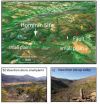
(Press-News.org) Our earliest ancestors preferred to settle in locations that have something in common with cities such as San Francisco, Naples and Istanbul -- they are often on active tectonic faults in areas that have an earthquake risk or volcanoes, or both.
An international team of scientists has established a link between the shape of the landscape and the habitats preferred by our earliest ancestors. The research, by scientists at the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa, the University of York and the Institut de Physique du Globe Paris (IPGP), is published in the March 2011 issue of the Journal of Human Evolution.
The four-year study examines the geomorphology (literally the shape of the landscape) around ancient sites in southern Africa.
Lead author, South African Dr Sally Reynolds, a palaeoanthropologist at Witwatersrand who conducted the research during a postdoctoral fellowship at IPGP, says: "We were stunned when during a fieldwork trip in South Africa in 2007, Professor Geoffrey King and I discovered evidence that hominin sites such as Taung, Sterkfontein and Makapansgat, show landscape features in combinations that are not random, but result from tectonic motions, such as earthquakes."
Several lines of scientific evidence suggest that Australopithecus africanus (like the 'Mrs Ples' fossil from Sterkfontein) was adapted to mixed, or mosaic habitats -- landscapes with trees and open grassland, with some wetland marshy areas. The study suggests that it was the type of mosaic environment created by tectonic earth movements near rivers or lakes.
These features including cliffs, sedimented valleys, river gorges and drier plateau areas in close proximity of about 10 kilometres, are created when sections of the earth's crust move in response to pressure, then blocks of land are lifted up, while others are forced downwards. When this happens next to a river, the result is the creation of wetland, marshy areas close to drier plateaus and areas of erosion.
Professor Geoff Bailey, from the University of York, who is the lead author on an accompanying paper, also published in the same issue of the Journal of Human Evolution, confirms: "This link between earthquakes and human habitation is one we've long suspected was there. Regions vulnerable to earthquake and volcanic activity often create landscapes with long-term benefits for human settlement. But the tragic events in Christchurch are a graphic illustration of the attendant risk of these locations."
Professor King, a tectonic geomorphologist at the IPGP, adds: "The original idea was developed in Greece over a decade ago, with the surprising discovery that the sites there were clearly associated with ongoing tectonic activity.
"Even though South Africa appears to be tectonically stable, there are landscape features that indicate that modest levels of activity are preserved in the hard, southern African rocks. This means that the landscape model we developed in Greece is equally applicable to East Africa, and now also to the well-known fossil sites of the South Africa's Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site."
Dr Reynolds, who is also an honorary research fellow at the School of Natural Sciences and Psychology at Liverpool John Moores University, explains "Our hominin ancestors would have been unaware of the tectonic influence on their habitats, but instead would have been attracted by the range of food and shelter offered."
The combination of drinking water, steep cliffs that provided shelter from predators, together with a range of feeding sources constitute the key ingredients for an ideal habitat for our ancestors.
INFORMATION:
Our ancestors lived on shaky ground
Scientists find link between tectonically active landscapes and ancient sites
2011-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Microsoft SharePoint Partners Launch Group Blog Site Focused on Educating SharePoint Buyers
2011-03-04
Microsoft SharePoint experts have joined forces at www.sharepoint-blog.com to provide reviews, comparisons and opinions to assist clients in selecting the right collaboration software.
Group blog sites combine resources of firms to create active blog sites that build trust, get attention and attract visitors. Following the model of successful group blog sites for Microsoft Dynamics Partners including www.erpsoftwareblog.com and www.crmsoftwareblog.com this blog site will provide objective articles from Microsoft SharePoint experts nationwide. Rather than being focused ...
Am I safe here?: How people with HIV/AIDS perceive hidden prejudices in their communities
2011-03-04
People in marginalized groups, such as the disabled or racial minorities, feel stigmatized—condemned, feared, or excluded—when other people stigmatize them. That's obvious. But they can also feel stigma when nobody blatantly discriminates against them or says a negative word.
These folks aren't paranoid, suggests a new study of HIV-positive people and their communities to be published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association of Psychological Science. Rather, they're picking up subtle clues from their communities.
"Society is changing when it comes to ...
Next - Scentiliciously Yours
2011-03-04
Escape the humdrum tedium of everyday life, and enter Next's magical world of fabulous fragrances and indulgent beauty treats. In this deliciously sweet-smelling universe, feminine allure is complemented by olfactory art.
GET THE LOOK showcases on-trend additions to Next's RUNWAY COLLECTION colour cosmetics range including a volumising black mascara for truly luscious lashes... and oh-so-very-kissable cherry lip glosses that will certainly pump up a pout! While lush fashion lashes are wonderfully seductive, there's a terrific new dry shampoo kissed with OH MY GORGEOUS ...
Scientists identify susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder
2011-03-04
A new study provides fascinating insight into the genetic basis of bipolar disorder, a highly heritable mood disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of mania and depression. The research, published by Cell Press online February 24 in the American Journal of Human Genetics, identifies a previously unrecognized susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) provide a way to systematically sort through all the DNA of many individuals in order to identify genetic variations associated with a particular disease. However, thus far these ...
Drop in temperature may explain the increase in dry eye suffering
2011-03-04
Springtime may be just what the doctor orders for individuals suffering from dry eye condition, a disorder resulting from insufficient tear production or altered tear film composition. According to a study published in Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, a temperature less than 30 degrees Celsius on the eye and eyelid could be the cause for the onset or worsening of the disorder.
The study, (Meibomian Lipid Films and the Impact of Temperature) showed that the cold temperature causes the meibum, the oily substance which helps to form the outermost layer of the ...
Discrimination creates racial battle fatigue for African-Americans
2011-03-04
University Park, Pa. -- Just as the constant pressure soldiers face on the battlefield can follow them home in the form of debilitating stress, African Americans who face chronic exposure to racial discrimination may have an increased likelihood of suffering a race-based battle fatigue, according to Penn State researchers.
African Americans who reported in a survey that they experienced more instances of racial discrimination had significantly higher odds of suffering generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) some time during their lives, according to Jose Soto, assistant professor, ...
Study Suggests Correlation Between Low APGAR Scores and Low Birth Weights by Silvers, Langsam, Weitzman, P.C.
2011-03-04
Physicians have debated the relationship between a low APGAR score and cerebral palsy, especially in children with low birth weight. Although this relationship has previously been inconclusive, a new study by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH) indicates a direct association between cerebral palsy and low APGAR scores in children with less than normal birth weights.
What is an APGAR score?
The APGAR test is a newborn assessment given directly after birth that measures five criteria to determine the child's health:
Appearance/skin color -- pink, pale ...
Men in low income neighborhoods drink more than women: Study
2011-03-04
TORONTO, On – March 3, 2011 – Men living in low-income neighbourhoods consume more than three times as many alcoholic drinks each week compared to women in these neighbourhoods, according to a study led by St. Michael's researcher Flora Matheson.
The findings, published in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, suggest neighbourhood affluence affects men and women differently when it comes to alcohol consumption. Heavy drinking is associated with higher death rates and a greater risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, cancer and liver cirrhosis.
"While ...
Grazing of cattle pastures can improve soil quality
2011-03-04
A team of U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists has given growers in the Piedmont guidance on how to restore degraded soils and make the land productive. Researchers with the USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS) found that if cattle are managed so that they graze moderately, soil quality can be restored and emissions of carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) can be reduced.
ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency. The research, published in the Soil Science Society of America Journal, supports the USDA priority of responding to climate ...
Traumatic Brain Injury is a Cause of Concern in the U.S.
2011-03-04
Many people have heard about traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), but few realize how common these injuries are in the United States. Data from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that an estimated 52,000 people die every year in the United States as a result of a TBI. Another 275,000 are hospitalized and 1.365 million more receive emergency services annually. In all, nearly 1.7 million people suffer a TBI each year. One Oxford University report estimates the combined direct and indirect costs of TBI to have reached $60 billion in 2000.
CDC data indicates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Our ancestors lived on shaky groundScientists find link between tectonically active landscapes and ancient sites