(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Atu had a brief but memorable life last week, and NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a day-by-day look at its growth and death.
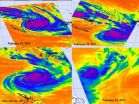
AIRS provides infrared images of atmospheric phenomena, oceans and land areas around the world. Basically, infrared data takes the temperature of these things. When NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu from February 21 through the 25 it saw thunderstorm cloud tops grow colder as the clouds grew higher and thunderstorms became more powerful. When cloud top temperatures reached the threshold of -63 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius they indicated strong thunderstorms dropping heavy rainfall. By the 25th, Atu had run into strong wind shear and had dissipated north of New Zealand.
On Feb. 21 at 02:17 UTC, NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone Atu when it was over New Caledonia and Vanuatu bringing rainfall and gusty winds. On Feb. 22 at 13:53 UTC, AIRS showed an intensifying tropical Storm Atu with a developing eye.
Tropical Cyclone Atu was at its strongest on February 22 near 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST), when it was about 315 miles (506 km) east of Noumea, New Caledonia, near 22.7 South and 172.1 East. It had maximum sustained winds of 95 knots (109 mph/175 kmh) at that time. It was moving at 15 knots (17 mph/28 kmh) in a southerly direction, and was starting to weaken. By mid-day on Feb. 22, the warnings for Vanuatu had been discontinued, and there were some warnings still in effect for New Caledonia for winds in excess of 20 knots (23 mph/37 kmh) and high ocean swells.
On Feb. 23 at 02:05 UTC, AIRS data showed a powerful cyclone with strong thunderstorms, heavy rain and a visible eye on infrared imagery. On February 23, at 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST), Tropical Cyclone Atu had maximum sustained winds of 70 knots (80 mph/129 kmh) with higher gusts. Tropical storm-force winds extended out to 140 miles (225 km) from the center of Atu. Cyclone-force winds extended to a much smaller area, only about 60 miles (95 km) in diameter. It was located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean near 28.5S and 176.5E, about 500 miles (804 km) south-southwest of Nadi, Fiji. At that time, it was moving southeast near 22 knots (25 mph/40 kmh). Atu was generating high waves in the open ocean, with wave heights reaching 30 feet (9 meters). Atu was weakening and becoming an extra-tropical cyclone north of New Zealand.
The AIRS infrared data on Feb. 24 at 01:11 UTC showed Atu as a small rounded area of weak convection. By 9:46 a.m. EST that day, Atu had dissipated north of New Zealand.
INFORMATION:
NASA tracks the brief life of Tropical Cyclone Atu in the southern Pacific
NASA's AIRS instrument covers Atu's Life
2011-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's Glory Satellite scheduled for launch March 4
2011-03-02
WASHINGTON -- NASA's Glory spacecraft is scheduled for launch on Friday, March 4. Technical issues with ground support equipment for the Taurus XL launch vehicle led to the scrub of the original Feb. 23 launch attempt. Those issues have been resolved.
The March 4 liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., is targeted for 5:09:43 a.m. EST, in the middle of a 48-second launch window. Spacecraft separation occurs 13 minutes after launch.
Data from the Glory mission will allow scientists to better understand how the sun and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols ...
Tanning bed exposure can be deadly when complicated by medication reactions
2011-03-02
INDIANAPOLIS – Tanning bed exposure can produce more than some tanners may bargain for, especially when they self-diagnose and use the radiation to treat skin eruptions, according to research conducted by the Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Dermatology.
"There are many reasons to be cautious of tanning bed radiation but some people use tanning beds to 'self-treat' skin eruptions," said Jeffrey B. Travers, M.D., Ph.D., senior author of a study published online in the Archives of Dermatology. "If the skin eruption is eczema or even psoriasis, a tanning ...
Discovery of source of glycogen 'manufacturing' errors sheds light on fatal disease
2011-03-02
Indiana University scientists have solved a perplexing mystery regarding one of the body's main energy storage molecules, in the process shedding light on a possible route to treatment of a rare but deadly disease in teenagers.
The disease occurs when a genetic mutation causes excessive amounts of phosphate to build up in glycogen. Glycogen is a chain-like molecule the body uses to temporarily store glucose when it's not needed to provide energy for cellular activities. The excess phosphate causes unnatural glycogen structures to appear in the body, including the brain, ...
Emergency mental health lessons learned from Continental Flight 3407 disaster
2011-03-02
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- When a disaster's physical evidence is gone -- debris removed, shooter arrested, ashes cold -- the psychological effects of the disaster on emergency responders and civilians involved still may burn.
Emergency mental health, a field often overlooked in the chaos, is a vital component of any disaster response, but may not be well represented in emergency preparedness planning.
Trained mental health responders to the Continental Flight 3407 disaster outside Buffalo in 2009 share their lessons learned on mental health preparedness in an article that ...
Queen's University professor uses nanotechnology to prolong machine and engine life
2011-03-02
Guojun Liu has discovered a way to use nanotechnology to reduce friction in automobile engines and machines.
"The technology should be useful in a wide range of machineries other than automobile engines," says Dr. Liu, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and an expert in polymer synthesis. "If implemented industrially, this nanotechnology should help prolong machine life and improve energy efficiency."
Dr Liu's team prepared miniscule polymer particles that were only tens of nanometers in size. These particles were then dispersed in automobile engine base oils. ...
Relaxation leads to lower elasticity
2011-03-02
This press release is available in German.
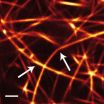
Many materials, when observed over a sufficiently long period of time, show changes in their mechanical properties. The exact course of these developments depends on the underlying microscopic mechanisms. However, the microscopic structure and the complexity of the systems make direct observation extremely difficult.
That is why a team led by Professor Andreas Bausch from the Chair of Cellular Biophysics resorted to a model system that can be precisely controlled using actin filaments, a biopolymer that, among other things, ...
The dusty disc of NGC 247
2011-03-02
The spiral galaxy NGC 247 is one of the closest spiral galaxies of the southern sky. In this new view from the Wide Field Imager on the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope in Chile large numbers of the galaxy's component stars are clearly resolved and many glowing pink clouds of hydrogen, marking regions of active star formation, can be made out in the loose and ragged spiral arms.
NGC 247 is part of the Sculptor Group, a collection of galaxies associated with the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253, also shown in eso0902 - http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso0902/ - and eso1025 - http://www.eso.org/public/news/eso1025/). ...
Effectiveness of wastewater treatment may be damaged during a severe flu pandemic
2011-03-02
Existing plans for antiviral and antibiotic use during a severe influenza pandemic could reduce wastewater treatment efficiency prior to discharge into receiving rivers, resulting in water quality deterioration at drinking water abstraction points.
These conclusions are published this week (2 March 2011) in a new paper in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, which reports on a study designed to assess the ecotoxicologic risks of a pandemic influenza medical response.
The research was carried out by a team from the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UK), the Institute ...
Research suggests alcohol consumption helps stave off dementia
2011-03-02
Experts agree that long-term alcohol abuse is detrimental to memory function and can cause neuro-degenerative disease. However, according to a study published in Age and Ageing by Oxford University Press today, there is evidence that light-to-moderate alcohol consumption may decrease the risk of cognitive decline or dementia.
Estimates from various studies have suggested the prevalence of alcohol-related dementia to be about 10% of all cases of dementia. Now researchers have found after analyzing 23 longitudinal studies of subjects aged 65 years and older that the impact ...
Study shows pine bark naturally improves kidney function in patients with metabolic syndrome
2011-03-02
(Mar. 2, 2011) – HOBOKEN, NJ – The American Heart Association estimates 35 percent of adults in the U.S. suffer from metabolic syndrome, a group of risk factors characterized by obesity and the simultaneous presence of heart disease risk factors with high blood pressure, blood sugar and lipids. In patients with metabolic syndrome, high blood pressure and blood glucose gradually impair kidney function, which in turn affects the organ's ability to filter waste from the body. A study published in the June 2010 issue of Panminerva Medica reveals Pycnogenol® (pic-noj-en-all), ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] NASA tracks the brief life of Tropical Cyclone Atu in the southern PacificNASA's AIRS instrument covers Atu's Life