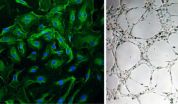
(Press-News.org) Tampa, Fla. (March 10, 2011) – When prostate cancer stem cells (CSCs) were enclosed in self-assembling nanomaterials made of peptides (SAP), the SAP stopped cancer stem cell colony formation and also stopped the division of cancer cells in laboratory cultures (in vitro). According to the international team of researchers who built and tested the nano-sized traps and published their results in a recent issue of Cell Transplantation (20:1), which is freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/ , the cancer cells grew and multiplied after they were "liberated" from their SAP prisons.
In their article, the researchers suggested that CSCs may be the origin of prostate tumor metastasis, making them an "ideal target" for inhibiting disease metastasis. The group's previous work in building nanomaterials showed that by using SAPs they were able to control the proliferation, elongation and maturation of cells in vitro.
"In this study, we have shown that prostate CSCs can be placed into stasis for an extended period of time without causing them to differentiate," said study corresponding author Dr. Rutledge Ellis-Behnke of the Heidelberg University-based Nanomedicine Translational Think Tank. "If cells are prevented from migrating away from the treatment, they could be subjected to additional targeting."
For the researchers, the isolation of cancer cells with stem-like characteristics "provides solid evidence" that CSCs may exist within the tumor. Additionally, CSCs may account for some treatment failures when treatments are unable to successfully target cancer stem cells, which may be resistant to chemotherapy drugs. Too, CSCs have been found to be more invasive than non-CSCs. The authors speculated that by injecting the material directly into the tumor, it may be possible to stop the spread of metastatic cells.
The research team also suggested that trapping CSCs in the nanomaterial would allow for loading of the SAP with chemotherapy agents, thus offering an increased effectiveness of a localized treatment when targeted cancer cells were unable to 'escape' their chemical enemies. This approach for treating metastatic hormone refractory prostate cancer (HRPC) - a cancer for which all current therapies fail - may offer hope as a successful treatment.
"The goal of cancer therapy is to reduce the ability of cancer cells to divide and migrate," said Dr. Ellis-Behnke. "Accordingly, we have shown that SAP can completely inhibit a prostate CSC from self-renewal while preserving its viability and stem cell properties."
Their study concluded that SAP may be "an effective nanomaterial for inhibiting cancer progression and metastasis."
"The ability to sequester cancer stem cells in SAP to prevent the spread of a prostate cancer is a big step toward finding effective treatments for cancer," Shinn-Zong Lin, professor of neurosurgery at China University Medical Hospital, Taiwan and chair of the Pan Pacific Symposium on Stem Cell Research where this work was first presented. "It will be of considerable interest to se how this technology develops."
###
Contact: Dr. Rutledge Ellis-Behnke, Nanomedicine Translational Think Tank, Medical Faculty Mannheim of the Ruprecht-Karls-University of Heidelberg, Theodor-Kutzer-Ufer 1-3 Mannheim 68167, Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 621 383 6078 Email: Rutledge@medma-uni.heidelberg.de or rutledg@mit.edu. Voicemail: +1 617 253 4556.
Citation : Ling, P. M. T.; Cheung, S. W. H.; Tay, D. K. C.; Ellis-Behnke, R. G. Using Self-Assembled Nanomaterials to Inhibit the Formation of Metastatic Cancer Stem Cell Colonies In Vitro. Cell Transplantation 20(1):127-131; 2011.
The editorial offices for CELL TRANSPLANTATION are at the Center of Excellence for Aging and Brain Repair, College of Medicine, the University of South Florida and the Diabetes Research Institute, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. Contact, David Eve, PhD. at celltransplantation@gmail.com or Camillo Ricordi, MD at ricordi@miami.edu
News release by Randolph Fillmore, Florida Science Communications, www.sciencescribe.net
Trapping prostate cancer cells to keep them from spreading provides hope
2011-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds usage of, recommendations for supplements common within various physician specialties
2011-03-11
WASHINGTON, D.C., March 10, 2011—For physicians within several medical specialties, including dermatology, cardiology and orthopedics, personal usage of and patient recommendations for dietary supplements are quite common¹, according to a study published in Nutrition Journal, a peer-reviewed, on-line journal that focuses on the field of human nutrition.
The 2008 "Life…supplemented" Healthcare Professionals (HCP) Impact Study found that 75 percent of dermatologists personally use dietary supplements and 66 percent recommend supplements to their patients; 57 percent of ...
Early male friendship as a precursor to substance abuse in girls
2011-03-11
Montreal, QC —March 10, 2011 —In childhood, boys and girls tend to form friendships almost exclusively with same-sex peers. Around early adolescence, they gradually begin to include other-sex friends in their network. A new study published in Journal of Research on Adolescence suggests that girls and boys experience this transition very differently. The findings show that girls tend to initiate the transition to a mixed-gender friendship network earlier than boys, and continue this transition at a faster pace during adolescence. As a result girls who experienced this transition ...
Scientists identify molecule that can increase blood flow in vascular disease
2011-03-11
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Circulating through the bloodstream of every human being is a rare and powerful type of cell, one that can actually create new blood vessels to bypass blockages that cause heart attacks and peripheral artery disease. Though everyone has these cells – called endothelial progenitor cells – they are often dysfunctional in people prone to vascular disease.
Now researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have discovered that a molecule – called Wnt1 – can improve the function of endothelial progenitor cells, increasing the blood flow ...
Referral to high-volume hospitals for operations fails to improve outcomes statewide
2011-03-11
Referring patients to hospitals that have the largest volume of surgical procedures does not necessarily lead to improved outcomes for the overall population, according to the results of a new study in the February issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
The findings of studies that suggest the higher the volume of specialty surgical procedures performed at any given hospital, the better that hospital's outcomes will be, has resulted in calls for volume-based referrals. Most notably leading that call has been the Leapfrog Group's Evidence-Based Hospital ...
Syracuse University research team shapes cell behavior research
2011-03-11
A team led by James Henderson, assistant professor of biomedical and chemical engineering in Syracuse University's L.C. Smith College of Engineering and Computer Science (LCS) and researcher in the Syracuse Biomaterials Institute, has used shape memory polymers to provide greater insight into how cells sense and respond to their physical environment.
Most cell biomechanics research has examined cell behavior on unchanging, flat surfaces. "Living cells are remarkably complex, dynamic and versatile systems, but the material substrates currently used to culture them are ...
A glove on your hand can change your mind
2011-03-11
Unconsciously, right-handers associate good with the right side of space and bad with the left. But this association can be rapidly changed, according to a study published online March 9, 2011 in Psychological Science, by Daniel Casasanto (Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics) and Evangelia Chrysikou (University of Pennsylvania). Even a few minutes of using the left hand more fluently than the right can reverse right-handers' judgments of good and bad, making them think that the left is the 'right side' of space. Conceptions of good and bad are rooted in people's ...
Lover's lane for birds found in Arctic
2011-03-11
NEW YORK (March 9, 2011) – A new study by the Wildlife Conservation Society reveals the critical importance of western Arctic Alaska's Teshekpuk Lake region to tens of thousands of birds that breed in the area during the brief, but productive arctic summers, and makes clearer the case for permanent protection of the area.
Results of the four-year study—the first to look at the full suite of bird species from around the world that descend on the Teshekpuk Lake region—showed that the region contains some of the highest nesting bird densities and nest productivity across ...
Alcohol has stronger impact on gastric bypass patients, study finds
2011-03-11
Patients who have had a gastric bypass operation take longer to process alcohol, potentially leading some of them to overindulge when drinking, according to the results of a new study in the February issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Previous studies have shown that gastric bypass patients often find it difficult adjusting to physical and psychological changes after the procedure. An increased risk of depression, alcoholism, and other substance abuse issues for this patient population led researchers to take a more in-depth look at how these patients ...
New model shows importance of feet, toes in body balance
2011-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers are using a new model to learn more about how toe strength can determine how far people can lean while keeping their balance.
The results could help in building robotic body parts that will closely imitate human movement, and might lead to a new generation of advanced prosthetics.
Hooshang Hemami, professor of electrical and computer engineering at Ohio State University built a complex computational model of the human foot to look at the role of the feet and toes in determining the body's movement and balance.
Many studies concerning ...
Erectile dysfunction drug improves exercise tolerance in young people with congenital heart disease
2011-03-11
Sildenafil, a drug used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension, has another possible use—helping children and young adults with congenital heart disease to better tolerate exercise. Sildenafil significantly improved measures of exercise performance during stress testing in patients with single-ventricle heart disease, according to researchers from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
This study was published online on March 7 in the journal Circulation. It is the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial to evaluate the ...