(Press-News.org) Obesity may be associated with higher eye pressure and a decreased risk of open-angle glaucoma in women but not men, according to a report posted online today that will appear in the May issue of Archives of Ophthalmology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Open-angle glaucoma is a chronic eye disease characterized by glaucomatous optic neuropathy and corresponding glaucomatous visual field loss," the authors write as background information in the article. Previous research has identified several risk factors for open-angle glaucoma, including intraocular pressure (pressure within the eye), age, sex, myopia (nearsightedness) and ethnicity.
Wishal D. Ramdas, M.D., M.Sc., of the Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and colleagues examined data from 3,939 participants in the Rotterdam Study. This population-based study included participants 55 years of age and older living in a suburb of Rotterdam, the Netherlands, who did not have open-angle glaucoma when the study began between 1991 and 1993.
Over an average of 9.7 years of follow-up, 108 participants (2.7 percent) developed open-angle glaucoma. Those who developed the condition were significantly older, more often had high myopia (severe nearsightedness) and were more often male, compared with those who did not. No statistically significant effect of socioeconomic status, smoking or alcohol intake was found on the development of open-angle glaucoma.
Among women, there was a significant association between increased body mass index and intraocular pressure. However, each one-unit increase in body mass index was associated with a 7 percent decreased risk of developing open-angle glaucoma. These associations were not present in men.
Excess fat tissue could place increasing pressure on the eye sockets, thereby increasing pressure within the eye, the authors note. The higher intraocular pressure among obese women should have resulted in an increased risk for glaucoma. "However, this effect was not observed and thus the multivariate analysis yielded a protective effect of body mass index on open-angle glaucoma incidence in women," they write. "Another explanation might be that high estrogen levels and hormone therapy might be protective to open-angle glaucoma, and obesity seems to be positively related with postmenopausal plasma estrogen levels."
"Obesity appears to be associated with a higher intraocular pressure and a lower risk of developing open-angle glaucoma," the authors conclude. "These associations were only present in women. Other lifestyle-related factors, such as socioeconomic status, smoking and alcohol consumption, were not associated with open-angle glaucoma."
###
(Arch Ophthalmol. Published online February 14, 2011.doi:10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.373. Available pre-embargo to the media at www.jamamedia.org.)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
To contact corresponding author Johannes R. Vingerling, M.D., Ph.D., e-mail j.vingerling@erasmusmc.nl.
For more information, contact JAMA/Archives Media Relations at 312/464-JAMA (5262) or e-mail mediarelations@jama-archives.org.
Obese women may be less likely to develop glaucoma
2011-02-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An early step in Parkinson's disease: Problems with mitochondria
2011-02-15
For the last several years, neurologists have been probing a connection between Parkinson's disease and problems with mitochondria, the miniature power plants of the cell.
Toxins that mimic Parkinson's effects act specifically to poison mitochondria, and mitochondria appear to be damaged in the brain cells that are endangered in the disease. But one unresolved question has been: are mitochondria simply the vulnerable "canaries in the coal mine" or is their deterioration a key step on the way to neurodegeneration?
Now researchers at Emory University School of Medicine ...
Hershey scientists improve methods for analysis of healthful cocoa compounds
2011-02-15
Two scientific publications report on improved methods for determining the amounts of flavanol antioxidants in cocoa and chocolate. The research, sponsored by The Hershey Center for Health and Nutrition, was a collaboration between scientists at The Hershey Company and other scientific laboratories.
Scientists at Planta Analytica (Danbury, CT) isolated and separated cocoa flavanol antioxidants on a large scale. The Hershey scientists and collaborating scientists at the Pennsylvania State University-M.S. Hershey Medical Center (Hershey, PA) teamed up to determine the ...
Commonly prescribed osteoporosis drug associated with very low risk of serious jaw disease
2011-02-15
(PORTLAND, Ore.) February 14, 2011 — A commonly prescribed osteoporosis drug is associated with a slightly elevated risk of developing the rare, but serious condition, osteonecrosis of the jaw; nonetheless the risk remains extremely low. These findings are published online in the Journal of Dental Research, the official journal of the International and American Associations for Dental Research. Although the findings are provocative, study authors say they should be carefully considered against the large benefit of these drugs to prevent and treat osteoporosis.
The study ...
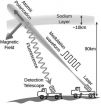
Ground-based lasers vie with satellites to map Earth's magnetic field
2011-02-15
Mapping the Earth's magnetic field – to find oil, track storms or probe the planet's interior – typically requires expensive satellites.
University of California, Berkeley, physicists have now come up with a much cheaper way to measure the Earth's magnetic field using only a ground-based laser.
The method involves exciting sodium atoms in a layer 90 kilometers above the surface and measuring the light they give off.
"Normally, the laser makes the sodium atom fluoresce," said Dmitry Budker, UC Berkeley professor of physics. "But if you modulate the laser light, when ...
The UK is a nation of happy couples
2011-02-15
Researchers at the Institute for Social and Economic Research asked both individuals in the couple to rate their happiness on a seven point scale; from the lowest score of 'extremely unhappy' to the middle point of 'happy', the highest point being 'perfect'. The self-reported happiness rating revealed that 90 percent of married women and 88 percent of cohabiting women are happy in their relationships. Ninety-three percent of married men and 92 percent of cohabiting men said they were happy in their relationship.
The findings indicate the happiest couples are those in ...
British scientists develop control system to allow spacecraft to think for themselves
2011-02-15
The world's first control system that will allow engineers to programme satellites and spacecraft to think for themselves has been developed by scientists from the University of Southampton.
Professor Sandor Veres and his team of engineers have developed an artificially intelligent control system called 'sysbrain'.
Using natural language programming (NLP), the software agents can read documents written in English, rather than needing specially programmed code to be uploaded, to obtain new instructions or new information. This gives the vehicles advanced guidance, navigation ...
Estrogen reduces aggression in breast cancer
2011-02-15
A team of researchers at CIC bioGUNE has revealed that oestrogen can reduce the risk of breast cancer. Their work shows that oestrogen is capable of reducing the number of breast cancer stem cells, which may explain the lower aggression of the tumour and, as a consequence, the possibility of a better prognosis. The project was published in Breast Cancer Research and Treatment and the team will present the results under the auspices of the International Conference on Breast Cancer to be held in Madrid. The research combined the use of human samples and laboratory cell lines.
The ...
Moderate-to-heavy alcohol intake may increase risk of atrial fibrillation
2011-02-15
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm). Its name comes from the fibrillating (i.e., quivering) of the heart muscles of the atria, instead of a coordinated contraction. The result is an irregular heartbeat, which may occur in episodes lasting from minutes to weeks, or it could occur all the time for years. Atrial fibrillation alone is not in itself generally life-threatening, but it may result in palpitations, fainting, chest pain, or congestive heart failure.
There is no doubt that heavy alcohol intake and binge drinking ...
Total cooperation among people is not viable
2011-02-15
The objective of this research is to understand how cooperation works in nature in general, and among humans in particular. "From the evolutionary point of view it is very difficult to understand why we would help others when what interests us is helping ourselves," explained the authors of this study, which was recently published in the journal PLoS ONE. One of the most striking conclusions drawn is that there are different types of people: those who always try to help their neighbors (around 5 percent), those who never do so (35 percent), and others who cooperate depending ...
Hand movements in children with ADHD hold clues to understanding and predicting symptom severity
2011-02-15
(Baltimore, MD) – Two research studies published today in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, found markers for measuring the ability of children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) to control impulsive movements, which may reveal insights into the neurobiology of ADHD, inform prognosis and guide treatments.
In one of two studies conducted by researchers at the Kennedy Krieger Institute in Baltimore, MD and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, children with ADHD performed a finger-tapping task. Any unintentional ...