(Press-News.org) (Boston) - When the human genome project produced a map of human genes, the number of genes in humans turned out to be relatively small, approximately the same number as in primitive nematode worms. The difference in complexity between human and primitive organisms results from the ways in which the functions of genes are elaborated, rather from just the number of genes. Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) researchers are showing how heparan sulfate, a carbohydrate that is expressed on the surface of all human cells, adjusts the functions of growth factor proteins. These findings currently appear on-line in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Each cell responds to signals in the form of growth factor proteins that bind to cell surfaces. "The heparan sulfate on each cell helps the growth factor proteins connect with a growth factor receptor that is necessary for the signaling to occur," explained Joseph Zaia, PhD, an associate professor of Biochemistry at BUSM. Cells can change the way they respond to growth factors by altering the structure of the heparan sulfate on their surfaces.
Under the direction of Zaia, researchers from BUSM's department of Biochemistry have produced a new picture of the structure of the heparan sulfate and how it interacts with growth factor proteins. These new results demonstrate that growth factors home into regions of the heparan sulfate chains known as non-reducing ends. "Such binding of growth factors to the non-reducing ends of heparan sulfate chains may be a general means whereby normal cell growth is maintained. Conversely, a breakdown in such signaling may contribute to abnormal cell growth," he added.
### END
Researchers show heparan sulfate adjusts functions of growth factor proteins
2011-05-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USGS economic analysis updated for the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska
2011-05-05
The U.S. Geological Survey assessment on the economic recoverability of undiscovered, conventional oil and gas resources within the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPRA) and adjacent state waters is now available.
This economic analysis is based on a 2010 USGS resource assessment (http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2010/3102/) that determined how much undiscovered, conventional oil and gas in the NPRA is technically recoverable. These reports provide updates from the USGS 2003 economic analysis (http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2003/of03-044/) and 2002 resource assessment (http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2002/fs045-02/) ...
Hitting target in cancer fight now easier with new nanoparticle platform, UCLA scientists say
2011-05-05
The ability to use nanoparticles to deliver payloads of cancer-fighting drugs to tumors in the body could herald a fundamental change in chemotherapy treatment. But scientists are still at a relatively early stage in the implementation of this technology.
Although developing nanoparticles that work as "magic bullets" — selectively targeting tumors while sparing normal, healthy tissues — is still the goal, the reality is that most of these nanocarriers are removed through the liver and spleen before ever reaching their intended target. And many of the encapsulated drugs ...
Estimated costs of environmental disease in children at $76.6 billion per year
2011-05-05
In three new studies published in the May issue of the journal Health Affairs, Mount Sinai School of Medicine researchers reveal the staggering economic impact of toxic chemicals and air pollutants in the environment, and propose new legislation to mandate testing of new chemicals and also those already on the market.
Leonardo Trasande, MD, Associate Professor of Preventive Medicine and Pediatrics at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, analyzed the costs of conditions – including lead poisoning, childhood cancer, asthma, autism, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ...
Newly discovered plant fossil reveals more than age
2011-05-05
Over 100 million years ago, the understory of late Mesozoic forests was dominated by a diverse group of plants of the class Equisetopsida. Today, only one genus from this group, Equisetum (also known as horsetail or scouring rush), exists—and it is a prime candidate for being the oldest extant genus of land plant.
There is some debate as to the evolutionary beginnings of the genus Equisetum. Molecular dating places the divergence of the 15 extant species of the genus around 65 million years ago (mya), yet the fossil record suggests that it occurred earlier than that, ...
New algorithm significantly improves imaging for full-body MRIs
2011-05-05
A new study reveals an improved algorithm that can dramatically improve how radiologists capture and interpret full-body MRIs, particularly in the abdominal region.
Motion artifacts in MRIs, such as patient movement, often appear as ghosting artifacts which may obscure clinical information says Dr. Candice Bookwalter, presenting author for the study. "Almost every acquisition during an MR abdominal exam requires a breath hold to limit motion. For example, a routine liver exam includes at least nine breath holds. Even with fast imaging techniques, these breath holds are ...
AllTernative Gym Transforms the Lives of Those With Special Needs
2011-05-05
AllTernative Gym is transforming lives with its state-of-the-art fitness and therapy programs developed specifically for those with special needs. Founded by Certified Fitness Trainer and Expert, Angie Gomez, AllTernative Gym provides Adeli Suit Therapy, Fitness Training and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.
"As a parent of a child with special needs, I truly understand what parents are looking for in a therapy center. And, I treat each child as if he were my own and each adult as if they were a family member," states Angie Gomez, founder of AllTernative Gym. Angie ...
Sonography complements physical exam in identifying juvenile inflammatory arthritis in children
2011-05-05
Juvenile Inflammatory Arthritis (JIA) is a potentially debilitating childhood disease. Early detection and treatment of active arthritis may avert long term joint damage and disability. Research has shown that sonography with power Doppler can facilitate making assessments in joint activity and sub-clinical disease, according to research being presented at the 2011 American Roentgen Ray Society's annual meeting.
The study, performed at Albert Einstein College of Medicine's Montefiore Medical Center, in Bronx, NY, compares sonography with power Doppler to physical examination ...
Ultrasound combined with pre-operative MRI is cost effective in evaluating rotator cuff tears
2011-05-05
While ultrasound is usually viewed as more cost effective, MRI is most often used to evaluate the rotator cuff. When performing a cost utility analysis, utilizing an ultrasound as the initial imaging test for rotator cuff tear, along with pre-operative MRI to identify alternative and concurrent diagnoses, can be a very effective hybrid imaging strategy, according to research being presented at the 2011 American Roentgen Ray Society's annual meeting.
The study, performed at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, NC and Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, IL, ...
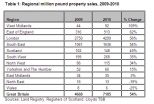
Million Pound Home Sales Rise at Fastest Rate Since 2006
2011-05-05
The number of million pound property sales in 2010 increased at the fastest rate for four years, according to research by Lloyds TSB. There were 7,185 million pound property sales in Great Britain in 2010: 54% higher than in 2009. This is the largest annual increase since 2006 (62%) and suggests a real resurgence at the very top end of the mortgage market. In total, there are now an estimated 184,0001 homes in Britain worth at least one million pounds.
Despite this significant increase, million pound property sales remain 13% below the levels they reached before the ...
Racial disparities still exist in colorectal cancer screening despite increased Medicare coverage
2011-05-05
PHILADELPHIA — Despite expanded Medicare coverage for colorectal cancer screening tests, lower rates still exist among blacks and Hispanics compared to other ethnic groups, according to research published in Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Researchers from the University of Texas School of Public Health used data from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER), a National Cancer Institute database, to determine the prevalence of colorectal cancer screenings among Medicare beneficiaries ...