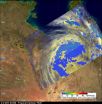
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Yasi has continued moving through inland Queensland, Australia and has weakened to a tropical depression today. NASA and JAXA's TRMM satellite passed over Yasi as it continued to drop moderate to heavy rainfall.
On February 3 at 0300 UTC (Feb. 2 at 10 p.m. EST/1 p.m. Australia local time) Tropical cyclone Yasi continued over land as a tropical storm. Yasi's maximum sustained winds were near 60 knots (69 mph/111 kmh). It was moving west-southwest near 20 knots/23 mph/37 kmh). It was located about 200 miles (321 km) southwest of Cairns, Australia near 19.3 South and 143.4 East.
Just 39 minutes after the position of Yasi's center was determined, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew above the cyclone at 0339 UTC (Feb. 2 at 10:39 p.m. EST/1:39 p.m. Australia local time) collecting data on rainfall rates. Yasi had weakened to tropical storm strength but TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data reveal that the storm was still dropping moderate to heavy rain over Australia in an area southeast of the Gulf of Carpentaria.
Just about an hour later, another NASA satellite passed over Yasi capturing the massive size of the strom in a visible image. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured data on Yasi at 04:15 UTC (Feb. 2 at 11:15 p.m. EST/2:15 p.m. Australia local time. The center of Yasi had already moved inland and the eye of the storm had become obscured by clouds.
The Australia Bureau of Meteorology (ABoM) website has been updating residents of Yasi's movement and affects. To see the ABoM's radar, visit: http://www.bom.gov.au/products/national_radar_sat.loop.shtml.
At 9:30 a.m. EST (14:30 UTC) on Feb. 3 (or 12:30 a.m. Australia local time on Feb. 4) Yasi was approaching the border of the Northern Territory and had weakened into a tropical depression. The ABoM noted that isolated thunderstorms, heavy rains, flash flooding and damaging winds with gusts greater than 48 knots (55 mph/90 kmh) are possible in the western interior of Queensland. Updates from the ABoM can be found at: www.bom.gov.au.
INFORMATION:
NASA measuring Tropical Storm Yasi's inland rainfall from space
2011-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
OHSU fixes complex heart problems without open-heart surgery
2011-02-04
PORTLAND, Ore. -- The pediatric cardiac team at Oregon Health & Science University Doernbecher Children's Hospital is the first in the region and one of a handful in the nation to implant a pulmonary heart valve without open-heart surgery.
To date, four patients have received the landmark valve in the OHSU Pediatric and Adult Congenital Cardiac Catheterization Lab. All reported immediate improvement in their energy level and stamina.
The device, called the Medtronic Melody® Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve, recently was approved by the Food and Drug Administration. The ...
Cornell researchers find a strong community protects adolescents from risky health behavior
2011-02-04
ITHACA, N.Y. – Growing up poor increases a person's likelihood of health problems as an adult, but a new study led by a Cornell University environmental psychologist shows that being raised in a tight-knit community can help offset this disadvantage of poverty.
The study, "Loosening the Link Between Childhood Poverty and Adolescent Smoking and Obesity : The Protective Effects of Social Capital" published in the January 2011 edition of the peer-reviewed journal Psychological Science, found that poor adolescents who live in communities with more social cohesiveness are ...
Social and emotional learning programs found to boost students' skills
2011-02-04
Being successful in school requires a combination of social, emotional, and academic competencies. A new analysis of more than 200 school-based social and emotional learning programs has found that such programs improve students' attitudes and behaviors, and in some cases, even boost academic performance.
The study appears in the January/February issue of the journal, Child Development. It was conducted by researchers at Loyola University Chicago and the University of Illinois at Chicago.
In the first large-scale meta-analysis of school programs that enhance students' ...
Family mealtimes play a role in health of children with asthma
2011-02-04
The amount of time families spend eating meals together has been linked to the health and well-being of children and teens, with families who eat together regularly reporting declines in substance abuse, eating disorders, and unhealthy weight in their children. Now, a new study that looks at children with asthma has found that the quality of family interactions during mealtime affected the children's health.
The study appears in the January/February issue of the journal, Child Development. It was conducted by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, ...
Working more than 20 hours a week in high school found harmful
2011-02-04
Many teens work part-time during the school year, and in the current economic climate, more youths may take jobs to help out with family finances. But caution is advised: Among high school students, working more than 20 hours a week during the school year can lead to academic and behavior problems.
That's the finding of a new study by researchers at the University of Washington, University of Virginia, and Temple University. It appears in the January/February issue of the journal, Child Development.
In a reanalysis of longitudinal data collected in the late 1980s, researchers ...
Children's BMI found to rise the longer their mothers work
2011-02-04
Childhood obesity in the United States has more than tripled in the past three decades, and prior research has linked maternal employment to children's body mass index (BMI), a measure of their weight-for-height. A new study in the January/February issue of the journal Child Development has found that children's BMI rose the more years their mothers worked over their children's lifetimes.
Researchers at American University, Cornell University, and the University of Chicago used longitudinal information from the Study of Early Child Care and Youth Development, which was ...
School-based child-parent center yields high economic benefits
2011-02-04
The Child-Parent Center (CPC) early education program is a large-scale, federally funded intervention providing services for disadvantaged 3- to 9-year-olds in Chicago. A new cost-benefit analysis of the program has found that benefits exceeded costs in a number of areas, including increased earnings and savings.
The longitudinal analysis appears in the January/February issue of Child Development, the journal of the Society for Research in Child Development. It was done by researchers at the University of Minnesota, and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill.
"Our ...
Child care quality key for children from disadvantaged homes
2011-02-04
Decades of research have demonstrated the importance of the resources in children's homes and the benefits of high-quality interactions with parents in supporting healthy development. High-quality child care plays a similar, albeit less powerful, role. Children who come from more difficult home environments and have lower-quality child care have more social and emotional problems, but high-quality child care may help make up for their home environments.
Those are the findings of a new study by researchers at the University of Denver, Georgetown University, American University, ...
Report says economic development could change worldwide face of cancer
2011-02-04
ATLANTA, February 4, 2011—A new American Cancer Society report says cancers associated with lifestyles and behaviors related to economic development, including lung, breast, and colorectal cancers, will continue to rise in developing countries if preventive measures are not widely applied. The finding comes from the second edition of Global Cancer Facts & Figures and its academic publication, Global Cancer Statistics, published in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. Both publications are being released on World Cancer Day, Feb. 4, 2011. The latest edition of Global Cancer ...
Early childhood education program yields high economic returns, U of Minnesota researchers find
2011-02-04
For every $1 invested in a Chicago early childhood education program, nearly $11 is projected to return to society over the children's lifetimes -- equivalent to an 18 percent annual return on program investment, according to a study led by University of Minnesota professor of child development Arthur Reynolds in the College of Education and Human Development.
For the analysis, Reynolds and other researchers evaluated the effectiveness of the Chicago Public Schools' federally funded Child Parent Centers (CPCs) established in 1967. Their work represents the first long-term ...