sites to publish results from the national programme.
Green social prescribing is a practice whereby a healthcare professional refers a patient to community-based nature activities ...
New genomics tool accelerates biomedical breakthroughs
2025-04-16
A University of Virginia School of Medicine scientist and collaborators have developed a much-needed new tool to increase the efficiency of genomic research and accelerate the development of new ways to improve human health.
UVA researcher Nathan Sheffield, PhD, has spent four years developing a new data standard to ensure that scientists are comparing apples to apples when doing genomic analysis. This type of analysis helps researchers understand the operating instructions for our cells and see how those instructions are carried out. The resulting insights help us understand the workings of both healthy cells and unhealthy ones, pointing us to new ways to treat and prevent disease.
Genomics ...
DNA methylation entropy: A new way to track and predict aging
2025-04-16
“We find that epigenetic clocks based on the entropy of methylation states predict chronological age with similar accuracy as common approaches that are based on methylation levels of individual cytosines.”
BUFFALO, NY — April 16, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 3, on March 12, 2025, titled “DNA methylation entropy is a biomarker for aging.”
Researchers Jonathan Chan, Liudmilla Rubbi, and Matteo Pellegrini from the University of California, Los Angeles, led a study that discovered a new way to measure changes in DNA that can help predict a person’s ...
Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital recognized by Press Ganey for patient experience excellence
2025-04-16
The Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital’s cardiology faculty practice has received the 2024 Human Experience Pinnacle of Excellence Award® from Press Ganey, one of the nation’s leading patient experience organizations.
The faculty practice is located at The Mount Sinai Hospital and has several physicians with top expertise in cardiovascular care. It is one of 10 heart centers across the country, and the only one in New York, to receive this prestigious award placing it on the leading ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
[Press-News.org] Immediate skin-to-skin contact in very preterm neonates and early childhood neurodevelopmentJAMA Network Open