(Press-News.org) Children who are taught how to think and act like scientists develop a clearer understanding of the subject, a study has shown.
The research project led by The University of Nottingham and The Open University has shown that school children who took the lead in investigating science topics of interest to them gained an understanding of good scientific practice.
The study shows that this method of 'personal inquiry' could be used to help children develop the skills needed to weigh up misinformation in the media, understand the impact of science and technology on everyday life and help them to make better personal decisions on issues including diet, health and their own effect on the environment.
The three-year project involved providing pupils aged 11 to 14 at Hadden Park High School in Bilborough, Nottingham, and Oakgrove School in Milton Keynes with a new computer toolkit named nQuire, now available as a free download for teachers and schools.
Running on both desktop PCs and handheld notebook-style devices, the software is a high-tech twist on the traditional lesson plan — guiding the pupils through devising and planning scientific experiments, collecting and analysing data and discussing the results.
The pupils were given wide themes for their studies but were asked to decide on more specific topics that were of interest to them, including heart rate and fitness, micro climates, healthy eating, sustainability and the effect of noise pollution on birds.
The flexible nature of the toolkit meant that children could become "science investigators", starting an inquiry in the classroom then collecting data in the playground, at a local nature reserve, or even at home, then sharing and analysing their findings back in class.
Professor Mike Sharples, who led the project at Nottingham, said: "Mobile devices such as smartphones and netbooks are sophisticated scientific instruments, with built-in cameras, voice recorders, and location sensors. The children quickly learned how to use the nQuire toolkit to follow investigations.
"The results from the trials we conducted showed a positive effect on learning outcomes, a maintained enjoyment of science lessons and a small but genuine improvement in pupils' understanding of the scientific process.
"Science can be a hard sell in terms of persuading young people to consider it as an option for further education or as a career, particularly those from socially-disadvantaged backgrounds. However, it shapes the world in which we live and it is incredibly important that people develop the skills necessary to navigate the huge amount of 'bad science' and misinformation which is propagated in the media. Our results show that the personal inquiry learning process can take pupils in the right direction."
Professor Eileen Scanlon, Associate Director (Research & Scholarship), who led the project at The Open University, said: "We wanted to examine whether we could effectively use technology and the process of investigation — or 'personal inquiry' — to get pupils to start thinking like scientists.
"The tool this project has produced enables teachers to construct the kind of support pupils need to really engage with a subject area. Using mobile devices gave the pupils support wherever they were, which is an important element of learning. Teaching doesn't have to be confined to the classroom and in fact, as our research shows, can be much more effective when it's allowed to extend beyond the typical learning environment. Our focus at the OU has been on support for the geography elements of the curriculum, so it has been particularly important for us to encourage pupils to investigate, and engage with, their local environment."
The trials showed that after using nQuire, the pupils were able to better grasp the principles underpinning sound scientific practice and whether decisions made during the course of their inquires could threaten the validity of their investigations.
The project has been supported by ScienceScope, a company that develops sensing and data logging equipment, and funded with £1.2 million from the joint Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) Technology Enhanced Learning Research Programme.
The nQuire software is now available to teachers and schools as an Open Source application, available for free download at www.nquire.org.uk and can by run on a Windows, Macintosh or Linux PC, on mobile device web browsers such as the Apple iPad or can be downloaded to a USB data stick to allow it to be run from the stick rather than installed as software on a computer.
### END
Giving children the power to be scientists
2011-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers selectively control anxiety pathways in the brain
2011-03-10
A new study sheds light--both literally and figuratively--on the intricate brain cell connections responsible for anxiety.
Scientists at Stanford University recently used light to activate mouse neurons and precisely identify neural circuits that increase or decrease anxiety-related behaviors. Pinpointing the origin of anxiety brings psychiatric professionals closer to understanding anxiety disorders, the most common class of psychiatric disease.
A research team led by Karl Deisseroth, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and bioengineering, identified ...
Researchers develop synthetic compound that may lead to drugs to fight pancreatic, lung cancer
2011-03-10
DALLAS – March 10, 2011 – Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have identified a chemical compound that may eventually lead to a drug that fights cancers that are dependent on a particular anti-viral enzyme for growth.
The researchers are testing the compound's effectiveness at fighting tumors in mice. If it is successful, they will then work to develop a drug based on the compound to combat pancreatic and non-small cell lung cancer, two cancer types in which this particular enzyme, TBK-1, often is required for cancer cell survival.
"Our prediction is that ...
Report: International collaboration between researchers results in greater recognition
2011-03-10
U.S. researchers who collaborate with international scientists are more likely to have their work cited than peers who do not utilize overseas expertise, according to a new study released this week by Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy. U.S. collaborators with international scientists are also more likely to receive greater recognition and produce work with greater impact.
The study, "International Stem Cell Collaboration: How Disparate Policies Between the United States and the United Kingdom Impact Research," was authored by Kirstin Matthews, a fellow ...
New UF study shows some sharks follow 'mental map' to navigate seas
2011-03-10
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — A new study led by a University of Florida researcher uses tracking data of three shark species to provide the first evidence some of the fish swim directly to targeted locations.
Researchers found tiger and thresher sharks showed the ability to orient at large distances, with tiger sharks swimming in direct paths at least 4 miles away and reaching specific resource areas about 30 miles away, said lead author Yannis Papastamatiou, a marine biologist in the division of ichthyology at the Florida Museum of Natural History on the UF campus.
A research ...
Researchers identify new biomarker for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the human form of mad cow disease
2011-03-10
Neena Singh, MD, PhD and colleagues at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine have identified the first disease-specific biomarker for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD), a universally fatal, degenerative brain disease for which there is no cure. sCJD is one of the causes of dementia and typically leads to death within a year of disease onset.
The finding, published in the March 9th issue of PLoS ONE, a scientific journal produced by the Public Library of Science, provides a basis for developing a test to diagnosis sCJD while patients are still alive. ...
Nottingham scientists identify trigger in cat allergy
2011-03-10
A breakthrough by scientists at The University of Nottingham could provide hope for any allergy sufferers who have ever had to choose between their health and their household pet.
The team of immunologists led by Drs Ghaem-Maghami and Martinez-Pomares in the University's School of Molecular Medical Sciences, and funded by the charity Asthma UK, have identified a cell component which plays a key role in triggering allergic responses to cat dander.
The discovery furthers our understanding of how the body's immune system identifies and reacts to allergens, which could ...
Passive smoking increases risk to unborn babies, study says
2011-03-10
Pregnant non-smokers who breathe in the second-hand smoke of other people are at an increased risk of delivering stillborn babies or babies with defects, a study led by researchers at The University of Nottingham has found.
The study, published in the April edition of the journal Pediatrics, found passive smoking increased the risk of still birth by almost one-quarter (23 per cent) and was linked to a 13 per cent increased risk of congenital birth defects.
The findings underline the importance of discouraging expectant fathers from smoking around their pregnant partners ...
Hopkins Children's study finds some patients with cerebral palsy have asymmetric pelvic bones
2011-03-10
Johns Hopkins Children's Center researchers have discovered that most children with severe cerebral palsy have starkly asymmetric pelvic bones. The newly identified misalignment can affect how surgeries of the pelvis, spine and surrounding structures are performed, the researchers say.
The study will be published online on March 10 in the Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics.
Previous studies of patients with cerebral palsy have reported asymmetry above the pelvis and misalignment of the hips, but this new report, the researchers say, is the first one to show misalignment ...
Brandeis researchers use lasers, custom microscope to show gene splicing process in real time
2011-03-10
From neurosurgery to bar code readers, lasers have been used in a myriad of applications since they were first introduced in the late 1950's. Now, with the work being done in Jeff Gelles' Lab at Brandeis University, researchers have developed a way to use lasers to study the splicing of pre-messenger RNA molecules, an essential process in creating proteins to sustain advanced organisms, including human life. This process of splicing is carried out by a cellular micro-machine called the spliceosome.
"Understanding how these micro-machines function inside the cell is important ...
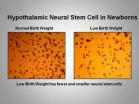
Study provides explanation for connection between low birth weight and obesity later in life
2011-03-10
Providing further understanding of the link between low birth weights and obesity later in life, researchers found nutritionally deprived newborns are "programmed" to eat more because they develop less neurons in the region of the brain that controls food intake, according to an article published today in the journal, Brain Research.
The study by a team of researchers at Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (LA BioMed) suggests that overeating is programmed at the level of stem cells before birth when the mother has poor or inadequate ...