(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – On average, one hundred billion cells in the human body divide over the course of a day. Most of the time the body gets it right but sometimes, problems in cell replication can lead to abnormalities in chromosomes resulting in many types of disorders, from cancer to Down Syndrome.
Now, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Medicine have defined the structure of a key molecule that plays a central role in how DNA is duplicated and then moved correctly and equally into two daughter cells to produce two exact copies of the mother cell. Without this molecule, entire chromosomes could be lost during cell division.
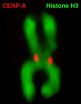
Ben Black, PhD, assistant professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics, and Nikolina Sekulic, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in the Black lab, report in the September 16 issue of Nature the structure of the CENP-A molecule, which defines a part of the chromosome called the centromere. This is a constricted area to which specialized molecules called spindle fibers attach that help pull daughter cells apart during cell division.
"Our work gives us the first high-resolution view of the molecules that control genetic inheritance at cell division," says Black. "This is a big step forward in a puzzle that biologists have been chipping away at for over 150 years."
Investigators have known for the last 15 years that part of cell division is controlled by epigenetic processes, the series of actions that affect the protein spools around which DNA is tightly bound, rather than encoded in the DNA sequence itself. Those spools are built of histone proteins, and chemical changes to these spool proteins can either loosen or tighten their interaction with DNA. Epigenetics alter the readout of the genetic code, in some cases ramping a gene's expression up or down. In the case of the centromere, it marks the site where spindle fibers attach independently of the underlying DNA sequence. CENP-A has been suspected to be the key epigenetic marker protein.
However, what hasn't been known is how CENP-A epigenetically marks the centromere to direct inheritance. The Black team found the structural features that confer CENP-A the ability to mark centromere location on each chromosome. This is important because without CENP-A or the centromere mark it creates, the entire chromosome—and all of the genes it houses—are lost at cell division.
In this study, Black solved CENP-A's structure to determine how it specifically marks the centromere on each chromosome and surmise from that how the epigenetic mark is copied correctly in each cell division. They found that CENP-A changes the shape of the nucleosome of which it's a part, also making it more rigid than other nucleosomes without CENP-A. The nucleosome is the combination of DNA wound around a histone protein core --the DNA thread wrapped around the histone spool. The CENP-A nucleosome is copied several times to create a unique epigenetic area, different from the rest of the chromosome. CENP-A replaces histone H3 in the nucleosomes located at the centromere.
This CENP-A centromere identifier attracts other proteins, and in cell division builds a massive structure, the kinetochore, for pulling the duplicated chromosomes apart during cell division.
Besides the major advance in the understanding of the molecules driving human inheritance, this work also brings about the exciting prospect that the key epigenetic components are now in hand to engineer clinically useful artificial chromosomes that will be inherited alongside our own natural chromosomes—and with the same high fidelity, says Black.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are graduate student Emily A. Bassett and research specialist Danielle J. Rogers. The work was funded by National Institute for General Medical Sciences, the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, the Rita Allen Foundation, the American Cancer Society, and the American Heart Association.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $3.6 billion enterprise.
Penn's School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools, and is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $367.2 million awarded in the 2008 fiscal year.
Penn Medicine's patient care facilities include:
The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania – the nation's first teaching hospital, recognized as one of the nation's top 10 hospitals by U.S. News & World Report.
Penn Presbyterian Medical Center – named one of the top 100 hospitals for cardiovascular care by Thomson Reuters for six years.
Pennsylvania Hospital – the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751, nationally recognized for excellence in orthopaedics, obstetrics & gynecology, and behavioral health.
Additional patient care facilities and services include Penn Medicine at Rittenhouse, a Philadelphia campus offering inpatient rehabilitation and outpatient care in many specialties; as well as a primary care provider network; a faculty practice plan; home care and hospice services; and several multispecialty outpatient facilities across the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2009, Penn Medicine provided $733.5 million to benefit our community.
At the crossroads of chromosomes
Penn study reveals structure of cell division's key molecule
2010-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Emotional robot pets
2010-09-17
Designers of robot pets are fighting a never-ending battle with consumers to provide entertaining and realistic gadgets that respond to human interaction in ever more nuanced ways, mimicking the behavior of real pet animals or even people. Researchers in Taiwan are now looking at a new design paradigm that could see the development of a robot vision module that might one-day recognize human facial expressions and respond appropriately.
Part of the problem is that robot design takes a long time, while the consumer life cycle of any given product is very short. Moreover, ...
Physicists cross hurdle in quantum manipulation of matter
2010-09-17
Finding ways to control matter at the level of single atoms and electrons fascinates many scientists and engineers because the ability to manipulate single charges and single magnetic moments (spins) may help researchers penetrate deep into the mysteries of quantum mechanics and modern solid-state physics. It may also allow development of new, highly sensitive magnetometers with nanometer resolution, single-spin transistors for coherent spintronics, and solid-state devices for quantum information processing.
Recently, a collaboration of experimentalists from the Kavli ...
More effective weight control strategies are urgently needed
2010-09-17
New Rochelle, NY, September 17, 2010—September is National Childhood Obesity Awareness Month, drawing attention to the epidemic of obesity among children and adolescents in the United States. A multidisciplinary approach to assessment and intervention is crucial for effective weight management and should draw from the latest medical evidence, best practices, and innovative educational and policy initiatives, all of which are presented and debated in the new bimonthly, print and online journal Childhood Obesity, published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The inaugural issue is ...
When the Earth mantle finds its core
2010-09-17
The Earth's mantle and its core mix at a distance of 2900 km under our feet in a mysterious zone. A team of geophysicists has just verified that the partial fusion of the mantle is possible in this area when the temperature reaches 4200 Kelvin. This reinforces the hypothesis of the presence of a deep magma ocean. The originality of this work, carried out by the scientists of the Institut de minéralogie et de physique des milieux condensés (UPMC/Université Paris Diderot/Institut de Physique du Globe/CNRS/IRD), lies in the use of X-ray diffraction at the European Synchrotron ...
Study finds possible 'persistence' switch for tuberculosis
2010-09-17
HOUSTON -- (Sept. 17, 2010) -- An examination of a portion of the tuberculosis genome that responds to stress has allowed Rice University bioengineers Oleg Igoshin and Abhinav Tiwari to zero in on a network of genes that may "switch" the disease into dormancy.
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB), Mycobacterium tuberculosis, can transition into a dormant state to ward off attacks from antibiotics and the immune system. A new report from Igoshin and Tiwari in this month's issue of Physical Biology examines a network of genes that may make this possible. A computer ...
Lack of access to healthy food may contribute to health disparities in kidney disease
2010-09-17
Processed and fast foods enriched with phosphorus additives may play a role in health disparities in chronic kidney disease, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). Previously, genetics was considered the leading reason blacks are four times more likely to progress to end stage renal disease than whites and have much higher rates of cardiovascular disease and mortality in early chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Phosphorus, a mineral found naturally in foods such as milk, cheese, beans and peanut butter, ...
Newly identified genetic marker involved in aggressive Alzheimer's disease
2010-09-17
A gene variation that appears to predict the rate at which Alzheimer's disease will progress has been uncovered by an international team of Alzheimer's disease experts, led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Published in the open-access journal PLoS Genetics, the findings help determine how rapidly Alzheimer's patients may develop full-blown dementia after their diagnosis.
Alzheimer's disease, one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders, affects over 4.5 million people in the United States alone. Recent studies have found the presence of ...
Healthy diet rocks when it comes to fighting kidney stones
2010-09-17
Certain key ingredients of a diet designed to prevent high blood pressure can ward off kidney stones, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society Nephrology (CJASN). The results suggest how low-fat dairy products and/or plants may have potent kidney stone–fighting properties.
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet—which is high in fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes, dairy products, and whole grains and is low in sweetened beverages and red and processed meats—effectively lowers blood pressure. ...
Native Hawaiians: Vulnerability to early death at all ages
2010-09-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Throughout their lives, Native Hawaiians have higher risks of death than white Americans, according to a University of Michigan study.
The research is the first known study to assess mortality patterns among Native Hawaiians at the national level, including those living outside the state of Hawaii.
The study is published in the November 2010 issue of the American Journal of Public Health, online Sept. 16. It was funded by the National Center for Minority Health and Health Disparities, part of the National Institutes of Health.
"Native Hawaiians ...
Watch your seas: Marine scientists call for European marine observatory network
2010-09-17
Brussels, 16 September - More than 100 marine scientists, policy makers and members of industry unanimously call for action towards an integrated network of observatories monitoring Europe's seas, at the Marine Board-ESF Forum 'Towards a European Network of Marine Observatories'. This will give reliable, long-term data to underpin science and policy regarding the use of seas for fisheries, aquaculture, energy, shipping, as well as tourism and recreation.
"We should not take for granted the wealth and well-being provided by the seas and oceans" said Lars Horn from the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
[Press-News.org] At the crossroads of chromosomesPenn study reveals structure of cell division's key molecule