(Press-News.org) Global fisheries, a vital source of food and revenue throughout the world, contribute between US$225-$240 billion per year to the worldwide economy, according to four new studies released today. Researchers also concluded that healthier fisheries could have prevented malnourishment in nearly 20 million people in poorer countries.
This first comprehensive, peer-reviewed estimate of the global economic contribution of fisheries was published online today in four papers as part of a special issue of the Journal of Bioeconomics.
This research, conducted by the University of British Columbia's Fisheries Centre, with support from the Pew Environment Group, quantifies the social and economic value of fish around the world and also calculates the loss of both revenue and dependable protein sources from years of overfishing.
"We know fish play an important ecological role in the marine environment, but these studies assess their 'out-of-the-water' value to people across the globe," says lead economist Associate Professor Rashid Sumaila at the University of British Columbia's Fisheries Centre. "Whether you are looking at fish as a financial resource or a source of protein, our research shows that the benefits of healthy, robust fisheries have enormous value far beyond the fishing dock."
Dr. Sumaila and his team of researchers also found that:
Overfishing reduces revenue. Annually, estimated global catch losses from overfishing totaled up to seven to 36 per cent of the actual tonnage landed in a year, resulting in a landed value loss of between US$6.4-36 billion each year.
Fishing has a multiplier effect. The fishing industry's economic impact on related businesses, such as boat building, international transport and bait suppliers, is roughly three times larger than the value of fish at first sale.
Fisheries generate incomes. Wild fisheries generate more than US$63 billion in annual household incomes around the world.
Non-industrial uses of the oceans are a net positive for economies and jobs. Recreational use of ocean ecosystems by sport divers, whale watchers and recreational fishermen contributes US$47 billion each year to national economies worldwide and generates nearly 1.1 million jobs.
One of the four papers focused on global fisheries subsidies, or financial incentives that countries offer to their fishing industries, which may contribute to depleted fish stocks. Large developed countries are spending twice the amount of tax-payer money on global fisheries subsidies that encourage overfishing than they are on subsidies that protect oceans.
"Many economies are paying doubly for continued overfishing of our oceans," says Sumaila. "First, tax-payer money is directly contributing to the decline of worldwide fisheries, and second, fishermen and undernourished people are hurting from a steadily declining resource. From a socioeconomic standpoint, subsidies that promote overfishing are doing far more harm than good."
INFORMATION:
For more information, including copies of the research papers, please contact Brian Lin at brian.lin@ubc.ca or Jo Knight at jknight@pewtrusts.org.
The University of British Columbia Fisheries Centre (www.fisheries.ubc.ca) undertakes research to restore fisheries, conserve aquatic life and rebuild ecosystems. To that end, it promotes multidisciplinary study of aquatic ecosystems and broad-based collaboration with maritime communities, government, NGOs and other partners. The UBC Fisheries Centre is recognized globally for its innovative and enterprising research, with its academics winning many accolades and awards.
The Pew Environment Group is the conservation arm of The Pew Charitable Trusts, a non-governmental organization that applies a rigorous, analytical approach to improve public policy, inform the public and stimulate civic life. Visit www.pewenvironment.org.
Global fisheries research finds promise and peril
While industry contributes $240B annually, overfishing takes toll on people and revenue
2010-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GOES-13 sees system 92L looking more like a tropical depression
2010-09-14
GOES-13 captured a look at System 92L this morning as it continues moving through the central Caribbean, and it's looking more and more like a tropical depression.
As the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite called GOES-13 satellite keeps relaying data to NOAA (who manages the satellite) and the NASA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., the images created by the NASA GOES Project reveal that System 92L appears to be taking on the appearance of a tropical depression. In the imagery captured today, Sept. 14 at 1340 UTC (9:40 ...
Neuralstem stem cells survive and differentiate into neurons in rats with stroke
2010-09-14
ROCKVILLE, Maryland, September 14, 2010 – Neuralstem, Inc. (NYSE Amex: CUR) announced that its spinal cord stem cells survived in rat brains affected by stroke and differentiated predominantly into neurons. The transplanted animals showed significant improvement in some motor skill and strength measurements. The study entitled, "Intracerebral Implantation of Adherent Human Neural Stem Cells To Reverse Motor Deficits in Chronic Stroke Rats," was presented earlier today by senior study author, Dr. Shinn-Zong Lin, M.D., Ph.D., at the Stem Cells USA & Regenerative Medicine ...
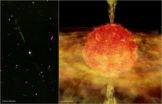
Enigmatic star devours companion; possibly pregnant with second-generation planets
2010-09-14
An astronomer may have caught a cannibalistic star in the act of devouring a companion and making a second generation of exoplanets from the resulting orbiting disk.
Using data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, Joel Kastner, professor at Rochester Institute of Technology, has found evidence that a variable star in the constellation of Pisces, BP Piscium, is not the young star it appears to be, but is more likely a one billion-year-old red giant that has gobbled up a star or planet in its vicinity.
The star's extreme properties have puzzled astronomers since Kastner ...
International Fertility Societies call for harmonization of cross-border reproductive care standards
2010-09-14
"The IFFS's 'Surveillance 2010' report, compiled by Professor Ian Cooke and published on 14 September 2010, illustrates this for over 100 countries. The survey highlights how widely assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are being used and how different cultures are regulating services in different ways. In most countries there is no state or insurance support, so these services are costly and frequently beyond the reach of many families. In some countries access to donor gametes is denied or supply is limited.
To address the safety of patients that seek treatment abroad, ...
September/October 2010 Annals of Family Medicine tip sheet
2010-09-14
Low Adherence with Regular Fecal Occult Blood Test Screening Among Insured Patients
In a large U.S. health plan, nearly one-half of patients who initiated biennial fecal occult blood test (FOBT) screening did not adhere to subsequent colorectal screening in the ensuing 2-year period, compromising the effectiveness of the screening endeavor which hinges on regular screening. Analyzing data on 11,110 patients enrolled in a Washington State health plan who completed an FOBT during the baseline period (2000-2001), researchers found 47 percent received no colorectal screening ...
Farm management choice can benefit fungi key to healthy ecosystems
2010-09-14
Farming practices have a significant impact on the diversity of beneficial microbial fungi known to play important roles in crop productivity, soil recovery and maintenance of healthy ecosystems, according to new research published today (14 September 2010) in the journal Environmental Microbiology. The conclusions could have important implications for the way humans manage the agricultural landscape and tackle food security issues.
The study was led by Dr Christopher van der Gast at the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH), UK and Dr Gary Bending from the University ...
Childhood cancer survivors show sustained benefit from common ADHD medication
2010-09-14
A medicine widely used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) also provides long-term relief from the attention and behavior changes that affect many childhood cancer survivors, according to a multicenter trial led by St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators.
Researchers reported that one year after starting the drug methylphenidate, young cancer survivors scored better on tests of sustained attention and other measures of attention, social skills and behavior than did a similar group of unmedicated survivors. While taking methylphenidate, ...
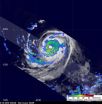
Igor now a Category 4 hurricane with icy cloud tops and heavy rainfall
2010-09-14
NASA Satellites have noticed two distinct features in Igor that both indicate how powerful he has become, icy cold, high cloud tops and very heavy rainfall. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites have provided that insight to forecasters who are predicting Igor's next move as a powerful Category 4 Hurricane.
Last week, Igor was a tropical storm who faded into a tropical depression. The National Hurricane Center had forecast that over the weekend Igor would approach more favorable conditions (low wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures) causing it to strengthen into a hurricane ...
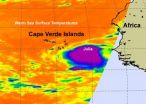
NASA sees Tropical Storm Julia born with strong thunderstorms and heavy rainfall
2010-09-14
Tropical Depression 12 was born in the far eastern Atlantic Ocean yesterday, Sept. 12 and two NASA satellites saw factors that indicated she would later strengthen into Tropical Storm Julia. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed strong convection in its center that powered the storm into tropical storm status by 11 p.m. EDT. NASA's TRMM satellite indicated very heavy rainfall from that strong area of convection.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite gives scientists and meteorologists clues about how a tropical ...
Targeted agent shows promise for chronic lymphoid leukemia
2010-09-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center-Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC-James) have identified an experimental agent that targets chronic lymphocytic leukemia and perhaps other proliferative disorders of lymphocytes.
Their study shows that the small-molecule inhibitor CAL-101 directly promotes cell death by apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells and disrupts several external survival pathways needed for CLL cell viability and proliferation.
The agent blocks ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Global fisheries research finds promise and perilWhile industry contributes $240B annually, overfishing takes toll on people and revenue