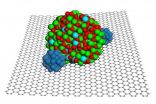
New techniques for stapling peptides could spur development of drugs for cancer
2011-02-09
(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Researchers at the University at Buffalo have devised two new ways of "stapling" peptide helices to prevent these medically important molecules from losing their shape and degrading in the presence of enzymes.
The discovery could help speed the development of peptide-based drugs against diseases including cancer. UB scientists say the methods they pioneered are simpler than existing techniques, one of which employs an expensive ruthenium catalyst to connect chemical side chains that protrude from the main body of helical peptides.
"There's a lot of potential here. Our chemistry is unique," said Qing Lin, the UB assistant professor of chemistry who led the research. "There are not that many new drug targets out there today, which partly explains the declining number of FDA-approved new drugs in recent years. So there's a need to come up with new technologies that can overcome this barrier. To this end, stapled peptides could open a whole host of new targets for therapies."
Stapled peptides work as treatments against disease by binding tightly to target proteins within cells, thus disrupting specific protein-protein interactions that regulate many biological processes, including response to stress, signaling within cells, and cell death.
In their native state, peptides -- short strings of amino acids -- shift between different shapes, including a helix, sheet and random coil. Stapling the peptides' side chains encourages the peptides to adopt and stay in a helix, which enables them to enter cells more easily. The helical conformation also makes it more difficult for enzymes to break the peptides down, Lin said.
The two processes Lin's team developed for stapling peptides are efficient, producing stapled peptides in high yields, said Timothy Dee, a commercialization manager for UB's Office of Science, Technology Transfer and Economic Outreach (STOR). Through STOR, UB is applying for patents to cover both stapling methods.
"Photoclick stapling," the first approach, involves synthesizing peptides that have alkenes in one side chain and tetrazoles in another. Under ultraviolet light, the two side chains form chemical bonds with one another.
A paper on photoclick stapling appeared online in Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters in January and will appear later this year in the journal's print edition. Researchers first published on the subject in 2009 in Chemical Communications.
The second stapling technique Lin and his colleagues devised requires the synthesis of peptides carrying a pair of amino acids called cysteines that contain sulfur in their side chains. When scientists expose these peptides to a chemical that reacts selectively with the sulfur atoms, the chemical forms a "staple" that connects the two cysteine side chains.
Experts believe stapled peptides could treat a wide variety of health problems, including cancer and inflammatory, metabolic and infectious diseases. As evidence of the technology's promise, a company formed in 2005 to commercialize a ruthenium-based stapling method developed at Harvard University has reportedly raised about $60 million in venture capital and landed a deal with pharmaceutical giant Roche that could be worth more than $1 billion over time.
"The field is large enough for multiple players," Lin said. "Stapling is a technology that many people believe will create a new class of drug therapies, hitting new targets that other therapies can't. Our chemistry is distinct from what's already out there."
Lin and his group are particularly interested in developing anti-cancer therapeutics that increase the efficacy of chemotherapy by instructing cancer cells to self-destruct through "programmed cell death," a process called apoptosis.###
The University at Buffalo is a premier research-intensive public university, a flagship institution in the State University of New York system and its largest and most comprehensive campus. UB's more than 28,000 students pursue their academic interests through more than 300 undergraduate, graduate and professional degree programs. Founded in 1846, the University at Buffalo is a member of the Association of American Universities.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene protects lung from damage due to pneumonia, sepsis, trauma, transplants
2011-02-09
Lung injury is a common cause of death among patients with pneumonia, sepsis or trauma and in those who have had lung transplants. The damage often occurs suddenly and can cause life-threatening breathing problems and rapid lung failure.
There are no effective treatments. Patients usually are put on ventilators to give their lungs a chance to heal, but there is little else doctors can do but wait and hope for the best.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have identified a gene that limits damage to the lung during acute ...
Electronic cigarettes hold promise as aid to quitting
2011-02-09
A study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researchers reports that electronic cigarettes are a promising tool to help smokers quit, producing six-month abstinence rates nearly double those for traditional nicotine replacement products.
In a study published online ahead of print in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers found that 31 percent of respondents reported having quit smoking six months after first purchasing an electronic cigarette, a battery-powered device providing tobacco-less doses of nicotine in a vaporized solution. ...
Not just for raincoats
2011-02-09
Researchers from Northwestern University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have studied individual water droplets and discovered a miniature version of the "water hammer," an effect that produces the familiar radiator pipe clanging in older buildings.
In piping systems, the water hammer occurs when fluid is forced to stop abruptly, causing huge pressure spikes that can rupture pipe walls. Now, for the first time, the researchers have observed this force on the scale of microns: such pressure spikes can move through a water droplet, causing it to be impaled ...
Growing population of adult survivors of congenital heart disease requires specialized care
2011-02-09
Philadelphia, PA, February 8, 2011 – For the one in 200 adults in Western societies born with congenital heart disease, adult survivors face a lifelong process of medical interactions. Treatments received during neonatal, childhood, and adolescent years affect future adult events. In the January/February issue of Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases ten articles explore our current understanding of adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) in survivors.
This issue of Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases is dedicated to exploring the path to and current understanding of lifelong ...
Medication education key to successful adherence in patients with diabetes
2011-02-09
Researchers at the Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of California, San Diego say that medication education is a key factor in helping patients with diabetes better stick to their drug treatments plans. The study, currently on line in the February issue of the journal Annals of Pharmacotherapy, points to the need for pharmacists and other health care providers to assess reasons why some patients don't adhere to their medication plans, and to provide counseling opportunities to help them.
"Counseling can be more effective if pharmacists ...
A paperweight for platinum
2011-02-09
RICHLAND, Wash. -- A new combination of nanoparticles and graphene results in a more durable catalytic material for fuel cells, according to work published today online at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. The catalytic material is not only hardier but more chemically active as well. The researchers are confident the results will help improve fuel cell design.
"Fuel cells are an important area of energy technology, but cost and durability are big challenges," said chemist Jun Liu. "The unique structure of this material provides much needed stability, good ...
Understanding patterns of seafloor biomass
2011-02-09
Analysis of a comprehensive database has revealed strong links between biological productivity in the surface oceans and patterns of biomass and abundance at the seafloor, helping to explain large regional differences. The research was conducted by an international, multi-institutional research team including scientists from the National Oceanography Centre (NOC), and incorporated data from the Census of Marine Life (CoML).
The vast majority of the biological production in the world's oceans occurs within sunlit surface waters – the so-called photic zone. Through the ...
Cross-border conservation vital to protect birds in a climate-change world
2011-02-09
Countries need to increase co-operation over conservation to protect birds and other wildlife in an era of climate change, according to a new continental-scale study.
Experts have established a new conservation index to help policy-makers to deal with the effects of climate change on birds in Africa, and it could assist governments across the world to protect wildlife areas and help species as climate change forces them to move to new areas.
It is the first categorisation of protected areas to show how conservationists might deal with climate change and the shuffling ...
Virtual laboratory predicts train vibrations
2011-02-09
The construction of new rail lines, or the relocation of old ones underground, has increased society's interest over recent years in the vibrations produced by trains, especially among people who live or work near the tracks. Now a study headed by the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV) has made it possible to estimate the trajectory of vibrations from the point at which they are generated (wheel-rail contact) through to the ground.
"The model acts as a "virtual train laboratory', meaning that, if the parameters of the train or the track ballast are changed, it is ...
Experts call for greater awareness of the links between diabetes and kidney disease
2011-02-09
The first time that many patients realise that diabetes can affect their kidneys is when they are referred to renal services, according to a multi-cultural study in the March issue of the Journal of Renal Care.
UK researchers who spoke to 48 patients with diabetes attending specialist renal services in Leicester, Luton and Ealing, discovered that awareness of the kidney risks posed by the disease was very low.
"The people we spoke to experienced feelings of surprise, fear and regret when they found out their kidney had been affected" says Professor Gurch Randhawa, ...