(Press-News.org) Cancer researchers have discovered an important protein, produced naturally inside cells, that appears to suppress the growth of prostate cancer cells in the laboratory. The findings, published tomorrow in the journal Cancer Research, offer promising leads for research towards new treatments.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the UK, with 37,500 men diagnosed with the disease every year. Many prostate cancers are slow growing, but in some cases the cancer is aggressive and spreads to other parts of the body, such as the bone. These cases are much more likely to be fatal.
In the new study, scientists at Imperial College London found that a protein called FUS inhibits the growth of prostate cancer cells in the laboratory, and activates pathways that lead to cell suicide.
The researchers also looked for the FUS protein in samples from prostate cancer patients. They found that in patients with high levels of FUS, the cancer was less aggressive and was less likely to spread to the bone. Higher levels of FUS also correlated with longer survival. The results suggest that FUS might be a useful marker that can give doctors an indication of how aggressive a tumour will be.
"At the moment, there's no way to say whether a prostate tumour will kill you or be fairly harmless," said Dr Charlotte Bevan, senior author of the study, from the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial College London. "Current hormonal therapies only work for a limited time, and chemotherapy is often ineffective against prostate cancer, so there's a real need for new treatments.
"These findings suggest that FUS might be able to suppress tumour growth and stop it from spreading to other parts of the body where it can be deadly. It's early stages yet but if further studies confirm these findings, then FUS might be a promising target for future therapies."
Prostate cancer depends on male hormones to progress as these hormones stimulate the cancer cells to divide, enabling the tumour to grow. Treatments that reduce hormone levels or stop them from working are initially effective, but eventually the tumour stops responding to this treatment and becomes more aggressive.
Dr Bevan and her team began by exposing prostate cancer cells to male hormones and looking at how the levels of different proteins changed. They discovered that the hormones made the cells produce less of the FUS protein, and examined further whether FUS might influence cell growth by inserting extra copies of the gene for FUS into cells grown in culture. They found that making the cells produce more FUS led to a reduction in the number of cancer cells in the dish.
Greg Brooke, first author of the study, from the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial College London said: "Our study suggests that FUS is a crucial link that connects male hormones with cell division. The next step is to investigate whether FUS could be a useful test of how aggressive prostate cancer is. Then we might look for ways to boost FUS levels in patients to see if that would slow tumour growth or improve response to hormone therapy.
"If FUS really is a tumour suppressor, it might also be involved in other cancers, such as breast cancer, which has significant similarities with prostate cancer."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by Prostate Action, the Medical Research Council, the Imperial College Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre (set up with a grant from Cancer Research UK and the Department of Health) and the Prostate Cancer Charity.
END
Boys predominantly pass on flu to other boys and girls to girls, according to a new study of how swine flu spread in a primary school during the 2009 pandemic, published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The results also suggest that flu transmission is most intensive between children of the same class, but that sitting next to an infected person does not significantly increase a child's risk of catching flu. The data will help researchers to model how epidemics spread and how interventions such as school closures can help contain an ...
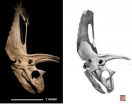
New Haven, Conn.—Triceratops and Torosaurus have long been considered the kings of the horned dinosaurs. But a new discovery traces the giants' family tree further back in time, when a newly discovered species appears to have reigned long before its more well-known descendants, making it the earliest known member of its family.
The new species, called Titanoceratops after the Greek myth of the Titans, rivaled Triceratops in size, with an estimated weight of nearly 15,000 pounds and a massive eight-foot-long skull.
Titanoceratops, which lived in the American southwest ...
Scientists have discovered why orchids are one of the most successful groups of flowering plants - it is all down to their relationships with the bees that pollinate them and the fungi that nourish them. The study, published tomorrow in the American Naturalist, is the culmination of a ten-year research project in South Africa involving researchers from Imperial College London, the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and other international institutions.
The orchid family is one of the largest groups of flowering plants, with over 22,000 species worldwide. Today's research suggests ...
Using funding provided under the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act, the U.S. Department of Energy's Savannah River National Laboratory has launched a demonstration project near one of the Savannah River Site's former production reactor sites to clean up chemically contaminated groundwater, naturally.
A portion of the subsurface at the Site's P Area has become contaminated with chlorinated volatile organic compounds that are essentially like dry-cleaning fluid. SRNL and Clemson University have patented a consortium of microbes that have an appetite for that kind ...
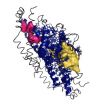
INDIANAPOLIS – A School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis biophysicist has developed a new method to identify communication pathways connecting distant regions within proteins.
With this tool, Andrew J. Rader, Ph.D., assistant professor of physics, has identified a mechanism for cooperative behavior within an entire molecule, a finding that suggests that in the future it may be possible to design drugs that target anywhere along the length of a molecule's communication pathway rather than only in a single location as they do today. The discovery ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Genetic research is showing that healthy steelhead runs in Pacific Northwest streams can depend heavily on the productivity of their stay-at-home counterparts, rainbow trout.
Steelhead and rainbow trout look different, grow differently, and one heads off to sea while the other never leaves home. But the life histories and reproductive health of wild trout and steelhead are tightly linked and interdependent, more so than has been appreciated, a new Oregon State University study concludes.
The research could raise new challenges for fishery managers ...
Numerous nanomaterials are currently at the focus of public attention. In particular silver nanoparticles are being investigated in detail, both by scientists as well as by the regulatory authorities. The assumption behind this interest is that they are dealing with a completely new substance. However, Empa researchers Bernd Nowack and Harald Krug, together with Murray Heights of the company HeiQ have shown in a paper recently published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology that nanosilver is by no means the discovery of the 21st century. Silver particles with ...
Offering the morning after pill free over the counter has not reduced the number of teenage pregnancies and may be associated with a rise in sexually-transmitted diseases (STIs), according to a report by experts at The University of Nottingham.
Professors David Paton and Sourafel Girma used local health authority data to study the impact that the introduction of Government-backed schemes to offer emergency birth control at pharmacies and without prescription have had on conception rates and the diagnosis of STIs among under-18s.
Their findings show that, on average, ...
Geneva, 31 January 2011. CERN today announced that the LHC will run through to the end of 2012 with a short technical stop at the end of 2011. The beam energy for 2011 will be 3.5 TeV. This decision, taken by CERN management following the annual planning workshop held in Chamonix last week and a report delivered today by the laboratory's machine advisory committee, gives the LHC's experiments a good chance of finding new physics in the next two years, before the LHC goes into a long shutdown to prepare for higher energy running starting 2014.
"If LHC continues to improve ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (1/31/2011) – Red Bull's red and gold logo can "give you wings" – for better or worse – even if consumers don't know it, according to a new study by two Boston College professors, who found the brand's edgy marketing efforts have sold a heavy dose of attitude to consumers.
Researchers put subjects at the controls of a car racing video game, supplying each with functionally identical racecars, but each car decorated with a different brand logo and color scheme.
Players put in control of the Red Bull car displayed the characteristics often attributed ...