(Press-News.org) The ultimate source of some cancers is embryonic cells. Research published in the June 24th Cell, a Cell Press publication, traces the precursor of deadly esophageal cancers to leftover embryonic cells found in all adults.
Some people with gastric reflux disease have a greater risk of developing esophageal cancer. These patients often have Barrett's esophagus, a condition in which intestinal-like cells appear in the esophagus. Esophageal cancers are difficult to treat and, together with gastric adenocarcinomas, kill more than a million people each year.
"A lot of cancers you can do little about, and new drugs are approved based on their ability to extend life by one or two months," said the senior author of this study, Frank McKeon of Harvard Medical School and the Genome Institute of Singapore. "Focus on the precursors of cancer may be our best hope for medicine. Here, we are looking at a precursor of a cancer precursor that is present in all of us."
"It's not clear that the embryonic stem cell precursors have any real purpose," says study author Wa Xian. "Methods to rid the body of those cells may therefore be the easiest and most cost-effective way to stop the disease before it even starts, particularly for those at the greatest risk."
The prevailing theory has been that the abnormal cells seen in Barrett's esophagus arise as the normal squamous stem cells "transcommit" in response to acid-reflux to a new, intestine-like fate. Using a mouse model of chronic acid-reflux disease, , Xian and McKeon now show that, even as embryos, the animals showed a vast expanse of intestine-like cells in their esophaguses with gene expression profiles very similar to those seen in Barrett's.
"The metaplasia developed very quickly, in a matter of days," Xian said. "This was shocking to us as we generally consider cancer precursors taking multiple genetic 'hits' and years to develop."
The speedy development suggested that the precancerous condition wasn't related to the slow accumulation of mutations. Their findings also argue against the idea that the normal stem cells were undergoing a change of fate.
The mice under study lack a gene called p63 that is required for the self-renewal of stem cells in all stratified epithelial tissues. Because of their genetic defect, the mice are born without the squamous epithelium that normally lines the esophagus. "Without p63, the stem cells run out of gas and cease to exist," McKeon said. "You can't transcommit a cell that isn't there."
The gene profiles of those cells were also very different from cells of the intestine, despite their intestine-like appearance. "It's not a transcommitment," Xian said. "The Barrett's structure has its own cellular origin."
The researchers also generated mouse models in which the esophageal tissue could be damaged at precise times, revealing that this damage triggers a rapid mobilization of embryonic cells that would otherwise be resting. Those cells take up the newly freed space in a process that might mimic the evolution of Barrett's. Again, the speed with which those cells were activated seemed to rule out mutations as an explanation in favor of competition between normal cells and the minority embryonic population.
"The dim prognosis for esophageal adenocarcinoma has driven therapeutic strategies aimed at destroying Barrett's esophagus, including Radio Frequency Ablation (RFA), before it progresses to aggressive cancer," McKeon said. "While RFA appears to be exceedingly effective in the short term, there are hints that Barrett's might be fairly resilient and poised for recurrence."
The new findings suggest it may be more effective to go after the precursor cells instead. To do that, Xian says they "will have to clone the stem cell for Barrett's and the Barrett's precursor cell in the junction to find the targets needed to eradicate them."
In a final note, McKeon and Xian say that they suspect an additional subset of cancers, especially those linked to inflammation and tissue damage, might arise from precursors derived in a manner similar to Barrett's. "If so, we anticipate rapid progress into a group of particularly aggressive cancers that typically outwit the best treatments we have."
INFORMATION: END
Betelgeuse, a red supergiant in the constellation of Orion, is one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It is also one of the biggest, being almost the size of the orbit of Jupiter — about four and half times the diameter of the Earth's orbit. The VLT image shows the surrounding nebula, which is much bigger than the supergiant itself, stretching 60 billion kilometres away from the star's surface — about 400 times the distance of the Earth from the Sun.
Red supergiants like Betelgeuse represent one of the last stages in the life of a massive star. In this short-lived ...
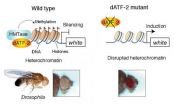
Researchers at RIKEN have uncovered a mechanism by which the effects of stress in the fly species Drosophila are inherited epigenetically over many generations through changes to the structure of chromatin, the material that makes up the cell nucleus. Published in the journal Cell, the results highlight the role of the transcription factor dATF-2 in chromatin assembly, marking a major advance in our understanding of non-Mendelian inheritance.
Recent years have seen growing interest in the phenomenon of epigenetic inheritance: the idea that our genome, through epigenetic ...
An app created by the Canadian based creators of Blackberry, Research In Motion, has recently been pulled off the company's online store after a formal request from four U.S. Senators.
Known as the "DUI app," it allows users to pinpoint the exact locations of local police checkpoints using GPS. The apps also locate traffic cameras and speed traps.
Web applications like these, however, are gaining widespread attention by law enforcement and legislative officials across the country.
Senators Harry Reid, D-Nevada; Charles Schumer, D-New York; Frank Lautenberg, ...
Prader-Willi syndrome is a rare genetic disorder which affects one child in 25,000. Children born with this syndrome have a range of complex neurological and developmental problems which continue into adult life. These can manifest as cognitive and behavioral difficulties, weight gain, problems in controlling their temper and attendant difficulties in socialization. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, demonstrates that the hormone oxytocin is able to positively affect patients by improving trust, mood, and reducing ...
Synthetic collagen has a wide range of applications in reconstructive and cosmetic surgery and in the food industry. For proper function in animals a certain number of prolines within the protein need to be hydroxylated. BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biotechnology reports that for the first time the α1 chain of type 1 collagen has been produced in maize with similar levels of proline hydroxylation to human collagen.
Most collagen used is derived from animals but there are risks associated with this collagen containing infectious agents or being rejected ...
Small heads, large bodies, and a slow metabolism -- these are the characteristics that make us think of dinosaurs as dull, lethargic and cold-blooded giants. However, this image seems to be deceiving. These giant saurians that have been extinct for 65 million years may have been high-performance models of evolution. In cooperation with colleagues from the US, researchers from the University of Bonn have just determined that the body temperature of some large herbivorous dinosaurs was between 36 and 38 degrees Celsius. "Originally, dinosaurs were considered to have been ...
Where Atlantic salmon feed in the ocean has been a long-standing mystery, but new research led by the University of Southampton shows that marine location can be recovered from the chemistry of fish scales. Surprisingly, salmon from different British rivers migrate to feed in separate places, and may respond differently to environmental change.
Numbers of Atlantic salmon have declined across their range since the early 1970s, and most researchers believe that conditions experienced at sea are largely to blame. Unfortunately, identifying where salmon go to feed in the ...
Oregon law requires that a parenting time plan be included in all judgments where minor children are involved.
In Oregon, "parenting time" (called "visitation" in some states) is the scheduled time that each parent has with the children. The parenting time plan is a document that states when the children will be with each parent and how decisions will be made for the parties' children.
The amount of parenting time that each parent has with the children is not necessarily related to whether or not a parent has legal custody in Oregon. In Oregon, ...
For years, it has been assumed that teachers—specifically math teachers—need to master the content they intend to teach. And the best way to do this is to take courses beyond that content.
Yet in a paper published today in the Education Forum of the journal Science, Dr. Brent Davis of the University of Calgary says research does not support this common belief. There is little evidence that advanced courses in mathematics contribute to more effective teaching.
"You know that feeling, when you try to explain to a child how to add multi-digit numbers, and you realize that ...
DALLAS – June 23, 2011 – We are one step closer to deciphering why some stressed people indulge in chocolate, mashed potatoes, ice cream and other high-calorie, high-fat comfort foods.
UT Southwestern Medical Center-led findings, in a mouse study, suggest that ghrelin – the so-called "hunger hormone" – is involved in triggering this reaction to high stress situations.
"This helps explain certain complex eating behaviors and may be one of the mechanisms by which obesity develops in people exposed to psychosocial stress," said Dr. Jeffrey Zigman, assistant professor ...