(Press-News.org) An examination of medication adherence among children with newly diagnosed epilepsy found that nearly 60 percent showed persistent nonadherence during the first 6 months of therapy, and that lower socioeconomic status was associated with higher non-adherence, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Epilepsy, a disorder of recurrent unprovoked seizures, affects 325,000 children younger than 15 years in the United States. "Because of epilepsy's common occurrence, the narrow therapeutic and safety margins of antiepileptic medications, and the recognized complications of medication non-adherence in adults with epilepsy, identifying the rates, patterns, and predictors of non-adherence in children with epilepsy is imperative. The onset and evolution of antiepileptic drug nonadherence in children with newly diagnosed epilepsy remains unknown," according to background information in the article.
Avani C. Modi, Ph.D., of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, and colleagues conducted a study to identify and characterize medication adherence trajectories over the first 6 months of therapy for children with new-onset epilepsy using electronic monitors and to identify sociodemographic and epilepsy-specific predictors of adherence trajectories. The study included 124 children (2-12 years old) with final data collection through September 2009. Adherence was measured electronically with a system in which the cap of the medication bottle contained a microelectronic circuit to register the dates and times the bottle was opened and closed.
Of the children in the study, 58 percent demonstrated persistent nonadherence during the first 6 months of therapy. The researchers identified 5 different adherence patterns with group-based trajectory models. The 5 groups, based on severity and course of non-adherence, were severe early nonadherence (n= 16; 13 percent), severe delayed nonadherence (n = 8; 7 percent), moderate nonadherence (n= 16; 13 percent), mild nonadherence (n = 32; 26 percent), and near-perfect adherence (n = 52; 42 percent).
"The adherence pattern of most patients was established by the first month of therapy. Socioeconomic status was the sole predictor of adherence trajectory group status, with lower socioeconomic status associated with higher non-adherence," the authors write.
"Socioeconomic status was the only significant predictor of nonadherence and may help identify patients at highest risk. Given that nonadherence is frequent, may compromise the benefits of drug therapy, may complicate interpretation of clinical response, and can be addressed through evidence-based interventions, clinicians should consider routinely assessing adherence to antiepileptic drug therapy in all children with epilepsy."
"…the rate of nonadherence over the course of the first 6 months of therapy is concerning and suggests a need for intervention studies that aim to optimize adherence early in the course of therapy," the researchers conclude.
###
(JAMA. 2011;305[16]1669-1676. Available pre-embargo to the media at www.jamamedia.org)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
To contact Avani C. Modi, Ph.D., call Jim Feuer at 513-636-4656 or email Jim.Feuer@cchmc.org.
For more information, contact JAMA/Archives Media Relations at 312/464-JAMA (5262) or e-mail mediarelations@jama-archives.org.
Medication nonadherence patterns among children with epilepsy associated with socioeconomic status
2011-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low health literacy associated with higher rate of death among heart failure patients
2011-04-27
An examination of health literacy (such as understanding basic health information) among managed care patients with heart failure, a condition that requires self-management, found that nearly one in five have low health literacy, which was associated with a higher all-cause risk of death, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Health literacy is the degree to which individuals can obtain, process and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions, as defined by the Institute of Medicine. According to background ...
Increase in evidence-based treatments followed by decreased risk of death in heart attack patients
2011-04-27
In an analysis of data from a coronary care registry in Sweden, between 1996-2007 there was an increase in the prevalence of use of evidence-based invasive procedures and pharmacological therapies for treatment of a certain type of heart attack, and a decrease in the rate of death at 30 days and one year after a heart attack for these patients, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Although recent population-based studies indicate a reduction in incidence, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI; a certain pattern on an electrocardiogram following a heart ...
Activation of biomarker linked with improved survival among obese patients with colorectal cancer
2011-04-27
Among obese patients, activation of the protein biomarker CTNNB1 was associated with better colorectal cancer-specific survival and overall survival, whereas post-diagnosis physical activity was associated with better colorectal cancer-specific survival among patients negative for CTNNB1, according to a study in the April 27 issue of JAMA.
Activation of the WNT signaling pathway (a network of proteins known for their roles in cancer) and cadherin-associated protein beta-1 (CTNNB1; [beta-catenin]) plays a critical role in colorectal carcinogenesis. Accumulating evidence ...
Studies of mutated protein in Lou Gehrig’s disease reveal new paths for drug discovery
2011-04-27
PHILADELPHIA -- Several genes have been linked to ALS, with one of the most recent called FUS. Two new studies in PLoS Biology, one from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, and the other from colleagues at Brandeis University, both examined FUS biology in yeast and found that defects in RNA biology may be central to how FUS contributes to ALS, or Lou Gehrig's disease. These findings point to new targets for developing drugs.
Proteins aggregate to form insoluble clumps in the brain and spinal cord of ALS patients. In some instances of ALS, the clumping ...
Teen sleep study adds to evidence of a 'neural fingerprint'
2011-04-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Teens are rarely described as stable, so when something about their rapidly changing brains remains placidly unaltered, neuroscientists take notice. Such is the case in a new study of electroencephalography (EEG) readings gathered from dozens of teens while they slept. Despite the major neural overhaul underway during adolescence, most individuals maintained a unique and consistent pattern of underlying brain oscillations. The work lends a new level of support to the idea, already observed in adults, that people produce a kind of brainwave ...
Will minorities be left out of health care law provision?
2011-04-27
Hospitals and physician practices that form care-coordinating networks called "Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)," under provisions of the new health-care law could reap cost-savings and other benefits. However, experts at Johns Hopkins and the University of Pennsylvania warn that such networks could potentially be designed to exclude minorities and widen disparities in health care.
In a commentary appearing in the April 27 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, a Johns Hopkins physician says that as a result of new provisions in the Patient Protection ...
Dr Isabel Driggers, of Coastal Kids Dental & Braces, Was Selected as the South Carolina Delegate for the American Academy of Pediatric Dentist (AAPD) 2011 Congressional Lobby Day
2011-04-27
Coastal Kids Dental & Braces is proud to announce that Dr. Isabel Driggers, Owner and Founder of Coastal Kids Dental & Braces, was selected as the South Carolina representative by the AAPD to attend the 2011 Congressional Lobby Day. This is the 2nd year that Dr. Isabel has attending the AAPD Lobby Day as the SC representative.
As part of the AAPD Congressional Lobby Day, Dr. Isabel visited Washington, DC and met with the offices of Senators Lindsey Graham and Jim DeMint and Congressmen Tim Scott and Jim Clyburn to discuss current issues in Pediatric Dentistry ...
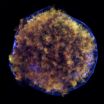
Chandra finds new evidence on origin of supernovas
2011-04-27
Astronomers may now know the cause of an historic supernova explosion that is an important type of object for investigating dark energy in the universe. The discovery, made using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, also provides strong evidence that a star can survive the explosive impact generated when a companion star goes supernova.
The new study examined the remnant of a supernova observed by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe in 1572. The object, dubbed Tycho for short, was formed by a Type Ia supernova, a category of stellar explosion useful in measuring astronomical ...
Canadians should demand commitments for pharmacare program, says CMAJ
2011-04-27
OTTAWA, ONTARIO, CANADA — Canada needs a national pharmacare program and federal leaders must commit adequate funding, states an editorial in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) http://www.cmaj.ca/cgi/doi/10.1503/cmaj.110643.
Unlike many countries in Europe and Australia and New Zealand, Canada lacks a national pharmacare program that provides consistent coverage across all regions of the country. Currently, drugs that are covered in some provinces may not be in others.
"The inevitable consequence is that some people are prevented from getting the drugs they ...
Men's and women's immune systems respond differently to PTSD
2011-04-27
Men and women had starkly different immune system responses to chronic post-traumatic stress disorder, with men showing no response and women showing a strong response, in two studies by researchers at the San Francisco VA Medical Center and the University of California, San Francisco.
While a robust immune response protects the body from foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses, an over-activated response causes inflammation, which can lead to such conditions as cardiovascular disease and arthritis.
In a study published in the March, 2011 issue of Brain, Behavior, ...