Improving care for bowel cancer patients
2011-02-05
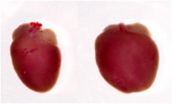
(Press-News.org) Rainer Kube and his working group report in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 108[4]: 41-6) on new treatment strategies in patients with colon cancer.
The findings of multicenter observational studies are a good basis for improvements to overall quality of patient care. Against this background, from 2000 to 2004 Kube and his coauthors collected data on over 31 000 patients in 346 German hospitals. From this data pool they extracted statements about the quality of care. They discovered, for example, that colonoscopy screening has led to only a marginal reduction in the percentage of tumors at an advanced stage of disease. In addition, patients in whom the surgeon had to convert intraoperatively from an endoscopic (keyhole) to an open procedure had a poorer oncological result. The authors' analysis produced new indicators of possible complication risks. For example, leakage from bowel sutures resulted in a markedly poorer long-term disease course for the patient. The authors emphasize that their study could contribute to optimization of surgical technique during operations.
INFORMATION:
http://www.aerzteblatt.de/v4/archiv/pdf.asp?id=80528
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-02-05
Compared to people in employment, men and women who are unemployed suffer more often and longer from both physical and emotional complaints. Why the un-employed should have health problems more often is discussed by Lars E. Kroll and his coauthor in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 4: 47-52), along with a report on the findings of the GEDA study.
The GEDA study (Gesundheit in Deutschland Aktuell, or Current Health in Germany) was carried out in 2008-2009 by the Robert Koch Institute. The results showed that unemployed people ...
2011-02-05
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Everyone knows chocolate is critical to a happy Valentine's Day. Now scientists are one step closer to knowing what makes a heart happy the rest of the year.
It's a gene called DOT1L, and if you don't have enough of the DOT1L enzyme, you could be at risk for some types of heart disease. These findings from a study led by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine appear in the Feb. 1, 2011 issue of the journal Genes and Development.
The team created a special line of mice that were genetically predisposed to ...
2011-02-05
The first stars in the universe were not as solitary as previously thought. In fact, they could have formed alongside numerous companions when the gas disks that surrounded them broke up during formation, giving birth to sibling stars in the fragments. These are the findings of studies performed with the aid of computer simulations by researchers at Heidelberg University's Centre for Astronomy together with colleagues at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Garching and the University of Texas at Austin (USA). The group's findings, published in Science Express, ...
2011-02-05
Things are not always what they seem when it comes to fish—something scientists at the Smithsonian Institution and the Ocean Science Foundation are finding out. Using modern genetic analysis, combined with traditional examination of morphology, the scientists discovered that what were once thought to be three species of blenny in the genus Starksia are actually 10 distinct species. The team's findings are published in the scientific journal ZooKeys, Feb. 3.
Starksia blennies, small (less than 2 inches) fish with elongated bodies, generally native to shallow to moderately ...
2011-02-05
The vaccine for human papillomavirus (HPV) can prevent 90 percent of genital warts in men when offered before exposure to the four HPV strains covered by the vaccine, according to a new multi-center study led by H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and UCSF.
The four-year, international clinical trial, which also found a nearly 66 percent effectiveness in the general population of young men regardless of prior exposure to these strains, provides the first reported results of using the HPV vaccine as a prophylactic in men.
Initial data from this study informed the Food and Drug ...
2011-02-05
NEW YORK (February 4, 2011) – Researchers at the NYU Child Study Center demonstrated that a brief program for families of Pre-Kindergarten students attending schools in disadvantaged urban communities improved children's behavior at school. The study, called "Promoting effective parenting practices and preventing child behavior problems in school among ethnically diverse families from underserved, urban communities," was published in the February 2011 issue of Child Development.
Dr. Laurie Miller Brotman and her colleagues spent several years developing ParentCorps, ...
2011-02-05
Since the days of Darwin, the "tree of life" has been the preeminent metaphor for the process of evolution, reflecting the gradual branching and changing of individual species.
The discovery that a large cluster of genes appears to have jumped directly from one species of fungus to another, however, significantly strengthens the argument that a different metaphor, such as a mosaic, may be more appropriate.
"The fungi are telling us something important about evolution … something we didn't know," said Antonis Rokas, assistant professor of biological sciences at Vanderbilt. ...
2011-02-05
An ambitious hunt by Johns Hopkins scientists for actively "jumping genes" in humans has yielded compelling new evidence that the genome, anything but static, contains numerous pesky mobile elements that may help to explain why people have such a variety of physical traits and disease risks.
Using bioinformatics to compare the standard assembly of genetic elements as outlined in the reference human genome to raw whole-genome data from 310 individuals recently made available by the 1000 Genomes Project, the team revealed 1,016 new insertions of RIPs, or retrotransposon ...
2011-02-05
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have developed a little bomb that promises a big bang for cancer patients.
Preliminary tests show an anti-cancer drug loosely attached to gold nanoparticles starts accumulating deep inside tumors within minutes of injection and can be activated for an effective treatment within two hours. The same drug injected alone takes two days to gather and attacks the tumor from the surface – a far less effective route.
The work, titled "Deep Penetration of a PDT Drug into Tumors by Noncovalent Drug-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates," ...
2011-02-05
Mice know fear. And they know to fear the scent of a predator. But how do their brains quickly figure out with a sniff that a cat is nearby?
It's a complex process that starts with the scent being picked up by specific receptors in their noses. But until now it wasn't clear exactly how these scent signals proceeded from nose to noggin for neural processing.
In a study to be published in Nature (available online now to subscribers), Stanford researchers describe a new technique that makes it possible to map long-distance nerve connections in the brain. The scientists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Improving care for bowel cancer patients