(Press-News.org) It's a common problem in the business world—throwing good money after bad. People cling to bad investments, hoping that more time, effort, and money will rescue their turkey of a project. A new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, finds that changing people's mindsets can make them more likely to abandon a failing investment.
"These situations happen all the time," says Assistant Professor Daniel C. Molden, of Northwestern University, who conducted the study with his graduate student Chin Ming Hui. "They happen with businesses; they happen in the Pentagon with weapons systems." The producers of Spider-Man: Turn off the Dark are making the most expensive musical of all time, plagued with cost overruns and cast injuries. "If they had at any point objectively reevaluated their position and thought, 'What is the probability that this is going to make money?' they might have just pulled the plug," Molden says. Now the musical will have to be wildly successful to make back the estimated $65 million that went into its production.
Molden and Hui devised an experiment to find out if they could change how people dealt with the "sunk costs" from their previous investments. Volunteers were first asked to write generally about either their personal duties and obligations or their personal hopes and aspirations. Then they were asked to imagine that they were the president of an aviation company who had committed $10 million to building a special kind of airplane. But with $9 million already spent and the project nearly done, another company had announced they had made a better, cheaper plane. They were asked whether they would spend the last $1 million or cancel the project.
People who had thought about their hopes and aspirations were more likely to say they would abandon the project. On the other hand, people who had written about their duties and obligations felt it was their responsibility to finish the project—thus throwing good money after bad. Molden suggests that this is because people who focus on their own hopes are thinking positively about opportunities for growth, and are therefore more likely to appreciate what else might be accomplished with the remaining $1 million, whereas people who focus on duties and obligations are feeling anxious and thinking about how abandoning the project would be accepting complete failure.
"At the very least, when things start to go wrong, people should stop and evaluate the costs and benefits of going forward," Molden says. Instead, it seems that people think, "I've already committed so much to this, I can't quit now."
Of course, not everything that appears to be going badly will fail. Buildings, movies, or government programs that run over cost could still be a success in the end. Spider-Man could turn out to be the best musical of all time. "Things can work out," says Molden. "The problem is that when people decide to push ahead because of what has already been invested versus some reasonable expectations of what will happen next, more often than not, they don't."
###
For more information about this study, please contact Daniel Molden at molden@northwestern.edu.
The APS journal Psychological Science is the highest ranked empirical journal in psychology. For a copy of the article "Promoting Deescalation of Commitment: A Regulatory Focus Perspective on Sunk Costs" and access to other Psychological Science research findings, please contact Keri Chiodo at 202-293-9300 or kchiodo@psychologicalscience.org.
Thoughts of hopes, opportunities keep people from clinging to failing investments
2011-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows delayed-enhancement MRI may predict, prevent strokes
2011-02-09
SALT LAKE CITY, Feb. 8, 2011 – Researchers at the University of Utah's Comprehensive Arrhythmia and Research Management (CARMA) Center have found that delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (DE-MRI) holds promise for predicting the risks of strokes, the third leading cause of death in the U.S. Their latest study on a novel application of this technology appears in the Feb. 15 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. (http://content.onlinejacc.org/cgi/content/abstract/57/7/831)
The study included 387 patients who were treated for atrial fibrillation ...
Brief diversions vastly improve focus, researchers find
2011-02-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study in the journal Cognition overturns a decades-old theory about the nature of attention and demonstrates that even brief diversions from a task can dramatically improve one's ability to focus on that task for prolonged periods.
The study zeroes in on a phenomenon known to anyone who's ever had trouble doing the same task for a long time: After a while, you begin to lose your focus and your performance on the task declines.
Some researchers believe that this "vigilance decrement," as they describe it, is the result of a drop in one's "attentional ...
JAMA features NJIT biomedical engineer helping stroke patients
2011-02-09
The Journal of the American Medical Society ("Medical News & Perspectives", Jan. 19, 2011) featured the research of NJIT Associate Professor Sergei Adamovich, a biomedical engineer. Adamovich and his research partners, physical therapists Alma Merians, PhD, PT, and Eugene Tunik, PhD, PT, at the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, have developed innovative robotic and virtual reality-based video game therapies to help stroke patients regain use of hands and arms.
JAMA reported that the efforts of this team are making headway. Twenty-four patients who ...
Why leatherback turtles linger in South Pacific Gyre, and why it matters
2011-02-09
VIDEO:
Tagging and tracking leatherback sea turtles has produced new insights into the turtles' behavior in a part of the South Pacific Ocean long considered an oceanic desert. The new data...
Click here for more information.
Leatherbacks. They are the Olympians of the turtle world – swimming farther, diving deeper and venturing into colder waters than any other marine turtle species. But for all their toughness, they have still suffered a 90 percent drop in their population ...
Tool makes search for Martian life easier
2011-02-09
RICHLAND, Wash. – Finding life on Mars could get easier with a creative adaption to a common analytical tool that can be installed directly on the robotic arm of a space rover.
In a recent paper published online in the journal Planetary and Space Science, a team of researchers propose adding a laser and an ion funnel to a widely used scientific instrument, the mass spectrometer, to analyze the surfaces of rocks and other samples directly on Mars' surface. The researchers demonstrated that the combined system could work on the spot, without the sample handling that mass ...
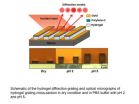
Hydrogels used to make precise new sensor
2011-02-09
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are developing a new type of biological and chemical sensor that has few moving parts, is low-cost and yet highly sensitive, sturdy and long-lasting.
The "diffraction-based" sensors are made of thin stripes of a gelatinous material called a hydrogel, which expands and contracts depending on the acidity of its environment.
Recent research findings have demonstrated that the sensor can be used to precisely determine pH - a measure of how acidic or basic a liquid is - revealing information about substances in liquid environments, said ...
Detecting pathogens in waterways: An improved approach
2011-02-09
This press release is available in Spanish.
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists have come up with a way to detect pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella bacteria in waterways at lower levels than any previous method. Similar methods have been developed to detect pathogenic E. coli in meat products, but the approach by the scientists with USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS) represents a first for waterways.
ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports the USDA priority of ensuring food safety.
When ...
UT Study: Charismatic leadership can be measured, learned
2011-02-09
KNOXVILLE -- How do you measure charisma? That's the question UT professor Kenneth Levine seeks to answer.
Much has been written in business management textbooks and self-help guides about the role that personal charisma plays in leadership. But according to a newly published study co-authored by Levine, a University of Tennessee, Knoxville, communications studies professor, until recently no one was able to describe and measure charisma in a systematic way.
Levine said the large amount of academic literature on charismatic leadership never defined what it means to ...
The hitch in the drug? The itch in the drug
2011-02-09
Scratching deep beneath the surface, a team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and three South Korean institutions have identified two distinct neuronal signaling pathways activated by a topical cream used to treat a variety of skin diseases. One pathway produces the therapeutic benefit; the other induces severe itching as a side effect.
The findings, published in this week's early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, point to the possibility of designing future drugs that effectively treat ...
Dramatic improvement in Parkinson disease symptoms
2011-02-09
New Rochelle, NY, February 8, 2011—Successful intranasal delivery of stem cells to the brains of rats with Parkinson disease yielded significant improvement in motor function and reversed the dopamine deficiency characteristic of the disease. These highly promising findings, reported in Rejuvenation Research, a peer-reviewed journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. highlight the potential for a noninvasive approach to cell therapy delivery in Parkinson disease–a safer and effective alternative to surgical transplantation of stem cells. The article is available free online. ...