(Press-News.org) A year after the BP explosion and oil spill, those trying to find someone to blame are misguided, says psychological scientist E. Scott Geller, Alumni Distinguished professor at Virginia Tech, and author of a new paper published in Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. Geller has spent much of his 42-year career developing interventions to keep people safe, particularly helping companies develop a culture that promotes occupational safety.
There's almost never one person to blame for an injury; instead, companies need to develop a culture where individual workers feel empowered to point out problems and raise concerns about each other's safety. Media reports have suggested workers on the Deepwater Horizon oil rig were discouraged from reporting hazards, minor injuries, and other close calls. "The disaster would have been prevented if people were willing to speak up and report the hazards," Geller says. Many companies have policies that reward a supervisor for having a low number of injuries per work hour. But that discourages the reporting of injuries, and provides no incentive for analyzing close calls.
Indeed, Geller objects to the idea the disaster, or any crash, collision, or explosion, has a root cause. "Root cause? No. There are contributing factors," Geller says. For example, take someone who falls and breaks a bone at work because he climbed on a chair to reach something. In that case, you should listen to what excuses are given. "He might say, 'I didn't use the right ladder because it wasn't available, or I didn't go and get the right ladder because my supervisor is pushing me to get the job done fast," Geller says. Listening to workers can lead to a safer workplace—keeping the ladder closer to where it's needed, or emphasizing that safety is more important than speed.
Having a culture of safety also means using positive reinforcement rather than threats. "Psychologists know threats have only a temporary effect, if any," Geller says. And threats have undesirable side effects. People don't want to be around a supervisor who threatens them. Threats of enforcement influence some people to try and beat the system in order to assert individual freedom.
But the reflexive response to something dangerous is to make a law or policy against the related behavior. A few years ago, Geller and his students tried two ways of getting people to fasten their vehicle safety belts. They stood near the exit to parking lots at the university, and when they saw someone driving without a safety belt, they held up a sign: either one with the popular slogan "Click It or Ticket" or one that read "Please Buckle Up—I Care." The positive sign got significantly more drivers to buckle up. "Click It or Ticket" provoked some rude gestures.
The main message is that people should take safety personally, Geller says. Countless drivers have sent a text message while at the wheel and survived. But a video circulating on the internet tells the story of real people who were killed because of a texting driver. That makes the danger seem real. "We know from experience that emotions are motivating," Geller says. Making safety a personal issue makes people care more; seeing that video may make them think twice and realize the text message can wait.
In fact, Geller says, caring about safety means actively caring for the people around you. It's caring enough to speak up when your coworker has forgotten his or her hard hat, or starting a serious conversation about safety on the assembly line. "The BP disaster got many people suddenly taking safety personally, but we've got to take it personally before the disaster," he says.
###
For more information about this study, please contact: E. Scott Geller at esgeller@vt.edu.
Current Directions in Psychological Science publishes reviews by leading experts covering all of scientific psychology and its applications. These reviews allow readers to stay apprised of important developments across subfields beyond their areas of expertise and bodies of research they might not otherwise be aware of. For a copy of the article, "Psychological Science and Safety: Large-Scale Success at Preventing Occupational Injuries and Fatalities" and access to other Current Directions in Psychological Science research findings, please contact Divya Menon at 202-293-9300 or dmenon@psychologicalscience.org.
END
Nanoparticles will soon be used as tiny shuttles to deliver genes to cells and drugs to tumors in a more targeted way than was possible in the past.
But as the scientists prepare to use the nanoparticles in medicine, concerns have arisen about their potential toxicity.
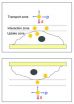
Studies of both the applications of nanoparticles and their toxicity rely on the ability of scientists to quantify the interaction between the nanoparticles and cells, particularly the uptake (ingestion) of nanoparticles by cells.
In the standard laboratory tests of the biological activity of nanoparticles, ...
The fishing industry usually discards fish livers, but a team of researchers from the University of Almeria (Spain) has confirmed that they are a good source of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial to health. Anchovies are one of the fish whose livers contain the highest levels of these substances.
Fish livers have hardly been used to date, with exceptions such as cod livers, which are used to produce the well-known medicinal oil. In general, fishermen tend to throw fish entrails away into the sea, and if they make it to processing plants they are one of ...
Dr. Michael Collins, Naval Research Laboratory scientist and bird watcher, has published an article titled "Putative audio recordings of the Ivory-billed Woodpecker (Campephilus principalis)" which appears in the March issue of the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. The audio recordings were captured in two videos of birds with characteristics consistent with the Ivory-billed Woodpecker. This footage was obtained near the Pearl River in Louisiana, where there is a history of unconfirmed reports of this species. During five years of fieldwork, Collins had ten ...
One of the most critical tasks that a dividing cell must accomplish is the successful delivery of a complete set of genetic information to each new daughter cell. Now, a study published by Cell Press in the April 29th issue of the journal Cell, provides fascinating new insight into the complex of proteins that orchestrates the proper segregation of human chromosomes during cell division.
During the process of mitosis, DNA and its associated packing proteins are arranged into structures called chromosomes that are duplicated and then segregated. Duplicated chromosomes ...
It's common knowledge that the perfect is the enemy of the good, but in the nanoscale world, perfection can act as the enemy of the best.
In the workaday world, engineers and scientists go to great lengths to make the devices we use as perfect as possible. When we flip on a light switch or turn the key on the car, we expect the lights to come on and the engine to start every time, with only rare exceptions. They have done so by using a top-down design process combined with the application of large amounts of energy to increase reliability by suppressing natural variability.
However, ...
The 25-story construction crane used since 1995 to investigate such things as how Pacific Northwest forests absorb carbon dioxide, obtain sufficient water and resist attacks by pests and diseases is being pruned back to just the tower.
The Wind River Canopy Crane, located in a 500-year-old forest near Stevenson in southwest Washington, has been operated cooperatively by the University of Washington, the Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Research Station and the Gifford Pinchot National Forest. The partners say the jib – the arm of the crane – is being removed because ...
A study of H1N1 and seasonal influenza vaccination in a sample of black and Hispanic children in Atlanta found a low rate of vaccine acceptance among parents and caregivers. Only 36 percent of parents and caregivers indicated they would immunize children against H1N1, and 22 percent indicated their children received the seasonal influenza vaccine in the previous three months. The majority of children in the sample (71 percent) were from households with less than $40,000 in annual income.
Researchers say this low level of vaccine coverage and acceptance highlights the ...
An international team of scientists, led by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, have developed a new method for discerning the functions of previously uncharacterized genes and placing them in interactive, functional networks that reveal how gene products interact to bring about cellular events.
The research is published in the April 29 issue of the journal Cell. It was led by principal investigators Karen Oegema, PhD, professor of cellular and molecular medicine and head of the Laboratory of Mitotic Mechanisms in the Ludwig Institute ...
The brain is apparently programmed from birth to develop the ability to determine sunrise and sunset, new research on circadian rhythms at the University of Chicago shows.
The research sheds new light on brain plasticity and may explain some basic human behaviors, according to Brian Prendergast, associate professor in psychology at the University of Chicago and co-author of a paper published April 27 in the journal PLoS One. The lead author is August Kampf-Lassin, an advanced graduate student at the University.
"This finding may show us why infants of many species eventually ...
The long-awaited TK Maxx store is nearly ready to open its doors at the Grand Junction Retail Park, Crewe. This new store is set to open on Thursday 28 April at 9am and will feature nearly 20,000 sq ft of famous label fashion, shoes and accessories for men and women plus homewares, kids and toys - all at up to 60% off the RRP.
The first lucky 500 customers through the doors at 9am will be treated to a GBP10 gift card to spend in the new store.
The TK Maxx concept is simple. TK Maxx buyers shop the world all year round working direct with designers and negotiating ...