(Press-News.org) Stanford researchers have developed a battery that takes advantage of the difference in salinity between freshwater and seawater to produce electricity.
Anywhere freshwater enters the sea, such as river mouths or estuaries, could be potential sites for a power plant using such a battery, said Yi Cui, associate professor of materials science and engineering, who led the research team.
The theoretical limiting factor, he said, is the amount of freshwater available. "We actually have an infinite amount of ocean water; unfortunately we don't have an infinite amount of freshwater," he said.
As an indicator of the battery's potential for producing power, Cui's team calculated that if all the world's rivers were put to use, their batteries could supply about 2 terawatts of electricity annually – that's roughly 13 percent of the world's current energy consumption.
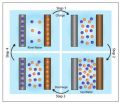
The battery itself is simple, consisting of two electrodes – one positive, one negative – immersed in a liquid containing electrically charged particles, or ions. In water, the ions are sodium and chlorine, the components of ordinary table salt.
Initially, the battery is filled with freshwater and a small electric current is applied to charge it up. The freshwater is then drained and replaced with seawater. Because seawater is salty, containing 60 to 100 times more ions than freshwater, it increases the electrical potential, or voltage, between the two electrodes. That makes it possible to reap far more electricity than the amount used to charge the battery.
"The voltage really depends on the concentration of the sodium and chlorine ions you have," Cui said. "If you charge at low voltage in freshwater, then discharge at high voltage in sea water, that means you gain energy. You get more energy than you put in."
Once the discharge is complete, the seawater is drained and replaced with freshwater and the cycle can begin again. "The key thing here is that you need to exchange the electrolyte, the liquid in the battery," Cui said. He is lead author of a study published in the journal Nano Letters earlier this month.
In their lab experiments, Cui's team used seawater they collected from the Pacific Ocean off the California coast and freshwater from Donner Lake, high in the Sierra Nevada. They achieved 74 percent efficiency in converting the potential energy in the battery to electrical current, but Cui thinks with simple modifications, the battery could be 85 percent efficient.
To enhance efficiency, the positive electrode of the battery is made from nanorods of manganese dioxide. That increases the surface area available for interaction with the sodium ions by roughly 100 times compared with other materials. The nanorods make it possible for the sodium ions to move in and out of the electrode with ease, speeding up the process.
Other researchers have used the salinity contrast between freshwater and seawater to produce electricity, but those processes typically require ions to move through a membrane to generate current. Cui said those membranes tend to be fragile, which is a drawback. Those methods also typically make use of only one type of ion, while his battery uses both the sodium and chlorine ions to generate power.
Cui's team had the potential environmental impact of their battery in mind when they designed it. They chose manganese dioxide for the positive electrode in part because it is environmentally benign.
The group knows that river mouths and estuaries, while logical sites for their power plants, are environmentally sensitive areas.
"You would want to pick a site some distance away, miles away, from any critical habitat," Cui said. "We don't need to disturb the whole system, we just need to route some of the river water through our system before it reaches the ocean. We are just borrowing and returning it," he said.
The process itself should have little environmental impact. The discharge water would be a mixture of fresh and seawater, released into an area where the two waters are already mixing, at the natural temperature.
One of Cui's concerns is finding a good material for the negative electrode. He used silver for the experiments, but silver is too expensive to be practical.
His group did an estimate for various regions and countries and determined that South America, with the Amazon River draining a large part of the continent, has the most potential. Africa also has an abundance of rivers, as do Canada, the United States and India.
But river water doesn't necessarily have to be the source of the freshwater, Cui said.
"The water for this method does not have to be extremely clean," he said. Storm runoff and gray water could potentially be useable.
A power plant operating with 50 cubic meters of freshwater per second could produce up to 100 megawatts of power, according to the team's calculations. That would be enough to provide electricity for about 100,000 households.
Cui said it is possible that even treated sewage water might work.
"I think we need to study using sewage water," he said. "If we can use sewage water, this will sell really well."
INFORMATION:
Stanford researchers use river water and salty ocean water to generate electricity
2011-03-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Soft Refurbishment at the Millennium Suite, Copthorne Hotel London Gatwick & Copthorne Hotel Effingham Gatwick
2011-03-30
The Millennium Suite, shared by both Copthorne Hotel London Gatwick and Copthorne Hotel Effingham Gatwick has recently undergone a soft refurbishment. Occupying approximately 1,126 square metres with a maximum capacity of 650 guests, the Millennium Suite is undoubtedly one of the largest meetings and event venues in the area and an ideal option if you're looking for hotels near Gatwick airport.
Featuring a new beige patterned carpet and curtains in a neutral shade of beige to lighten the venue's space, the modern Millennium Suite ensures that events can accommodate any ...
Older lesbians, gays have higher rates of chronic disease, mental distress, isolation
2011-03-30
Members of California's aging lesbian, gay and bisexual population are more likely to suffer from certain chronic conditions, even as they wrestle with the challenges of living alone in far higher numbers than the heterosexual population, according to new policy brief from the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research.
Half of all gay and bisexual adult men in California between the ages of 50 and 70 are living alone, compared with 13.4 percent of heterosexual men in the same age group. And although older California lesbians and bisexual women are more likely to live with ...
What choice do we have?
2011-03-30
Too much choice can be a bad thing—not just for the individual, but for society. Thinking about choices makes people less sympathetic to others and less likely to support policies that help people, according to a study published in an upcoming issue of Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In the U.S., important policy debates are often framed in terms of choice, such as whether people get to choose their own healthcare plan and a school for their children. "When Hurricane Katrina happened, people asked, why did those people choose ...
Stepchildren relate to stepparents based on perceived benefits, researchers find
2011-03-30
COLUMBIA, Mo. - More than 40 percent of Americans have at least one step relative, according to a recent Pew Center study. Relationships between stepchildren and stepparents can be complicated, especially for children. University of Missouri experts have found that stepchildren relate with stepparents based on the stepparents' treatment of them and their evaluations, or judgments, of the stepparents' behaviors.
"It takes both parties – children and adults – to build positive relationships in stepfamilies," said Larry Ganong, professor in the Department of Human Development ...
Innodep & Igloo Security Showcases 3D Monitoring Solution on a TYBIS VMS Platform at ISC West2011
2011-03-30
Innodep Inc., www.innodep.com, is a software development company focusing on IP Video Management Solution (VMS) & software H.264 Codec for security applications, under the brand name TYBIS and InnoCodec. Innodep today extended an open invitation to customers and interested parties to visit the Innodep booth #2051 at the ISC West2011 show in Las Vegas, NV, USA where industry professionals can see the latest IP VMS solution and H.264 Encoder and Decoder codecs for video surveillance. Innodep will be exhibiting together with Igloo Security, www.igloosec.com, a leader in integrated ...
Women's body image based more on others' opinions than their own weight
2011-03-30
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Women's appreciation of their bodies is only indirectly connected to their body mass index (BMI), a common health measure of weight relative to height, according to recent research.
The most powerful influence on women's appreciation of their bodies is how they believe important others view them, the study suggests. On the flip side, the more women are able to focus on the inner workings of their body – or how their bodies function and feel – rather than how they appear to others, the more they will appreciate their own bodies.
And the more a woman ...
The way to (kill) a bug's heart is through its stomach
2011-03-30
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A study at Michigan State University has revealed a potential new way for plants to fend off pests – starvation.
Gregg Howe, biochemistry and molecular biology professor, cites that this defense mechanism is just one example of a veritable evolutionary arms race between plants and herbivores.
Howe, in the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, offers insights to understanding the chemical weaponry of this war, which could lead to new approaches to protect crops.
All plants produce the enzyme threonine deaminase, ...
New Website Urges President Obama to End His War in Afghanistan
2011-03-30
A registered Republican that voted for President Barack Obama announces the launch of www.ObamaEndYourWar.com. The nonpartisan website is dedicated to ending the U.S. military involvement in Afghanistan. Americans are urged to drive with their headlights on during the day to illuminate a bright pathway for President Obama to find his way out of Afghanistan.
ObamaEndYourWar.com will serve to focus public attention on the 10 year old war. The call to action, driving with your headlights on during the day, gives Americans a simple method to express their opposition to ...
Annual Wild Art Weekend Offers Ultimate Eco Tourism Experience
2011-03-30
Travelers can immerse themselves in a blend of art and nature at the 10th Annual Mohican Wildlife Weekend, sponsored by Gander Mountain and held April 29-May 1, 2011. This unique celebration of wildlife habitat, heritage and natural history features six program sites throughout North Central Ohio's Ashland and Richland Counties. Each site will offer workshops and demonstrations designed to interest beginners and experienced naturalists alike. This fun and educational event-packed weekend is ideal for kids of all ages and perfect for the entire family.
Program sites include: ...
Annual sonograms are needed to verify correct IUD position, UT Southwestern obstetricians say
2011-03-30
DALLAS – March 29, 2011 – A retrospective study of women who became pregnant while using intrauterine devices shows that more than half of the IUDs were malpositioned.
Though the displacement may have occurred over time, a UT Southwestern Medical Center researcher suggests that routine sonograms after IUD placement would in the least confirm proper initial positioning.
"Gynecologists typically do a pelvic and speculum exam after placing an IUD, but there's no sonogram involved," said Dr. Elysia Moschos, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology and lead author ...