(Press-News.org) FRANKFURT. Salmonella is widely prevalent in the animal kingdom. The reason we do not suffer from severe intestinal infections very often is due to our body's defence system, which manages to digest invading bacteria. This is why, generally speaking, a healthy human being will only fall ill if he consumes more than 100.000 salmonella bacteria via a contaminated food source, such as eggs or meat. An international team of researchers, led by Prof. Ivan Dikic from the Goethe University in Frankfurt has now found out how body cells recognise salmonella and render it harmless. Understanding this process at a molecular level is crucial in identifying new targets for treatment. Tropical and sub-tropical countries in particular, where various sub-species of salmonella are common, are experiencing a rapid increase in resistance to antibiotics, with children at greatest risk.
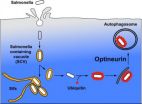
Salmonella infection begins with bacteria entering the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa. To prevent them multiplying there, special cell organelles, called autophagosomes are activated. These encircle the invaders and then become absorbed in other organelles – lysosomes – that contain certain special digestive enzymes, which break down the bacteria into their constituent parts. But how exactly do the autophagosomes recognise salmonella? Prof. Ivan Dikic and his research group at the Biochemistry Institute II have now shed light on this mechanism.
As reported in a current article in the scientific journal "Science", the salmonella are marked as 'waste material' by the molecule ubiquitin. In order for the autophagosomes to become active, the marked bacteria have to bind to another molecule – LC3 – on the autophagosomal membrane. Here, the protein optineurin plays a key role, linking the marked Salmonella to the autophagosmal LC3, thereby setting off a process of selective autophagy. But optineurin becomes active as a link only after being chemically modified by an enzyme, (in this case it is phosphorylated by the protein kinase TBK1). "We suspect that phosphorylation acts as a regulated switch to trigger selective autophagy of bacteria but might also prove significant in other cargoes like protein aggregates or damaged mitochondria" explains Prof. Ivan Dikic, underlining the importance of these findings. It is thought that impaired autophagy processes may be implicated in, among other things, the development of cancer as well as neurodegenerative diseases.
In the area of infectious diseases, these findings are particularly relevant in view of the fact that gastrointestinal disease caused by Salmonella enterica has rapidly increased since the mid-1980s. In Germany, approx. 30,000 cases were reported to the health authorities in 1985, but by 2005 the figure has risen to 52,000. Worldwide, 94 million people fall ill each year with acute gastroenteritis, and 155,000 of these die. Typhoid, a disease also caused by Salmonella, affects 16 million people annually and mortality rates reach 200,000, with children in particular falling victim to the disease. Bacteria are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics so that the potential for treating disease is limited. Chloramphenicol, a formerly popular broad-spectrum antibiotic, is now ineffective, and even Fluoroquinolones, currently a commonly prescribed antibiotic, is proving inadequate in fighting bacteria. As co-author Prof. Dirk Bumann from the Biozentrum at Basel University puts it: "There is a pressing need to find new forms of treatment for infectious diseases. A better understanding of how the body's own defence mechanism makes use of autophagy will certainly help."
INFORMATION:
Publication:
Philipp Wild et al: Phosphorylation of the Autophagy Receptor Optineurin restricts Salmonella growth, Science 26th May 2011 advanced online publication (Science DOI: 10.1126/science.1205405)
Intestinal cell defense mechanism against bacteria
Molecular mechanism of selected autophagy elucidated
2011-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dr. David Sloss, Named Medical Director at Casa Grande Regional Medical Center
2011-05-29
Dr. Sloss received his Bachelor of Science in Biomedical Engineering at The Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. He earned his medical degree from the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center School of Medicine in Denver, Colorado. Dr. Sloss completed his residency at Washington University, Barnes-Jewish Hospital, in St. Louis, Missouri. He was a staff physician at the Emergency Department at SSM St. Joseph Hospital West in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Sloss has training in incident response to terrorist bombings and prevention and response to suicide bombing ...
When cancer runs in the family
2011-05-29
5% to 10% of all breast cancers are monogenic in origin. In other words, there is a mutation of the genes BRCA1, BRCA2 or other high-risk genes. In this edition of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 108(19): 323 30), Alfons Meindl of the Klinikum rechts der Isar (Munich) and coauthors report on new insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer and newly-discovered risk genes.
Meindl et al. evaluated data including those derived from the work of the German Consortium for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer. ...
Dogs in motion
2011-05-29
The reason being: "So far scientific studies were limited mostly to the movement of sick animals or to single aspects of locomotion", says Fischer, Professor of Systematic Zoology and Evolutionary Biology. To change this, Professor Fischer and his team started a comprehensive study about the locomotion of healthy dogs in 2006 and have now presented the results.
With enormous technical effort the scientists measured, documented and compared the motion sequences of 327 dogs from 32 different breeds. The dogs were filmed by two high speed cameras in different gaits from ...
Investec: Attractive Closed End Funds Discounts Gives Rise To Latest Lending Proposition.
2011-05-29
Investec offers specialised lending for deals in the closed-end funds market
- Investec believes many closed-end funds are trading at attractive discounts to their net asset values (NAVs)
- Consolidation is expected in the closed-end fund space
- Investec's lending is expected to be concentrated around funds focusing on alternative asset classes
Investec Specialist Private Bank ('Investec') has launched a new lending proposition for fund managers looking for 'event driven financing' focused on the closed-end fund space. This includes financing mergers; the acquisition ...
Christian Brothers Automotive Corporation Honored with 2011 Houston Better Business Bureau Award
2011-05-29
Christian Brothers Automotive Corporation, a national automotive repair chain known for its upscale home-charm decor and ethical business practices, has been honored with the Houston Better Business Bureau's (BBB) coveted Excellence Winner of Distinction award. This marks the sixth time, and second-consecutive year, the corporate office has been recognized with this award.
The BBB Excellence Winner of Distinction award recognizes companies that demonstrate a consistent commitment to ethics, overall excellence and quality in the workplace.
"Christian Brothers ...
What fish is on your plate?
2011-05-29
Low-cost catfish fillets sold as expensive sole fillets or cod caught in the North Sea but declared as originating from the Baltic Sea are both examples of types of fraud in the fisheries sector. A European Commission report published today shows how molecular technologies - based on genetics, genomics, chemistry and forensics - can provide clear answers to questions such as "what species does this fish product come from….where was this fish caught….is it wild or farmed?". The report by the Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC), is called "Deterring illegal activities ...
MDC researchers discover key molecule for stem cell pluripotency
2011-05-29
Researchers of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch have discovered what enables embryonic stem cells to differentiate into diverse cell types and thus to be pluripotent. This pluripotency depends on a specific molecule – E-cadherin – hitherto primarily known for its role in mediating cell-cell adhesion as a kind of "intracellular glue". If E-cadherin is absent, the stem cells lose their pluripotency. The molecule also plays a crucial role in the reprogramming of somatic cells (body cells) into pluripotent stem cells (EMBO Reports, advance online ...
Federal Mortgage Relief Program Plans To Target 400,000 Borrowers Facing Foreclosure
2011-05-29
Most homeowners are waiting in anticipation for the commencement of the Federal mortgage relief program ( http://obamamortgagereliefplanqualifications.com/ ) this fall. The federal mortgage relief program offers hope to homeownersâEUR country wife with the promise of bailing borrowers out by lowering the monthly mortgage repayments.
With the commencement of the Federal mortgage relief program borrowers will be able to either get their interest rates reduced or part of their principal debt written off. However, it is important to note that this program will not to salvage ...
Fraunhofer MEVIS: New procedure to make brain surgery safer
2011-05-29
Brain interventions must be planned so that the neurosurgeon can access and remove the tumor without causing unnecessary damage. Before the brain tumor can be removed, crucial questions must be answered. Where do the functional areas of the cortex (gray matter) of the patient lie? What are the paths of the nerve fiber tracts that connect them? Answering these questions is important because the functional areas of the brain are interconnected via nerve pathways, also known as nerve fiber tracts. These nerve tracts must be protected as much as possible; otherwise, permanent ...
Outside Line wins Website Campaign of the year at International Food and Beverage Creative Excellence Awards
2011-05-29
Digital creative agency Outside Line has been recognised at the International Food and Beverage Creative Excellence Awards for the third year running following the outstanding success of its online marketing campaign for Cravendale.
The multi award-winning agency scooped the prize for the Best Website Campaign of 2011 following of its popular Make The Tea community site, which judges praised for its blend of innovation, eye-catching design and effective communication. Collecting the prestigious award at a packed London ceremony earlier this week, the social media and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
[Press-News.org] Intestinal cell defense mechanism against bacteriaMolecular mechanism of selected autophagy elucidated