(Press-News.org) This release is available in German.
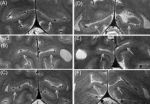
The Stripe of Gennari develops even in those who are blind from birth and does not degenerate, despite a lack of visual input. This was discovered by Robert Trampel and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences using magnetic resonance imaging. This bundle of nerve fibers, which is approximately 0.3 mm thick, is not exclusively responsible for optic information. In the blind, it might play a greater role in processing tactile stimuli. This could contribute to an enhanced sense of touch and support fast reading of Braille. (Cerebral Cortex, Online 10. 02. 2011)
The Stripe of Gennari – also known as the 'Stria of Gennari' – transverses the gray matter of the primary visual cortex as a distinct white line. "Although the visual cortex is one of the best-studied parts of the brain, and the Stripe of Gennari is a rather obvious structure, why it develops and what its function is has not previously been studied in detail", explains Robert Trampel from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences. "An obvious connection with sight was assumed."
However, as is now clear, this cannot be the only function of the stripe of Gennari: In a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study, the researchers found the stripe of Gennari in the brains of congenitally blind subjects. "This brain structure therefore can't exclusively be involved in vision and must be capable of carrying out other tasks", says Trampel. In the blind, the Stripe of Gennari could play a role in supporting the sense of touch, the scientists speculate. "This faculty is essential in reading Braille and the region carrying the Gennari-Stripe is known to show an increased activity in the blind when performing this task." All participants in the present study were highly proficient in reading Braille, having responded to an advertisement written in Braille in a newspaper for the visually impaired.
However, since the stripe of Gennari is already present in the first years of life and does not degenerate, it is likely to have an important role already in early infancy. In blind people, the brain uses tactile and acoustic stimuli to construct a rough spatial representation of the surroundings in the absence of visual information. The stripe of Gennari might play a role in this process and could later support highly demanding tactile tasks, like Braille-reading. In future studies with fMRI, the researchers aim to learn more about the work of this versatile nerve bundle in the human brain.
INFORMATION:
The blind also have a Stripe of Gennari
2011-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Feb. 23 NASA mission to tote $28 million CU-Boulder instrument and tiny student satellite
2011-02-24
A $28 million University of Colorado Boulder instrument developed to study changes in the sun's brightness and its impact on Earth's climate is one of two primary payloads on NASA's Glory mission set to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Feb. 23.
Designed and built by a team from CU-Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, the instrument called the Total Irradiance Monitor, or TIM, will point directly toward the sun to measure both short- and long-term fluctuations in the sun's energy output as it reaches the top of Earth's atmosphere. ...
Study suggests gender does not play a role in risk of death from heart attack
2011-02-24
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – A study led by the University of Michigan Cardiovascular Center shows being a woman may not increase your risk of dying from treatment for a severe heart attack.
U-M researchers and colleagues in the Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium found women who received treatment such as an angioplasty had higher unadjusted in-hospital heart attack deaths.
But these differences appear to be related to women's ages and additional health problems – not gender, says study lead author Elizabeth Jackson, M.D., M.P.H., an assistant professor of internal medicine ...
Nanoparticles increase survival after blood loss
2011-02-24
February 22, 2011 — (BRONX, NY) — In an advance that could improve battlefield and trauma care, scientists at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University have used tiny particles called nanoparticles to improve survival after life-threatening blood loss. Nanoparticles containing nitric oxide (NO) were infused into the bloodstream of hamsters, where they helped maintain blood circulation and protect vital organs. The research was reported in the February 21 online edition of the journal Resuscitation.
"The new nanomedicine was developed to address the need ...
E-health must be a priority, researchers say
2011-02-24
An electronic health record system should be the backbone of health care reform in Canada and more must be done to speed up the implementation of this initiative across the country. Furthermore for this system to be put in place effectively, doctors and front line health care workers and administrators must be encouraged to play a more active role. These are the findings of an innovative new study assessing the effectiveness Canada Health Infoway's e-health plan. The study, which was conducted by scientists at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre ...
Gender gap: Selection bias snubs scholarly achievements of female scientists
2011-02-24
Women scientists must confront sexism when competing for awards that recognize their research, according to a new analysis.
Research funded by the National Science Foundation and sponsored by the Association for Women in Science found that female scientists win service or teaching awards in proportion to the number of women in the PhD pool for their discipline, says sociologist Anne Lincoln at Southern Methodist University in Dallas. That's not the case, however, for awards for their research, says Lincoln, one of three authors on the research, which was reported in Nature.
The ...
MIT engineers design new nanoparticle that could lead to vaccines for HIV, malaria, other diseases
2011-02-24
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.- MIT engineers have designed a new type of nanoparticle that could safely and effectively deliver vaccines for diseases such as HIV and malaria.
The new particles, described in the Feb. 20 issue of Nature Materials, consist of concentric fatty spheres that can carry synthetic versions of proteins normally produced by viruses. These synthetic particles elicit a strong immune response — comparable to that produced by live virus vaccines — but should be much safer, says Darrell Irvine, author of the paper and an associate professor of materials science ...
Babies and toddlers can suffer mental illness, seldom get treatment
2011-02-24
WASHINGTON -- Infants and toddlers can suffer serious mental health disorders, yet they are unlikely to receive treatment that could prevent lasting developmental problems, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
One barrier to mental health care for young children is "the pervasive, but mistaken, impression that young children do not develop mental health problems and are immune to the effects of early adversity and trauma because they are inherently resilient and 'grow out of' behavioral problems and emotional difficulties," according ...
Even in a crowd, you remain unique, UCLA life scientists report
2011-02-24
It may seem paradoxical, but being part of a crowd is what makes you unique, according to UCLA life scientists.
Biologists Kimberly Pollard and Daniel Blumstein examined the evolution of individuality —personal uniqueness — by recording alarm-call vocalizations in eight species of rodents that live in social groups of various sizes. They found that the size of the groups strongly predicted the individual uniqueness in the animals' voices: The bigger the group, the more unique each animal's voice typically was and the easier it was to tell individuals apart.
Their ...
New Zealand earthquake damage illustrates risks posed by shallow crustal faults
2011-02-24
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The terribly destructive earthquake that just hit Christchurch, New Zealand, was only a moderate 6.3 magnitude, but had certain characteristics that offer an important lesson to cities up and down the West Coast of North America that face similar risks, experts say.
The New Zealand earthquake killed dozens – and some fear the death toll may rise to the hundreds – and was an aftershock of the much more powerful 7.1 magnitude earthquake that struck that nation last September near the same area, but caused no deaths.
Even though this earthquake was weaker ...
Stresses of unemployed spouse can hurt job performance of other spouse, says study
2011-02-24
Ignoring the stresses of an unemployed spouse's job search does not bode well for the employed spouse's job productivity or home life, says a University of Colorado Boulder professor.
Associate Professor Maw-Der Foo of CU-Boulder's Leeds School of Business studies employee workplace issues, including those related to interpersonal relationships.
Foo and lead author Professor Zhaoli Song of the National University of Singapore co-authored a paper titled "Unraveling the Stress Crossover Between the Unemployed and Their Spouses," which was published in last month's edition ...