(Press-News.org) Did I turn off the stove, or did I just imagine it? Memory isn't always reliable. Psychological scientists have discovered all sorts of ways that false memories get created, and now there's another one for the list: watching someone else do an action can make you think you did it yourself.
The team of psychological scientists who found the new way to create false memories weren't setting out to make a big discovery. They were trying to learn more about imagination, another way that false memories get created. But then in an experiment, they found that people who had watched a video of someone else doing a simple action—shaking a bottle or shuffling a deck of cards, for example—often remembered doing the action themselves two weeks later.
"We were stunned," says Gerald Echterhoff, of Jacobs University Bremen. He cowrote the study with Isabel Lindner of the University of Cologne, Patrick S.R. Davidson of the University of Ottawa, and Matthias Brand of the University of Duisburg-Essen. They changed course to examine this phenomenon more closely with a series of experiments.
In each experiment, participants performed several simple actions. Then they watched videos of someone else doing simple actions—some of which they had already performed, and some of which they had not. Two weeks later, they were asked which actions they had done. They were much more likely to falsely remember doing an action if they had watched someone else do it. This happened even when participants were told about the effect and warned that it could happen to them. The results are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Echterhoff says you shouldn't worry that this happens all the time—but it's worth remembering that your memory isn't always reliable. "It's good to have an informed doubt or informed skepticism about your memory performance, so you don't just easily trust whatever comes to your mind as true and for granted."
He thinks the mechanism may have something to do with internal simulation of what other people are doing while we are observing them. Intriguingly, if simulation was the mechanism, it would occur spontaneously and without our awareness. To speculate further, this simulation could involve brain structures like the 'mirror neuron system,' which seems to be involved both in performing actions ourselves as well as in observing other people's actions. Simulation is good when it helps you predict someone's next action, or to learn how to do things, but this could be an unfortunate side effect.
###
For more information about this study, please contact Gerald Echterhoff at g.echterhoff@uni-muenster.de.
The APS journal Psychological Science is the highest ranked empirical journal in psychology. For a copy of the article "Observation Inflation: Your Actions Become Mine" and access to other Psychological Science research findings, please contact Keri Chiodo at 202-293-9300 or kchiodo@psychologicalscience.org.
False memories of self-performance result from watching others' actions
2010-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
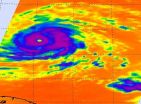
Stunning NASA infrared imagery of Hurricane Igor reveals a 170 degree temperature difference
2010-09-15
NASA satellites provide infrared images to forecasters that show temperature, and today's imagery of powerful Hurricane Igor showed the storm's perfect form and the warm ocean waters around it that are keeping it fueled. NASA's infrared data also revealed a huge difference of 170 degrees between the cold cloud tops in Hurricane Igor and the warm sea surface temperatures powering it below.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Igor on Sept. 14 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT) the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured icy cold cloud top temperatures in ...
Do children understand irony?
2010-09-15
New research findings from the Université de Montréal reveals that children as young as four are able to understand and use irony. This study, published recently in the British Journal of Developmental Psychology, may impact the way parents communicate with their family.
"Previous studies concluded that irony wasn't understood before the age of eight or ten," says Stephanie Alexander, a postdoctoral student at the Université de Montréal's Department of Social and Preventive Medicine and senior author of the study. "However, these studies were mostly done in a laboratory ...
ORNL scientists reveal battery behavior at the nanoscale
2010-09-15
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Sept. 14, 2010 -- As industries and consumers increasingly seek improved battery power sources, cutting-edge microscopy performed at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory is providing an unprecedented perspective on how lithium-ion batteries function.
A research team led by ORNL's Nina Balke, Stephen Jesse and Sergei Kalinin has developed a new type of scanning probe microscopy called electrochemical strain microscopy (ESM) to examine the movement of lithium ions through a battery's cathode material. The research, "Nanoscale mapping ...
Legal analysis: The health insurance mandate is constitutional
2010-09-15
(Garrison, NY) The most politically charged feature of the health reform law is the mandate that legal residents have health insurance. Within weeks of the law's passage, twenty states had filed lawsuits charging that the mandate is unconstitutional because it gives the federal government more power than it actually has. The state lawsuits are widely expected to reach the Supreme Court next year. Legal scholar Lawrence O. Gostin writes that the health insurance mandate rests on firm legal ground.
Under the mandate, which goes into effect in 2014, the federal government ...
Study identifies students at risk for difficulties in medical school
2010-09-15
Students who enter medical school with high debt levels, low scores on the Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT) or who are non-white are more likely to face difficulties that may prevent graduation or hinder acceptance into a residency program if they do graduate, according to a nationwide study of students enrolled in MD programs.
The research, from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is reported Sept. 15 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The study of more than 84,000 students who entered U.S. medical schools from 1994-1999 showed ...
Report shows federal poverty guidelines leave state's seniors destitute
2010-09-15
Data and research on what it really takes for seniors to make ends meet in each of California's 58 counties will be released today at the state Capitol in Sacramento.
The release is the latest update of the Elder Economic Security Standard Index (Elder Index), a tool that measures the actual costs of basic necessities for older adults. The Elder Index is quickly replacing federal poverty level (FPL) guidelines as a new standard for evaluating and meeting the needs of seniors across California.
"This year, the federal government officially acknowledged it's time ...
Blood test accurately predicts death from prostate cancer up to 25 years in advance
2010-09-15
NEW YORK, September 14, 2010 – A blood test at the age of 60 can accurately predict the risk that a man will die from prostate cancer within the next 25 years, according to researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, in New York, and Lund University, in Sweden. The findings, published today online in the British Medical Journal, could have important implications for determining which men should be screened after the age of 60 and which may not benefit substantially from continued prostate cancer screening.
The study analyzed blood samples from 1,167 men born ...
Adapting to darkness: How behavioral and genetic changes helped cavefish survive extreme environment
2010-09-15
VIDEO:
A cavefish (left) and surface fish (right) swimming in assay chambers in the presence of a 50 Hz vibrating rod. When the rod is vibrated, the cavefish, but not surface...
Click here for more information.
University of Maryland biologists have identified how changes in both behavior and genetics led to the evolution of the Mexican blind cavefish (Astyanax mexicanus) from its sighted, surface-dwelling ancestor. In research published in the August 12, 2010 online edition ...
Informatics = essential MD competency
2010-09-15
In an article published in the Sept. 15 edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association, (JAMA), author Edward H. Shortliffe, MD, PhD, points out that although information underlies all clinical work, and despite the growing role that information management and access play in healthcare delivery and clinical support, there is a dearth of informatics competency being developed in America's future corps of physicians. Formalized education in the application of informatics and the use and methodologies of health information technology and exchange, Dr. Shortliffe ...
For 4-year-olds, interactions with teacher key to gains
2010-09-15
Pre-kindergartners who spend much of their classroom day engaged in so-called free-choice play with little input from teachers make smaller gains in early language and math skills than children who receive input from teachers in a range of different activity settings. Low-income children benefit particularly when a higher proportion of their time is spent in individual instruction settings.
Those are the findings of a new study that appears in the September/October 2010 issue of Child Development.
"If early childhood education is to level the playing field by stimulating ...