(Press-News.org) COLLEGE PARK, MD (June 22, 2011)—Water and ice may not be among the first things that come to mind when you think about single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), but a Japan-based research team hoping to get a clearer understanding of the phase behavior of confined water in the cylindrical pores of carbon nanotubes zeroed in on confined water's properties and made some surprising discoveries.
The team, from Tokyo Metropolitan University, Nagoya University, Japan Science and Technology Agency, and National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, describes their findings in the American Institute of Physics' Journal of Chemical Physics.
Although carbon nanotubes consist of hydrophobic (water repelling) graphene sheets, experimental studies on SWCNTs show that water can indeed be confined in open-ended carbon nanotubes.
This discovery gives us a deeper understanding of the properties of nanoconfined water within the pores of SWCNTs, which is a key to the future of nanoscience. It's anticipated that nanoconfined water within carbon nanotubes can open the door to the development of a variety of nifty new nanothings—nanofiltration systems, molecular nanovalves, molecular water pumps, nanoscale power cells, and even nanoscale ferroelectric devices.
"When materials are confined at the atomic scale they exhibit unusual properties not otherwise observed, due to the so-called 'nanoconfinement effect.' In geology, for example, nanoconfined water provides the driving force for frost heaves in soil, and also for the swelling of clay minerals," explains Yutaka Maniwa, a professor in the Department of Physics at Tokyo Metropolitan University. "We experimentally studied this type of effect for water using SWCNTs."
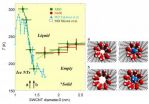
Water within SWCNTs in the range of 1.68 to 2.40 nanometers undergoes a wet-dry type of transition when temperature is decreased. And the team discovered that when SWCNTs are extremely narrow, the water inside forms tubule ices that are quite different from any bulk ices known so far. Strikingly, their melting point rises as the SWCNT diameter decreases—contrary to that of bulk water inside a large-diameter capillary. In fact, tubule ice occurred even at room temperature inside SWCNTs.
"We extended our studies to the larger diameter SWCNTs up to 2.40 nanometers and successfully proposed a global phase behavior of water," says Maniwa. "This phase diagram (See Figure) covers a crossover from microscopic to macroscopic regions. In the macroscopic region, a novel wet-dry transition was newly explored at low temperature."
Results such as these contribute to a greater understanding of fundamental science because nanoconfined water exists and plays a vital role everywhere on Earth—including our bodies. "Understanding the nanoconfined effect on the properties of materials is also crucial to develop new devices, such as proton-conducting membranes and nanofiltration," Maniwa notes.
Next up, the team plans to investigate the physical properties of confined water discovered so far inside SWCNTs (such as dielectricity and proton conduction). They will pursue this to obtain a better understanding of the molecular structure and transport properties in biological systems.
INFORMATION:
About AIP
The American Institute of Physics is an organization of 10 physical science societies, representing more than 135,000 scientists, engineers, and educators and is one of the world's largest publishers of scientific information in physics. AIP pursues innovation in electronic publishing of scholarly journals and offers full-solution publishing services for its Member Societies. AIP publishes 13 journals; two magazines, including its flagship publication Physics Today; and the AIP Conference Proceedings series.
About JCP
The Journal of Chemical Physics publishes concise and definitive reports of significant research in methods and applications of chemical physics. Innovative research in traditional areas of chemical physics such as spectroscopy, kinetics, statistical mechanics, and quantum mechanics continue to be areas of interest to readers of JCP. In addition, newer areas such as polymers, materials, surfaces/interfaces, information theory, and systems of biological relevance are of increasing importance. Routine applications of chemical physics techniques may not be appropriate for JCP. Content is published online daily, collected into four monthly online and printed issues (48 issues per year); the journal is published by the American Institute of Physics.
Researchers clarify properties of 'confined' water within single-walled carbon nanotube pores
2011-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sekisui Chemical Company and Avantium Chemicals Announce Collaboration Agreement
2011-06-23
This is a joint press release of Sekisui Chemical Company and Avantium Chemicals.
Sekisui Chemical Company and Avantium are proud to announce that today they have entered into a collaboration agreement. In this partnership Avantium will be contributing with its proprietary high-throughput technologies and experts to the development and improvement of catalysts and process optimization of Sekisui Chemicals product portfolio.
This agreement allows Sekisui Chemical Company to access Avantium's high-throughput methodologies and experts as part of the suite of tools used ...
Pitt study: Gay, lesbian, bisexual youth bullied, abused more often than peers
2011-06-23
PITTSBURGH, June 22 – Young people who identify themselves as gay, lesbian or bisexual, experience same-sex attractions or engage in same-sex sexual behaviors are more likely to experience sexual abuse, parental physical abuse and bullying from peers than other youth, according to a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health study.
In addition, these adolescents – identified as "sexual minority youth" in the study – are more likely to miss school due to fear. The American Public Health Association recently published the findings online; the study will ...
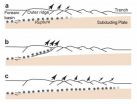
Stiff sediments made 2004 Sumatra earthquake deadliest in history
2011-06-23
An international team of geoscientists has discovered an unusual geological formation that helps explain how an undersea earthquake off the coast of Sumatra in December 2004 spawned the deadliest tsunami in recorded history.
Instead of the usual weak, loose sediments typically found above the type of geologic fault that caused the earthquake, the team found a thick plateau of hard, compacted sediments. Once the fault snapped, the rupture was able to spread from tens of kilometers below the seafloor to just a few kilometers below the seafloor, much farther than weak sediments ...
Experience a Piece of History That Will Never be Repeated: Two Celebrity Magic Shows in Commemoration of Legendary Magician and Film Star John Calvert's 100th Birthday!
2011-06-23
The shows will feature some of magic's biggest stars, including Liu Chen (Asia's number one magic superstar), Jeff McBride (Las Vegas star seen on Criss Angel's "Mindfreak"), David & Dania (award-winning quick-change act seen on "America's Got Talent"), and many more! Each show is only $45. For an additional $80 patrons can attend lectures and visit the dealer room, commingling with some of the world's greatest magicians and learning their most mystifying techniques!
The guest of honor, John Calvert, was the first magician to perform on Broadway ...
ISL - Building a New Future on Agricola St.
2011-06-23
ISL web marketing and development is pleased to announce it has relocated its head office to 5777 West St. The newly constructed 3 1/2-story building on the corner of West and Agricola St. will be home to the company and its 30 employees.
The move comes during the company's 15th year in operation. From the early stages of the Internet, ISL has been providing web based marketing solutions for its clients. The company has grown across the country, with offices in Halifax and Vancouver and is now the largest Internet marketing firm in Atlantic Canada.
Over the last ...
NASA and NOAA satellite video shows Tropical Storm Beatriz fizzle in 6 hours
2011-06-23
VIDEO:
GOES-11 satellite imagery from June 20 at 13:00 UTC (9 a.m. EDT/6 a.m. PDT) until June 22 at 1315 UTC (9:15 a.m. EDT) as Beatriz battered southwestern Mexico's coastline and...
Click here for more information.
Satellite data from NASA and NOAA showed that Tropical Storm Beatriz went from a strong tropical storm to a remnant low pressure area in six short hours after running into Mexico's western mountains. An animation of imagery from the GOES-11 satellite showed ...
Hubble sees Pandora's Cluster
2011-06-23
A team of scientists studying the galaxy cluster Abell 2744, nicknamed Pandora's Cluster, have pieced together the cluster's complex and violent history using telescopes in space and on the ground, including the Hubble Space Telescope, the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope, the Japanese Subaru telescope, and NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
The giant galaxy cluster appears to be the result of a simultaneous pile-up of at least four separate, smaller galaxy clusters. The crash took place over a span of 350 million years.
The galaxies in the cluster ...
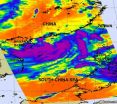
NASA sees heavy rainfall on southern side of Tropical Depression Haima as it nears Hong Kong
2011-06-23
Tropical Depression Haima, formerly known as 06W continues moving toward Hong Kong and NASA infrared satellite imagery shows strong rain-making thunderstorms in the southern quadrant of the storm. Rainfall is something that a rain-weary China doesn't need, so preparations are being made now.
Heavy rainfall is expected as Haima approaches in southern Taiwan, and also in southern areas of China's Fujian and Guangdong provinces, and Hainan Island. That heavy rainfall was spotted on an infrared image captured by NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on June ...
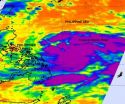
NASA satellite sees massive Tropical Storm Meari headed for Taiwan
2011-06-23
The AIRS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of the western North Pacific's seventh tropical depression become massive Tropical Storm Meari overnight. Meari is so large that it takes up almost the entire Philippine Sea and it's on track toward southeastern Taiwan.
Tropical Storm Meari's large area of cold thunderstorm cloud tops were captured on an infrared image from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on June 21 at 17:11 UTC (1:11 p.m. EDT). The strongest thunderstorms covered an area of hundreds of miles around what oddly ...
Tooth Pain a Sign of Allergy Season, Reports FocusedCareDental.com
2011-06-23
Everybody and his brother are reaching for tissues, eye drops and antihistamines to ward off the effects of pollen, mold and other seasonal allergy triggers. Some of America's 40 million sinusitis sufferers even have to resort to pain medicines to dull sinus-related headaches and tooth pain, says public health advocate Allan Melnick, a prominent clinical dentist in Encino, Calif.
"I have patients presenting with tooth pain, who don't realize it's linked to their sinus infection. They think they have a cavity, but the pain is actually a sinus 'plumbing' problem," ...