(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are developing a technology that aims to help make solar cells more affordable and efficient by using a new manufacturing method that employs an ultrafast pulsing laser.
The innovation may help to overcome two major obstacles that hinder widespread adoption of solar cells: the need to reduce manufacturing costs and increase the efficiency of converting sunlight into an electric current, said Yung Shin, a professor of mechanical engineering and director of Purdue University's Center for Laser-Based Manufacturing.
Critical to both are tiny "microchannels" needed to interconnect a series of solar panels into an array capable of generating useable amounts of power, he said. Conventional "scribing" methods, which create the channels mechanically with a stylus, are slow and expensive and produce imperfect channels, impeding solar cells' performance.
"Production costs of solar cells have been greatly reduced by making them out of thin films instead of wafers, but it is difficult to create high-quality microchannels in these thin films," Shin said. "The mechanical scribing methods in commercial use do not create high-quality, well-defined channels. Although laser scribing has been studied extensively, until now we haven't been able to precisely control lasers to accurately create the microchannels to the exacting specifications required."
The researchers hope to increase efficiency while cutting cost significantly using an "ultrashort pulse laser" to create the microchannels in thin-film solar cells, he said.
The work, funded with a three-year, $425,000 grant from the National Science Foundation, is led by Shin and Gary Cheng, an associate professor of industrial engineering. A research paper demonstrating the feasibility of the technique was published in Proceedings of the 2011 NSF Engineering Research and Innovation Conference in January. The paper was written by Shin, Cheng, and graduate students Wenqian Hu, Martin Yi Zhang and Seunghyun Lee.
"The efficiency of solar cells depends largely on how accurate your scribing of microchannels is," Shin said. "If they are made as accurately as possibly, efficiency goes up."
Research results have shown that the fast-pulsing laser accurately formed microchannels with precise depths and sharp boundaries. The laser pulses last only a matter of picoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second. Because the pulses are so fleeting the laser does not cause heat damage to the thin film, removing material in precise patterns in a process called "cold ablation."
"It creates very clean microchannels on the surface of each layer," Shin said. "You can do this at very high speed, meters per second, which is not possible with a mechanical scribe. This is very tricky because the laser must be precisely controlled so that it penetrates only one layer of the thin film at a time, and the layers are extremely thin. You can do that with this kind of laser because you have a very precise control of the depth, to about 10 to 20 nanometers."
Traditional solar cells are usually flat and rigid, but emerging thin-film solar cells are flexible, allowing them to be used as rooftop shingles and tiles, building facades, or the glazing for skylights. Thin-film solar cells account for about 20 percent of the photovoltaic market globally in terms of watts generated and are expected to account for 31 percent by 2013.
The researchers plan to establish the scientific basis for the laser-ablation technique by the end of the three-year period. The work is funded through NSF╒s Civil Mechanical and Manufacturing Innovation division.
INFORMATION:
Information about photovoltaic cells is available from the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory at http://www.nrel.gov/learning/re_photovoltaics.html
Related websites:
Yung Shin:
https://engineering.purdue.edu/ME/People/ptProfile?id=12309
Gary Cheng:
https://engineering.purdue.edu/IE/People/profile?resource_id=34940
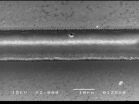
IMAGE CAPTION:
This image, taken with a scanning electron microscope, shows a microchannel that was created using an ultrafast-pulsing laser. (Purdue University School of Mechanical Engineering image/Yung Shin)
A publication-quality photo is available at http://www.purdue.edu/uns/images/2011/shin-solar.jpg
Abstract on the research in this research is available at: http://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/research/2011/110308ShinSolar.html
Ultrafast laser 'scribing' technique to cut cost, hike efficiency of solar cells
2011-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oldest known wild bird in US returns to Midway to raise chick
2011-03-09
MIDWAY ATOLL — The oldest known U.S. wild bird – a coyly conservative 60 -- is a new mother.
The bird, a Laysan albatross named Wisdom, was spotted a few weeks ago with a chick by John Klavitter, a U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service biologist and the deputy manager of the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge.
The bird has sported and worn out 5 bird bands since she was first banded by U.S. Geological Survey scientist Chandler Robbins in 1956 as she incubated an egg. Chandler rediscovered Wisdom in 2001. In 1956, he estimated Wisdom to be at least 5 years old then since ...
NYSCF – Robertson investigator publishes research to better understand pluripotent stem cells
2011-03-09
NEW YORK CITY (March 7, 2011)— Paul Tesar, PhD, of Case Western Reserve University, a member of the inaugural class of The New York Stem Cell Foundation – Robertson Investigators, published his research on the ability to isolate epiblast stem cells from preimplantation mouse embryos. This research enhances our understanding of the many forms of pluriportent stem cells that scientists use for researching so many debilitating diseases.
"I think that this paper will change the way people think about what human ES cells represent from a developmental perspective," said Dr. ...
ADAM-12 gene could hold key to cancer, arthritis and cardiac treatments
2011-03-09
COLUMBIA, Mo. ADAM-12 is not only the name of a 1970's television police drama – it's also the gene that University of Missouri researchers believe could be an important element in the fight against cancer, arthritis, and cardiac hypertrophy, or thickening of the heart's walls.
Alpana Ray, research associate professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, and a team of researchers including Bimal Ray, professor of Veterinary Pathobiology, have been studying the ADAM family of genes for several years. Alpana Ray's latest publication in the Proceedings of the National ...
Colonoscopy linked to decrease in colorectal cancer deaths, but many more could have been prevented
2011-03-09
OAK BROOK, Ill. – March 8, 2011 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month during March, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has published a special issue for March on colonoscopy and colorectal cancer. The issue includes a study showing that colonoscopy has prevented a substantial number of deaths from colorectal cancer and that many more could have been prevented with more widespread use. The analysis reports that approximately 13,800 to 22,000 colorectal cancer deaths could have been prevented in 2005, whereas 7,300 to 11,700 were actually prevented through ...
When work calls: Study shows that receiving work-related contact at home takes greater toll on women's well-being
2011-03-09
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE from the UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO
March 8, 2011
TORONTO, ON – Communication technologies that help people stay connected to the workplace are often seen as solutions to balancing work and family life. A new study, however, suggests there may be a "dark side" to the use of these technologies for workers' health – and these effects seem to differ for women and men.
Using data from a national survey of American workers, University of Toronto researchers asked study participants how often they were contacted outside the workplace by phone, email or text ...
The science behind the cape
2011-03-09
Bethesda, Md. (Mar. 8, 2011) -- What do you have when you line up a martial artist, acrobatic gymnast, police officer, firefighter, NASCAR driver, and NFL running back? "Watson," the IBM super-computer that recently routed humanity's best on Jeopardy might have guessed the answer was "the Village People," to which host Alex Trebek could have replied, "Sorry. The answer we were looking for is 'Batman'." At least that is the correct answer for physiologist E. Paul Zehr.
In a new article, Zehr, a professor at the University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia, describes ...
Passive news reports may lead readers to feel they can't find the truth
2011-03-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Passive news reporting that doesn't attempt to resolve factual disputes in politics may have detrimental effects on readers, new research suggests.
The study found that people are more likely to doubt their own ability to determine the truth in politics after reading an article that simply lists competing claims without offering any idea of which side is right.
"There are consequences to journalism that just reports what each side says with no fact checking," said Raymond Pingree, author of the study and assistant professor of communication at Ohio ...
Epilepsy-linked memory losss worries more patients than doctors
2011-03-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Patients with epilepsy worry more than their physicians do about the patients' potential memory loss accompanying their seizure disorder, according to a recent study.
In a survey, patients with epilepsy as a group ranked memory loss as their second-most important concern on a list of 20 potential medical or social concerns. Memory loss as a concern came in 12th in the frequency of responses among concerns recorded by physicians and nurse practitioners who completed the same survey.
Patients and practitioners agreed overall on three of the top five concerns: ...
ASGE initiative examines real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps
2011-03-09
OAK BROOK, Ill. – March 8, 2011 – In recognition of National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month during March, GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has put out a special issue for March on colonoscopy and colorectal cancer. In this issue is the first statement from a new initiative by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) called the Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI). The first PIVI document examines real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive (≤ 5 mm in size) colorectal polyps and is one in a ...
Brain implant surgeries at UCSF dramatically improve symptoms of debilitating condition
2011-03-09
Implanting electrodes into a pea-sized part of the brain can dramatically improve life for people with severe cervical dystonia – a rare but extremely debilitating condition that causes painful, twisting neck muscle spasms – according to the results of a pilot study led by Jill Ostrem, MD and Philip Starr, MD PhD at the University of California, San Francisco.
Today, people with cervical dystonia can be treated with medications or injections of botulinum toxin (e.g., Botox®), which interrupt signals from the brain that cause these spasms. However, those treatments do ...