(Press-News.org) Up to two-thirds of Earth's permafrost likely will disappear by 2200 as a result of warming temperatures, unleashing vast quantities of carbon into the atmosphere, says a new study by the University of Colorado Boulder's Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences.
The carbon resides in permanently frozen ground that is beginning to thaw in high latitudes from warming temperatures, which will impact not only the climate but also international strategies to reduce fossil fuel emissions, said CU-Boulder's Kevin Schaefer, lead study author. "If we want to hit a target carbon dioxide concentration, then we have to reduce fossil fuel emissions that much lower than previously thought to account for this additional carbon from the permafrost," he said. "Otherwise we will end up with a warmer Earth than we want."
The escaping carbon comes from plant material, primarily roots trapped and frozen in soil during the last glacial period that ended roughly 12,000 years ago, he said. Schaefer, a research associate at CU-Boulder's National Snow and Ice Data Center, an arm of CIRES, likened the mechanism to storing broccoli in a home freezer. "As long as it stays frozen, it stays stable for many years," he said. "But if you take it out of the freezer it will thaw out and decay."
While other studies have shown carbon has begun to leak out of permafrost in Alaska and Siberia, the study by Schaefer and his colleagues is the first to make actual estimates of future carbon release from permafrost. "This gives us a starting point, and something more solid to work from in future studies," he said. "We now have some estimated numbers and dates to work with."
The new study was published online Feb. 14 in the scientific journal Tellus. Co-authors include CIRES Fellow and Senior Research Scientist Tingjun Zhang from NSIDC, Lori Bruhwiler of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and Andrew Barrett from NSIDC. Funding for the project came from NASA, NOAA and the National Science Foundation.
Schaefer and his team ran multiple Arctic simulations assuming different rates of temperature increases to forecast how much carbon may be released globally from permafrost in the next two centuries. They estimate a release of roughly 190 billion tons of carbon, most of it in the next 100 years. The team used Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change scenarios and land-surface models for the study.
"The amount we expect to be released by permafrost is equivalent to half of the amount of carbon released since the dawn of the Industrial Age," said Schaefer. The amount of carbon predicted for release between now and 2200 is about one-fifth of the total amount of carbon in the atmosphere today, according to the study.
While there were about 280 parts per million of CO2 in Earth's atmosphere prior to the Industrial Age beginning about 1820, there are more than 380 parts per million of carbon now in the atmosphere and the figure is rising. The increase, equivalent to about 435 billion tons of carbon, resulted primarily from human activities like the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
Using data from all climate simulations, the team estimated that about 30 to 60 percent of Earth's permafrost will disappear by 2200. The study took into account all of the permanently frozen ground at high latitudes around the globe.
The consensus of the vast majority of climate scientists is that the buildup of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere is the primary reason for increasingly warm temperatures on Earth. According to NOAA, 2010 was tied for the hottest year on record. The hottest decade on record occurred from 2000 to 2010.
Greater reductions in fossil fuel emissions to account for carbon released by the permafrost will be a daunting global challenge, Schaefer said. "The problem is getting more and more difficult all the time," he said. "It is hard enough to reduce the emissions in any case, but now we have to reduce emissions even more. We think it is important to get that message out now."
INFORMATION:
CIRES is a joint institute of CU-Boulder and NOAA.
To view a short video of Schaefer talking about thawing permafrost visit http://www.colorado.edu/news and click on the story headline.
Thawing permafrost likely will accelerate global warming
2011-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MU researchers believe discovery could lead to testing that displaces colonoscopies
2011-02-17
VIDEO:
Nobody enjoys colonoscopies, including mice. University of Missouri researchers are excited about the potential of using genetic biomarkers to predict colon cancer caused by inflammation. A new method developed at...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Nobody enjoys colonoscopies, including mice. University of Missouri researchers are excited about the potential of using genetic biomarkers to predict colon cancer caused by inflammation. A new method developed ...
Most New Jersey residents see global health as critical to state's economy
2011-02-17
WASHINGTON—February 16, 2011—Despite the unpredictable economy, nearly three-quarters (73%) of New Jersey residents think spending money on research to improve health globally is important to jobs and incomes in the state, according to a new statewide poll commissioned by Research!America. The poll data will be released today at a meeting in Washington, DC, of prominent global health research and development (R&D) experts and New Jersey business, academia and nonprofit leaders. This is part of a six-state effort by Research!America.
According to the poll, most of the ...
California Health Interview Survey releases newest data on state residents' health
2011-02-17
The California Health Interview Survey (CHIS), the nation's largest state health survey and a primary source of information on California's diverse population, released its latest data today on more than 100 topics affecting the health and well-being of the state's residents.
The random–digit-dial telephone survey, conducted every two years by the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research, gathers essential information from tens of thousands of California households on a wide variety of topics, from health insurance and public program participation to diabetes, obesity ...
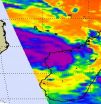
NASA satellite sees Tropical Storm Bingiza hugging the western Madagascar coastline
2011-02-17
Infrared satellite data from NASA is showing some strong thunderstorms over west-central Madagascar today as Tropical Storm Bingiza continues to hug the western coast of the island nation.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Bingiza today, Feb. 16 at 10:17 UTC (5:17 a.m. EST). The image revealed some strong convection over the west-central coast where thunderstorm cloudtops were high and dropping moderate to heavy rainfall. Infrared data can provide temperature information ...
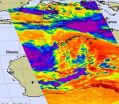
NASA sees tropical cyclone double-trouble for Australia
2011-02-17
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image today of tropical cyclones affecting Australia in the western and northern areas of the country. Newly formed Tropical Storm Carlos is bringing heavy rains and gusty winds to Darwin and the Northern Territory, while Tropical Storm Dianne is bringing rains and winds to Western Australia.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Australia today, Feb. 16 at 05:17 UTC (12:17 a.m. EST/ 2:47 p.m. Australia/Darwin local time. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of both tropical storms and found ...
Herschel finds less dark matter but more stars
2011-02-17
ESA's Herschel space observatory has discovered a population of dust-enshrouded galaxies that do not need as much dark matter as previously thought to collect gas and burst into star formation.
The galaxies are far away and each boasts some 300 billion times the mass of the Sun. The size challenges current theory that predicts a galaxy has to be more than ten times larger, 5000 billion solar masses, to be able form large numbers of stars.
The new result is published today in a paper by Alexandre Amblard, University of California, Irvine, and colleagues.
Most of the ...
Trial suggests statin may affect markers associated with progression of HIV
2011-02-17
A recent multicenter clinical trial of atorvastatin, a type of cholesterol-lowering drug, found that although the drug did not inhibit plasma HIV RNA levels, it did inhibit expression of cellular markers of immune activation and inflammation in patients with HIV infection. Since immune activation and inflammation are associated with progression of HIV infection, the implication is that the statin may inhibit disease progression and help in the infection's management. The findings are in a study, available online, published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
The investigators, ...
New test shows promise for accurate diagnosis of Turner syndrome
2011-02-17
As a child grows, a short stature is not usually cause for concern, but it is often the only sign of a condition called Turner syndrome. Prevalent in girls, Turner syndrome is a genetic defect that short-circuits normal growth and leads to cardiac and renal problems. It is not commonly detected until age 10 or older when a youngster's unusually short height raises suspicions.
This lag before diagnosis of the condition can delay the start of growth hormone therapy, which can help in achieving normal or near-normal adult stature. Yale School of Medicine researchers are ...
Drug therapy shows significant benefit in treating a leading cause of childhood blindness
2011-02-17
A readily available, inexpensive drug therapy showed a significant benefit in treating premature infants with the worst and historically most difficult-to-treat cases of retinopathy of prematurity.
The results of a multicenter clinical trial led by researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) are published in the Feb. 17 issue of The New England Journal of Medicine.
Retinopathy of prematurity is a leading cause of childhood blindness worldwide. In the immature retina of babies born before 30 weeks' gestational age, the disease results ...
Research improves diagnosis and treatment of bleeding disorder
2011-02-17
A rare bleeding disorder that can lead to life-threatening bleeding episodes is misdiagnosed in 15 per cent of cases according to findings from a new international research project led by a Queen's professor.
"Correct diagnosis is critical because it determines the treatment decision," says Maha Othman, a professor in the Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology who led the three-year research project on the rare platelet type of von Willebrand disease (VWD).
Patients with VWD are commonly treated with drugs that help control their condition. However, these drugs aggravate ...