(Press-News.org) The coconut (the fruit of the palm Cocos nucifera) is the Swiss Army knife of the plant kingdom; in one neat package it provides a high-calorie food, potable water, fiber that can be spun into rope, and a hard shell that can be turned into charcoal. What's more, until it is needed for some other purpose it serves as a handy flotation device.
No wonder people from ancient Austronesians to Captain Bligh pitched a few coconuts aboard before setting sail. (The mutiny of the Bounty is supposed to have been triggered by Bligh's harsh punishment of the theft of coconuts from the ship's store.)
So extensively is the history of the coconut interwoven with the history of people traveling that Kenneth Olsen, a plant evolutionary biologist, didn't expect to find much geographical structure to coconut genetics when he and his colleagues set out to examine the DNA of more than 1300 coconuts from all over the world.
"I thought it would be mostly a mish-mash," he says, thoroughly homogenized by humans schlepping coconuts with them on their travels.
He was in for a surprise. It turned out that there are two clearly differentiated populations of coconuts, a finding that strongly suggests the coconut was brought under cultivation in two separate locations, one in the Pacific basin and the other in the Indian Ocean basin. What's more, coconut genetics also preserve a record of prehistoric trade routes and of the colonization of the Americas.
The discoveries of the team, which included Bee Gunn, now of the Australian National University in Australia, and Luc Baudouin of the Centre International de Recherches en Agronomie pour le Développement (CIRAD) in Montpellier, France, as well as Olsen, associate professor of biology at Washington University in St. Louis, are described in the June 23 online issue of the journal PLoS One.
Morphology a red herring
Before the DNA era, biologists recognized a domesticated plant by its morphology. In the case of grains, for example, one of the most important traits in domestication is the loss of shattering, or the tendency of seeds to break off the central grain stalk once mature.
The trouble was it was hard to translate coconut morphology into a plausible evolutionary history.
There are two distinctively different forms of the coconut fruit, known as niu kafa and niu vai, Samoan names for traditional Polynesian varieties. The niu kafa form is triangular and oblong with a large fibrous husk. The niu vai form is rounded and contains abundant sweet coconut "water" when unripe.
"Quite often the niu vai fruit are brightly colored when they're unripe, either bright green, or bright yellow. Sometimes they're a beautiful gold with reddish tones," says Olsen.
Coconuts have also been traditionally classified into tall and dwarf varieties based on the tree "habit," or shape. Most coconuts are talls, but there are also dwarfs that are only several feet tall when they begin reproducing. The dwarfs account for only 5 percent of coconuts.
Dwarfs tend to be used for "eating fresh," and the tall forms for coconut oil and for fiber.
"Almost all the dwarfs are self fertilizing and those three traits — being dwarf, having the rounded sweet fruit, and being self-pollinating — are thought to be the definitive domestication traits," says Olsen.
"The traditional argument was that the niu kafa form was the wild, ancestral form that didn't reflect human selection, in part because it was better adapted to ocean dispersal," says Olsen. Dwarf trees with niu vai fruits were thought to be the domesticated form.
The trouble is it's messier than that. "You almost always find coconuts near human habitations," says Olsen, and "while the niu vai is an obvious domestication form, the niu kafa form is also heavily exploited for copra (the dried meat ground and pressed to make oil) and coir (fiber woven into rope)."
"The lack of universal domestication traits together with the long history of human interaction with coconuts, made it difficult to trace the coconut's cultivation origins strictly by morphology," Olsen says.
DNA was a different story.
Collecting coconut DNA
The project got started when Gunn, who had long been interested in palm evolution, and who was then at the Missouri Botanical Garden, contacted Olsen, who had the laboratory facilities needed to study palm DNA.
Together they won a National Geographic Society grant that allowed Gunn to collect coconut DNA in regions of the western Indian Ocean for which there were no data. The snippets of leaf tissue from the center of the coconut tree's crown she sent home in zip-lock bags to be analyzed.
"We had reason to suspect that coconuts from these regions —especially Madagascar and the Comoros Islands — might show evidence of ancient 'gene flow' events brought about by ancient Austronesians setting up migration routes and trade routes across the southern Indian Ocean," Olsen says.
Olsen's lab genotyped 10 microsatellite regions in each palm sample. Microsatellites are regions of stuttering DNA where the same few nucleotide units are repeated many times. Mutations pop up and persist pretty easily in these regions because they usually don't affect traits that are important to survival and so aren't selected against, says Olsen. "So we can use these genetic markers to 'fingerprint' the coconut," he says.
The new collections were combined with a vast dataset that had been established by CIRAD, a French agricultural research center, using the same genetic markers. "These data were being used for things like breeding, but no one had gone through and systematically examined the genetic variation in the context of the history of the plant," Olsen says.
Two origins of cultivation
The most striking finding of the new DNA analysis is that the Pacific and Indian Ocean coconuts are quite distinct genetically. "About a third of the total genetic diversity can be partitioned between two groups that correspond to the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean," says Olsen.
"That's a very high level of differentiation within a single species and provides pretty conclusive evidence that there were two origins of cultivation of the coconut," he says.
In the Pacific, coconuts were likely first cultivated in island Southeast Asia, meaning the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, and perhaps the continent as well. In the Indian Ocean the likely center of cultivation was the southern periphery of India, including Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and the Laccadives.
The definitive domestication traits —the dwarf habit, self-pollination and niu vai fruits — arose only in the Pacific, however, and then only in a small subset of Pacific coconuts, which is why Olsen speaks of origins of cultivation rather than of domestication.
"At least we have it easier than scientists who study animal domestication," he says. "So much of being a domesticated animal is being tame, and behavioral traits aren't preserved in the archeological record."
Did it float or was it carried?
One exception to the general Pacific/Indian Ocean split is the western Indian Ocean, specifically Madagascar and the Comoros Islands, where Gunn had collected. The coconuts there are a genetic mixture of the Indian Ocean type and the Pacific type.
Olsen and his colleagues believe the Pacific coconuts were introduced to the Indian Ocean a couple of thousand years ago by ancient Austronesians establishing trade routes connecting Southeast Asia to Madagascar and coastal east Africa.
Olsen points out that no genetic admixture is found in the more northerly Seychelles, which fall outside the trade route. He adds that a recent study of rice varieties found in Madagascar shows there is a similar mixing of the japonica and indica rice varieties from Southeast Asia and India.
To add to the historical shiver, the descendants of the people who brought the coconuts and rice are still living in Madagascar. The present-day inhabitants of the Madagascar highlands are descendants of the ancient Austronesians, Olsen says.
Much later the Indian Ocean coconut was transported to the New World by Europeans. The Portuguese carried coconuts from the Indian Ocean to the West Coast of Africa, Olsen says, and the plantations established there were a source of material that made it into the Caribbean and also to coastal Brazil.
So the coconuts that you find today in Florida are largely the Indian ocean type, Olsen says, which is why they tend to have the niu kafa form.
On the Pacific side of the New World tropics, however, the coconuts are Pacific Ocean coconuts. Some appear to have been transported there in pre-Columbian times by ancient Austronesians moving east rather than west.
During the colonial period, the Spanish brought coconuts to the Pacific coast of Mexico from the Philippines, which was for a time governed on behalf of the King of Spain from Mexico.
This is why, Olsen says, you find Pacific type coconuts on the Pacific coast of Central America and Indian type coconuts on the Atlantic coast.
"The big surprise was that there was so much genetic differentiation clearly correlated with geography, even though humans have been moving coconut around for so long."
Far from being a mish-mash, coconut DNA preserves a record of human cultivation, voyages of exploration, trade and colonization.
INFORMATION:
Deep history of coconuts decoded
Written in coconut DNA are two origins of cultivation, several ancient trade routes and the history of the colonization of the Americas
2011-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Apologies and Lawsuits: If the Defendant Is Sorry, Should You Care?
2011-06-25
Much has been written in recent years about the positive impact apologies may have in civil litigation, from personal injury cases like car accidents to medical malpractice. One of the foremost advocates of this idea, Professor Jennifer Robbennold of the University of Illinois College of Law, has published the results of a variety of empirical studies showing that apologies effectively encourage settlement of civil disputes.
But practical barriers to getting defense counsel to encourage clients to apologize exist. The biggest issue is the fact that such hearsay can be ...
Northern Eurasian snowpack could be a predictor of winter weather in US, team from UGA reports
2011-06-25
Every winter, weather forecasters talk about the snow cover in the northern U.S. and into Canada as a factor in how deep the deep-freeze will be in the states. A new study by researchers at the University of Georgia indicates they may be looking, at least partially, in the wrong place.
It turns out that snow piling up over a band of frozen tundra from Siberia to far-northern Europe may have as much effect on the climate of the U.S. as the much-better-known El Niño and La Niña.
The new work, just published in the International Journal of Climatology, reports that to ...
What Colorado Parents Should Know About the Family Car Doctrine
2011-06-25
When automobile accidents occur, drivers or their insurance companies, or both, are typically liable for any injury or property damage. However, when minor drivers are involved in car accidents, who is responsible for the resulting costs?
In some states, like Colorado, the liability may fall on the parents, who may or may not have heard about a law known as the family car doctrine. Parents should know this law's main points and how to financially protect themselves if their children are involved in automobile accidents while driving.
Family Car Doctrine
About 20 ...
Safer and more effective diabetes control with basal insulin analogs
2011-06-25
New Rochelle, NY, June 24, 2011—Basal insulin analogs have revolutionized diabetes care, and especially the treatment of type 2 diabetes, enabling patients to achieve better control of blood glucose levels while reducing hypoglycemic episodes. These revolutionary, long-acting basal insulin analogs, intended to replace the natural insulin missing in diabetes, and infusion pumps that provide subcutaneous, continuous delivery of insulin to mimic the function of a normal pancreas, are described in a special supplement to Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal ...
Pruhealth Becomes Nectar's Exclusive Healthcare Partner
2011-06-25
PruHealth customers can now collect up to 200 Nectar points and 10 Vitality points each week when buying GBP20 worth of healthy foods* during the weekly shop at Sainsbury's, under PruHealth's new and exclusive partnership with Nectar, the largest loyalty programme in the UK.
Enhancing PruHealth's existing partnership with Sainsbury's**, the innovative insurer that rewards healthy behaviour has become Nectar's exclusive healthcare partner within the programme.
Policyholders with Nectar membership can now receive 10 Nectar points per GBP1 spent in Sainsbury's on over ...
Syracuse University biologist discovers key regulators for biofilm development
2011-06-25
They can be found everywhere—organized communities of bacteria sticking to surfaces both inside and outside the body. These biofilms are responsible for some of the most virulent, antibiotic-resistant infections in humans; however, scientific understanding of how these communities develop is lacking.
A recent study led by a Syracuse University biologist sheds new light on the process. The scientists discovered that a complex cascade of enhancer binding proteins (EBPs) is responsible for turning on genes that initiate the formation of a biofilm. The study was published ...
Life expectancy for those with Type 1 diabetes improving, Pitt study says
2011-06-25
PITTSBURGH, June 24 – The life expectancy of people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes dramatically increased during the course of a 30-year, long-term prospective study, according to a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health study being presented at the 71st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The life expectancy for participants diagnosed with type 1 diabetes between 1965 and 1980 was 68.8 years – a 15-year improvement, compared to those diagnosed between 1950 and 1964, according to the study. Meanwhile, the life expectancy of the ...
Molton Brown Launches Mini Treats - Global Set
2011-06-25
Molton Brown has announced it will be launching a limited edition mini shower gel set for summer 2011.
The Mini Treats - Global Set is exclusive to Molton Brown, and will only be available for a limited time between the 20th June 2011 and the 13th July 2011.
The shower gel set is made up of ten 50ml bottles of some of Molton Brown's most popular shower gels and bathing products, including items from the best-selling Black Pepper and Heavenly Gingerlily ranges. The smaller sized bottles are ideal for summer travel and include a variety of scents designed for different ...
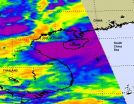
NASA sees Tropical Storm Haima poised for Vietnam landfall
2011-06-25
NASA satellite imagery revealed that Haima has regained minimal tropical storm status with some powerful thunderstorms south of its center. Haima is moving west through the Gulf of Tonkin in the South China Sea between Hainan Island and Vietnam and is expected to bring heavy rains to Vietnam this weekend.
On June 24. 2011 at 0600 UTC (2 a.m. EDT), Tropical Storm Haima's winds were back up to 35 knots (40 mph/65 kmh) making it a minimal tropical storm. Haima is headed west-southwest at 10 knots (11 mph/19 kmh). Its center was near 20.3 North and 107.0 East about 90 nautical ...
Pruhealth Introduces New Sustainable Commission Model
2011-06-25
PruHealth, the insurer that rewards people for engaging in healthy behaviour, has adopted what it believes to be a more sustainable and transparent commission model which rewards long-term partnerships with brokers and aims to deliver lasting client value. From April 2011, all Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) new business has been written on a 10:10 commission* basis, with 10% initial commission and 10% at each renewal.
Speaking at the Laing and Buisson conference, Dave Priestly, sales director at PruHealth, argued: "The current market focus on low new business ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Deep history of coconuts decodedWritten in coconut DNA are two origins of cultivation, several ancient trade routes and the history of the colonization of the Americas