(Press-News.org) A pixel is worth a thousand words? Not exactly how the saying goes, but in this case, it holds true: scientists at Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry have pioneered a new chemical mapping method that provides unprecedented insight into materials at the nanoscale. Moving beyond traditional static imaging techniques, which provide a snapshot in time, these new maps will guide researchers in deciphering molecular chemistry and interactions at the nanoscale—critical for artificial photosynthesis, biofuels production and light-harvesting applications such as solar cells.
"This new technique allows us to capture very high-resolution images of nanomaterials with a huge amount of physical and chemical information at each pixel," says Alexander Weber-Bargioni, a postdoctoral scholar in the Imaging and Manipulation of Nanostructures Facility at the Foundry. "Usually when you take an image, you just get a picture of what this material looks like, but nothing more. With our method, we can now gain information about the functionality of a nanostructure with rich detail."
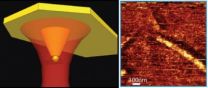
The Molecular Foundry is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science nanoscience center and national user facility. With the Foundry's state-of-the-art focused ion beam tool at their disposal, Weber-Bargioni and his team designed and fabricated a coaxial antenna capable of focusing light at the nanoscale, - a harnessing of light akin to wielding a sharp knife in a thunderstorm, Weber-Bargioni says.
Consisting of gold wrapped around a silicon nitride atomic force microscope tip, this coaxial antenna serves as an optical probe for structures with nanometer resolution for several hours at a time. What's more, unlike other scanning probe tips, it provides enough enhancement, or light intensity, to report the chemical fingerprint at each pixel while collecting an image (typically 256 x 256 pixels). This data is then used to generate multiple composition-related "maps," each with a wealth of chemical information at every pixel, at a resolution of just twenty nanometers. The maps provide information that is critical for examining nanomaterials, in which local surface chemistry and interfaces dominate behavior.
"Fabricating reproducible near-field optical microscopy probes has always been a challenge," says Frank Ogletree, acting Facility Director of the Imaging and Manipulation of Nanostructures Facility at the Foundry. "We now have a high-yield method to make engineered plasmonic probes for spectroscopy on a variety of surfaces."
To test out the capability of their new probe, the team examined carbon nanotubes, sheets of carbon atoms rolled tightly into tubes just a few nanometers in diameter. Carbon nanotubes are ideal for this type of interactive investigation as their unmatched electronic and structural properties are sensitive to localized chemical changes.
Users coming to the Molecular Foundry to seek information about light-harvesting materials or any dynamic system should benefit from this imaging system, Weber-Bargioni says.
Adds Jim Schuck, staff scientist in the Imaging and Manipulation of Nanostructures Facility at the Foundry, "We're very excited—this new nano-optics capability enables us to explore previously inaccessible properties within nanosystems. The work reflects a major strength of the Molecular Foundry, where collaboration between scientists with complementary expertise leads to real nanoscience breakthroughs."
INFORMATION:
A paper reporting this research titled, "Hyperspectral nanoscale imaging on dielectric substrates with coaxial optical antenna scan probes," appears in Nano Letters and is available to subscribers online. Co-authoring the paper with Weber-Bargioni, Ogletree and Schuck were Adam Schwartzberg, Matteo Cornaglia, Ariel Ismach, Jeffrey Urban, Yuanjie Pang, Reuven Gordon, Jeffrey Bokor, Miquel Salmeron, Paul Ashby and Stefano Cabrini.
This work at the Molecular Foundry was supported by DOE's Office of Science.
The Molecular Foundry is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers (NSRCs), national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale, supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit http://nano.energy.gov.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) national laboratory managed by the University of California for the DOE Office of Science. Berkeley Lab provides solutions to the world's most urgent scientific challenges including sustainable energy, climate change, human health, and a better understanding of matter and force in the universe. It is a world leader in improving our lives through team science, advanced computing, and innovative technology. Visit our Website at www.lbl.gov
Next-generation chemical mapping on the nanoscale
2011-03-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pelvic arterial embolization for postpartum hemorrhage saves lives, preserves uterus
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—Pelvic arterial embolization or PAE, a minimally invasive, life-saving therapy, is a safe and effective treatment for postpartum hemorrhage, say researchers at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting in Chicago, Ill.
"This large 225-patient study, in which 86 percent of the patients treated showed positive results illustrated that pelvic arterial embolization has the advantages of being a safe, rapid, economic and repeatable procedure—performed without general anesthesia," said Ji Hoon Shin, M.D., associate ...
R&D Solutions Team Selected by WeSave to Provide ProtectClub Service to its Members
2011-03-30
R&D Solutions Team, a leading national provider of service program warranty consulting services, has been selected by WeSave, Inc. to provide its ProtectClub service to their user community.
ProtectClub provides WeSave Members with the peace of mind of being able to protect all of their consumer electronics and appliance purchases from normal wear and tear damage beyond the expiration date of the original manufacturers warranty for one low monthly price.
"Do to the additional cost, most consumers unfortunately forgo the extended warranty when making their purchases," ...
No scalpel: Minimally invasive breakthrough for men’s enlarged prostates improves symptoms
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—A new interventional radiology treatment that blocks blood supply to men's enlarged prostate glands shows comparable clinical results to transurethral resection of the prostate (or TURP), considered the gold standard (or most common) treatment. However, this minimally invasive treatment—prostatic artery embolization—has none of the risks associated with TURP, such as sexual dysfunction, urinary incontinence, blood loss and retrograde ejaculation, noted researchers at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting ...
Fibroids cause women's lower urinary tract problems: uterine fibroid embolization helps
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—Uterine fibroid embolization—an interventional radiology treatment for the noncancerous yet very common growths that develop in the muscular wall of the uterus—improves a number of women's lower urinary tract problems that are specifically caused by those fibroids, confirm researchers at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting in Chicago, Ill.
"Uterine fibroid embolization or UFE continues to be an outstanding treatment choice for women with uterine fibroids, and—based on this study—this nonsurgical treatment ...
New Patient Education Brochure Available on The Hidden Dangers of Sleep Apnea and Snoring
2011-03-30
Myotronics, Inc. announces the immediate release of a new Sleep Apnea brochure for the dental office to educate patients on the signs and symptoms of sleep apnea as well as the dangers of not treating this condition.
Patients often aren't aware that their dental professional may be able to provide treatment for sleep apnea through new oral appliances. This brochure aims to educate the patient on this topic as well as provide insight on various treatment options provided by the medical and dental community.
While just about everyone knows someone who snores, few ...
Interventional radiologists provide hope in delaying growth, spread of breast cancer
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—The growth and spread of breast cancer tumors may be delayed with a promising treatment that combines two innovative strategies: blocking the enzyme needed to "energize" cancer cells and infusing a potent drug directly into the tumor, with minimum exposure to healthy tissues, indicate researchers at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting in Chicago, Ill.
"Once breast cancer metastases have been detected, current treatments (such as surgical resection or tumor removal) may be ineffective. We've found a way ...
Antioxidant formula prior to radiation exposure may prevent DNA injury
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—A unique formulation of antioxidants taken orally before imaging with ionizing radiation minimizes cell damage, noted researchers at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting in Chicago, Ill. In what the researchers say is the first clinical trial of its kind, as much as a 50 percent reduction in DNA injury was observed after administering the formula prior to CT scans.
"In our initial small study, we found that pre-administering to patients a proprietary antioxidant formulation resulted in a notable dose-dependent ...
New device uses submarine technology to diagnose stroke quickly
2011-03-30
CHICAGO, Ill. (March 29, 2011)—A medical device developed by retired U.S. Navy sonar experts, using submarine technology, is a new paradigm for the detection, diagnosis and monitoring of stroke, says a team of interventional radiologists at the Society of Interventional Radiology's 36th Annual Scientific Meeting in Chicago, Ill. Each type of stroke and brain trauma is detected, identified and located using a simple headset and portable laptop-based console. The device's portability and speed of initial diagnosis (under a couple of minutes) make it appropriate for many uses ...
Updating the Mary Poppins solution with a better bitter blocker
2011-03-30
Contact: Michael Bernstein
m_bernstein@acs.org
714-765-2012 (Meeting, March 27-31)
202-872-6042 (Before March 27)
Michael Woods
m_woods@acs.org
714-765-2012 (Meeting, March 27-31)
202-872-6293 (Before March 27)
American Chemical Society
Updating the Mary Poppins solution with a better bitter blocker
ANAHEIM, March 29, 2011 — With millions of adults and children avoiding nutritious foods because of the bitter taste, and gagging or vomiting when forced to take bitter liquid medicines, scientists today reported an advance toward a high-tech version ...
Household bleach can decontaminate food prep surfaces in ricin bioterrorist attack
2011-03-30
Contact: Michael Bernstein
m_bernstein@acs.org
714-765-2012 (Meeting, March 27-31)
202-872-6042 (Before March 27)
Michael Woods
m_woods@acs.org
714-765-2012 (Meeting, March 27-31)
202-872-6293 (Before March 27)
American Chemical Society
Household bleach can decontaminate food prep surfaces in ricin bioterrorist attack
ANAHEIM, March 29, 2011 — Help for a bioterrorist attack involving ricin, one of the most likely toxic agents, may be as close at hand as the laundry shelf, according to a report presented here today at the 241st National Meeting ...